Comparison of Hydroxypropylcellulose and Hot-Melt Extrudable Hypromellose in Twin-Screw Melt Granulation of Metformin Hydrochloride: Effect of Rheological Properties of Polymer on Melt Granulation and Granule Properties
High-molecular-weight hypromellose (HPMC) and hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) are widely known, extended-release polymers. Conventional high-molecular-weight HPMCs are preferred in extended-release applications but not widely used in twin-screw melt granulation due to processability difficulties at low operating temperatures and potential drug degradation if high processing temperatures are used. Conversely, high-molecular-weight grade HPC (Klucel®) can be used in melt granulation processes. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the processability and dissolution behavior of HPC GXF ((Klucel® GXF) and a recently introduced type of hot-melt extrudable HPMC (Affinisol®) in extended-release metformin hydrochloride formulations using twin-screw melt granulation. Powder blends were prepared with 75% w/w metformin HCl and 25% w/w polymeric binder.
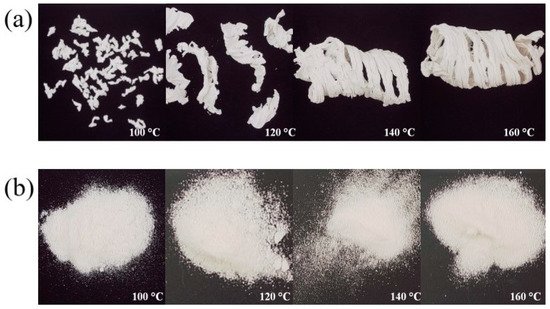
Blends were granulated at processing temperatures of 160, 140, 120 and 100 °C. HPMC HME 4M (Affinisol® 4M) provided a fine powder, indicating minimum granulation at processing temperatures lower than 160 °C, and the tablets obtained with these granules capped during tableting. In contrast, acceptable tablets could be obtained with HPC GXF at all processing temperatures. Rheological studies including capillary rheometry to measure steady shear rate viscosity, and rotational rheometry to obtain time and temperature superposition data, showed that HPC GXF had a greater thermoplasticity than HPMC HME 4M, which made granulation possible with HPC GXF at low temperatures. Tablets compressed with granules obtained at 160 °C with both binders showed comparable dissolution profiles. High-molecular-weight HPC GXF provided a better processability at low temperatures and adequate tablet strength for the melt granulation of metformin HCl.
Download the full article or continue reading here
About this article: Batra, A.; Yang, F.; Kogan, M.; Sosnowik, A.; Usher, C.; Oldham, E.W.; Chen, N.; Lawal, K.; Bi, Y.; Dürig, T. Comparison of Hydroxypropylcellulose and Hot-Melt Extrudable Hypromellose in Twin-Screw Melt Granulation of Metformin Hydrochloride: Effect of Rheological Properties of Polymer on Melt Granulation and Granule Properties. Macromol 2022, 2, 1-19. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol2010001
Materials
Metformin HCl was selected as a model of highly water-soluble drug. Metformin HCl was purchased from Harman Finochem Ltd. (Maharashtra, India).
Affinisol® HPMC HME 4M (HPMC HME 4M) is manufactured and marketed by IFF (Wilmington, DE, USA). HPMC HME polymers are pure hydroxypropyl methylcellulose without any additives present, and they differ among themselves and from other HPMC polymers, such as Methocel™ K100LV, in the level of chemical substitution [29,30]. Three molecular weight grades of Affinisol® HPMC HME are available—HPMC HME 15LV, HPMC HME 100LV, and HPMC HME 4M—with approximate molecular weights of 90, 180 and 550 kDa [29], respectively. Since metformin HCl is highly water-soluble, HPMC HME 4M, with the highest molecular weight of approximately 550 kDa, was selected for experimentation.
Klucel® GXF HPC (HPC GXF) was obtained from Ashland Specialty Ingredients (Wilmington, DE, USA). HPC GXF with a molecular weight of 370 kDa was selected. Due to the manufacturability, this grade has the most comparable molecular weight to HPMC HME 4M.

