Advancing non-destructive analysis of 3D printed medicines
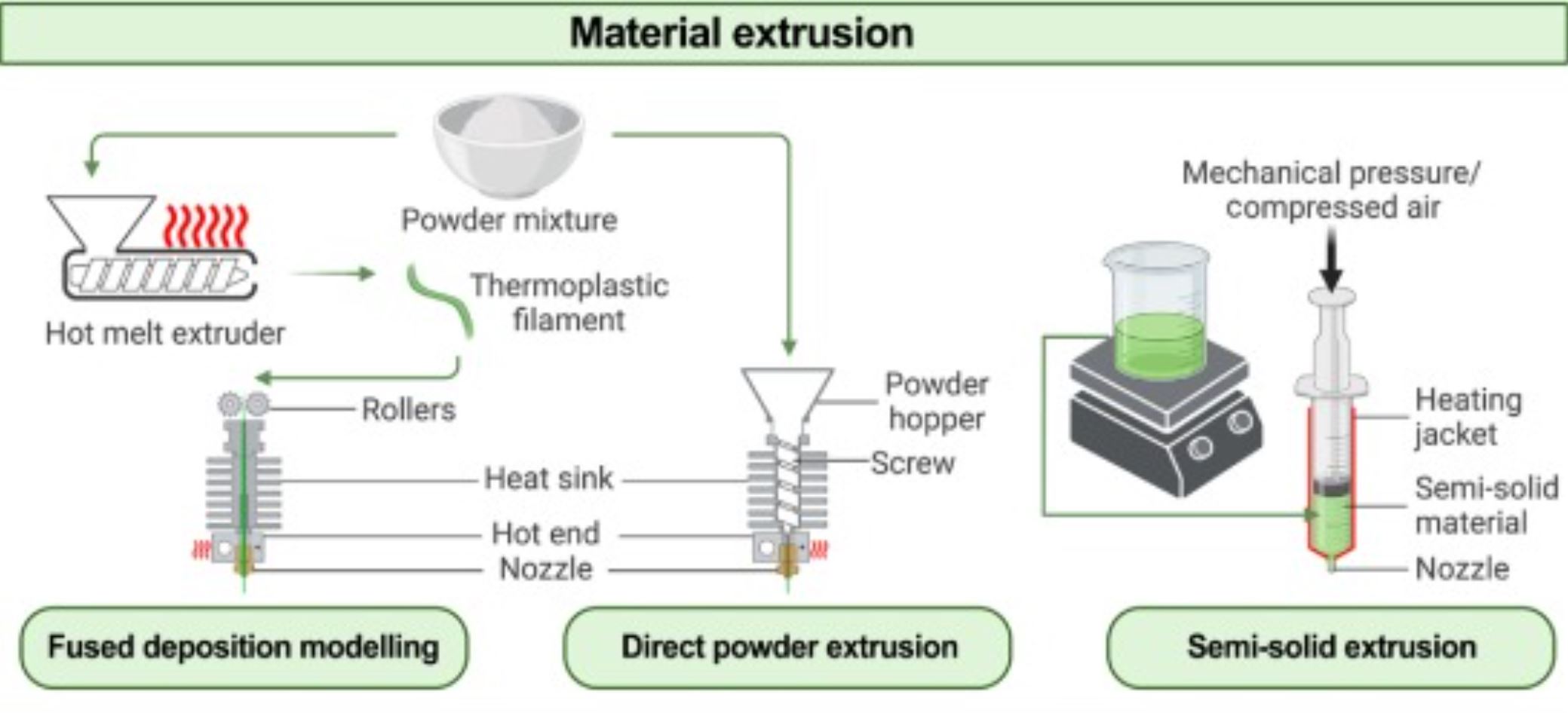
Pharmaceutical 3D printing (3DP) has attracted significant interest over the past decade for its ability to produce personalised medicines on demand. However, current quality control (QC) requirements for traditional large-scale pharmaceutical manufacturing are irreconcilable with the production offered by 3DP. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the UK Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) have recently published documents supporting the implementation of 3DP for point-of-care (PoC) manufacturing along with regulatory hurdles.
Highlights
The importance of process analytical technology (PAT) and non-destructive analytical tools in translating pharmaceutical 3DP has experienced a surge in recognition. This review seeks to highlight the most recent research on non-destructive pharmaceutical 3DP analysis, while also proposing plausible QC systems that complement the pharmaceutical 3DP workflow. In closing, outstanding challenges in integrating these analytical tools into pharmaceutical 3DP workflows are discussed.
Download the full article as PDF here: Advancing non-destructive analysis of 3D printed medicines
or read it here
Advancing non-destructive analysis of 3D printed medicines, Anna Kirstine Jørgensen, Jun Jie Ong, Maryam Parhizkar, Alvaro Goyanes, Abdul W. Basit, Open AccessPublished:April 24, 2023 DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2023.03.006
Read more on Overview of Pharmaceutical 3D printing here:


