In Situ Gelling Nasal Drug Delivery System
Abstract
In the nasal cavity, nasal mucosa had a high blood perfusion rate, due to this the absorption of the drug is high as compared to other routes, as well as has increased good bioavailability of drugs at the systemic circulation. To improve the nasal retention time of in-situ gel with nasal mucosa we have to use bio-compatible mucoadhesive polymer. In-situ gel nasal drug transfermethod is the type of mucoadhesive drug delivery system. When the drug is administered through nasal route then the first-pass metabolism gets reduced, had less enzymatic reaction occurrence, and prevents gastrointestinal tract ulceration. Drug release kinetic can be controlled by gelation strength of the formulation and viscosity of the in-situ gel formulation, so in-situ gel nasal drug delivery is also called a controlled and sustained drug delivery system. In-situ gels are prepared by various types of phenomenon and techniques that depend upon a different type of polymers and excipients used in the formulation.
Introduction
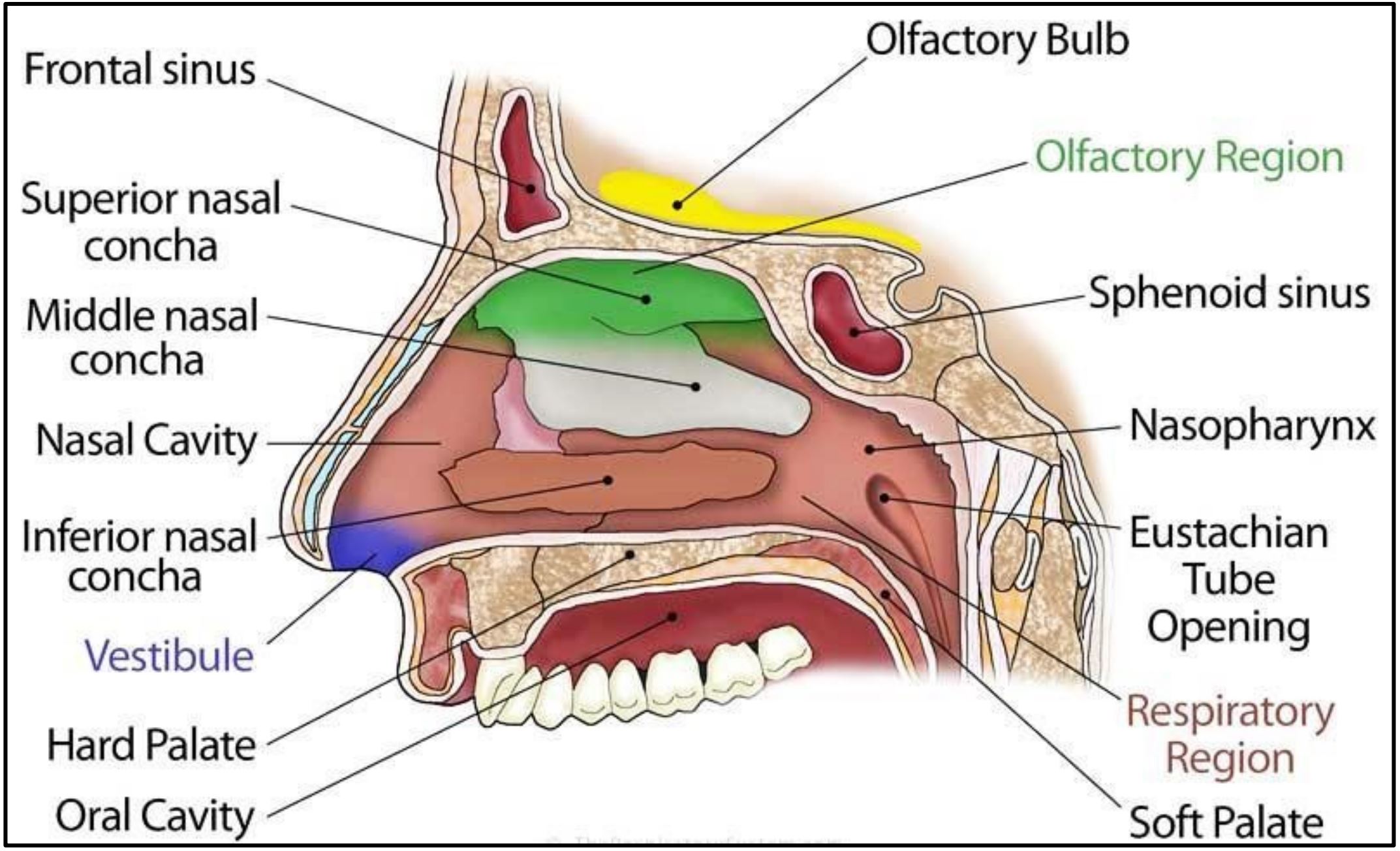
Therapy through intra-nasal administration has been arecognized form of treatment in the Ayurvedic system of Indian Medicine. In modern years many drugs have been shown toachieveimproved systemic bioavailability through nasal route than by oral administration or anyother route of administration. Nasal mucosa has been considered as a potentialadministration route to achieve a quicker and higher level of drug absorption because it ispermeable to more
compounds than the gastrointestinal tract because of lack of pancreatic andgastric enzymatic action, neutral pH of the nasal mucosa. In recent years many drugs have been shown to achieve better systemic bioavailability through nasal route than by oraladministration. The greater permeability of nasal mucosa with a huge surface area affords arapid onset of therapeutic effect. The low metabolic surroundings of the nose have the potential toovercome the limitation of the oral route and matching the benefit of intravenous administration. (1)
In addition to that, nasal administration diminishes the lag time related with oral drugdelivery and offers non-invasiveness, patient comfort, self-administration, and patientcompliance, which are the barrier in intravenous drug therapy. The appealing advantage ofnasal drug delivery is the possibility of targeting the central nervous system (CNS) by by passing the blood-brain barrier (BBB). (2) The drugs absorbed nasally via olfactory epithelium arereported to enter in olfactory neurons and supporting cells and subsequently into the brain,which reduced not only the systemic
toxicity of centrally acting drugs but also enhancedtherapeutic efficacy. The nasal route has received great attention as a route for vaccination. Nasal delivery of suitable antigen along with appropriate adjuvant to the nasalassociated lymphoid tissue (NALT) has the likely to induce humoral and cell mediated immunity. The nasal route is the route of choice for rapid mass immunization in developing countries. (3)
Table No 01:Polymers Used in Preparation of In SituGellingSystem
| Polymer Mucoadhesive | Origin | Charge | Solubility | Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH-sensitive polymers | ||||
| Carbomer | Synthetic | Anionic | Insoluble | +++ |
| Polyacrylic acid | Natural | Anionic | Insoluble | +++ |
| Cellulose acetate pthalate | Synthetic | Nonionic | Insoluble | ++ |
| Temperature-sensitive polymer | ||||
| Poloxamer | Synthetic | Nonionic | Soluble | ++ |
| Methyl cellulose | Natural | Nonionic | Soluble | + |
| Chitosan | Natural | Cationic | Soluble | ++ |
| Hydroxy propyl Methyl cellulose | Natural | Nonionic | Soluble | + |
| Ion sensitive polymer | ||||
| Xanthan gum | Natural | Anionic | Insoluble | + |
| Gellan gum (Gelrite) | Natural | Anionic | Soluble | ++ |
| Sodium alginate | Natural | Cationic | Insoluble | ++ |
Intranasal immunization may lead to the development of local, as well assystemic immunity. Despite having a large number of advantages, the bioavailability of nasaldosage form is hindered by various physicochemical, physiological, and formulationfactors.
Download the article as PDF here In Situ Gelling Nasal Drug Delivery System
V.T. Mankoskar, G. V.Lohiya, R. M. Somani, Dr.S.S.Dharashivkar, Dr. S. G. Gattani, R.R.Sarda, Dr.S.S.Tiwari, In Situ Gelling Nasal Drug Delivery System, Journal of University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, ISSN: 1007-6735, Volume 26, Issue 4, April – 2024
Read also our introduction article on Gellan Gum here:


