Printfills: 3D printed systems combining Fused Deposition Modeling and Injection Volume Filling. Application to colon-specific drug delivery
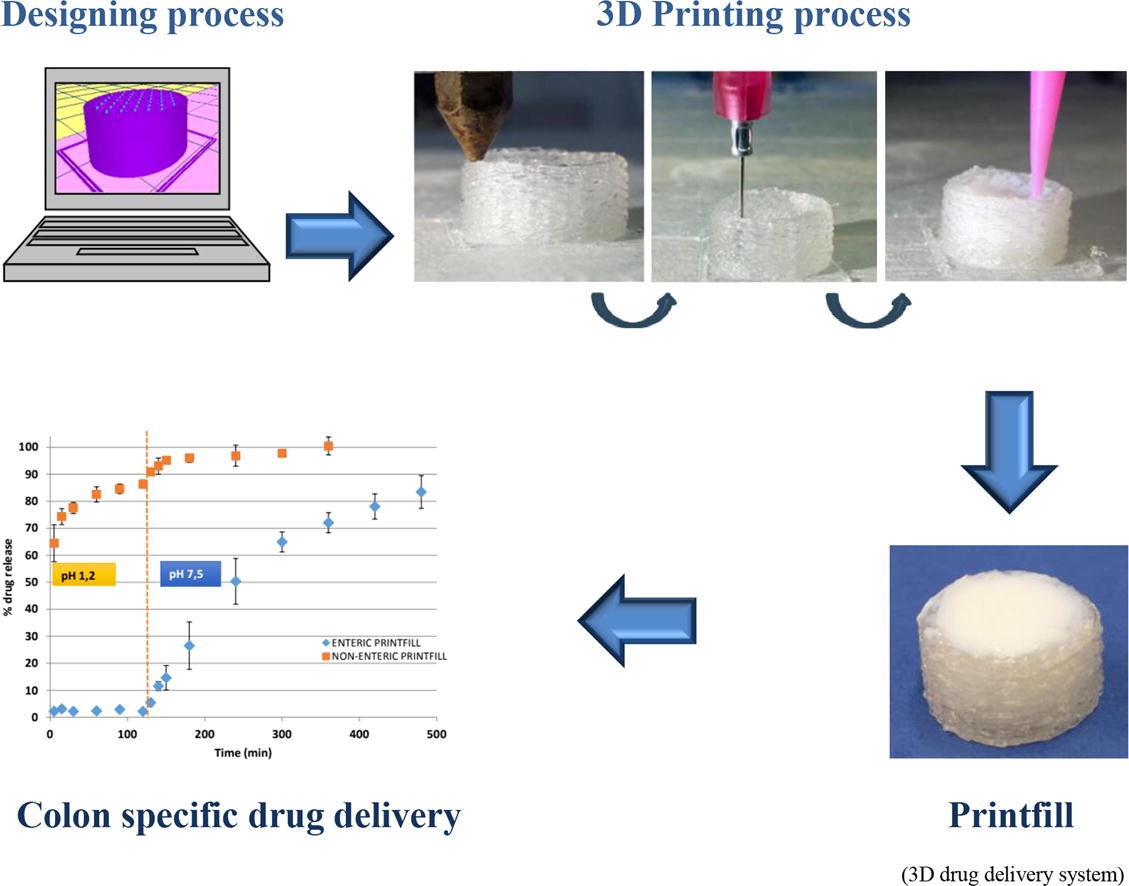
Three-dimensional printing has become a feasible manufacturing technique for pharmaceutical products providing cheap and accurate freeform systems with a great potential for personalized-dose drugs. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) highlights among other 3D technologies due to its low cost and easy to operate but, until now, it has the drawbacks of the low drug loaded and the impossibility to print thermosensitive drugs. So, intermediate processes such as hot melt extrusion are frequently associated with FDM. Here, pharmaceutical dosage forms have been manufactured for the first time with a 3D printer combining two different printing technologies: FDM and injection volume filling (IVF), performing customized extruded scaffolds in which a liquid or semisolid system can be injected at room temperature. A model drug and a pH-sensitive polymer were successfully incorporated during the construction of the extruded backbone of the systems, called printfills (printed systems filled with a liquid or semisolid). SEM microphotographs of printfills show the sealing of the structure in the perimeter and the homogeneity of the colonic film formed in the upper side. Thus, the addition of the pH-sensitive polymer does not need an additional process in a fluidized bed or coating pan. Results from drug release studies performed at different pH confirm the ability of printfills for colon-specific drug delivery. Therefore, IVF technology complements FDM, solving its main limitations providing an easy, automatized and versatile technology to manufacture tailored drug delivery platforms, avoiding other intermediate processes.

