Inhalable bedaquiline-loaded cubosomes for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
Highlights
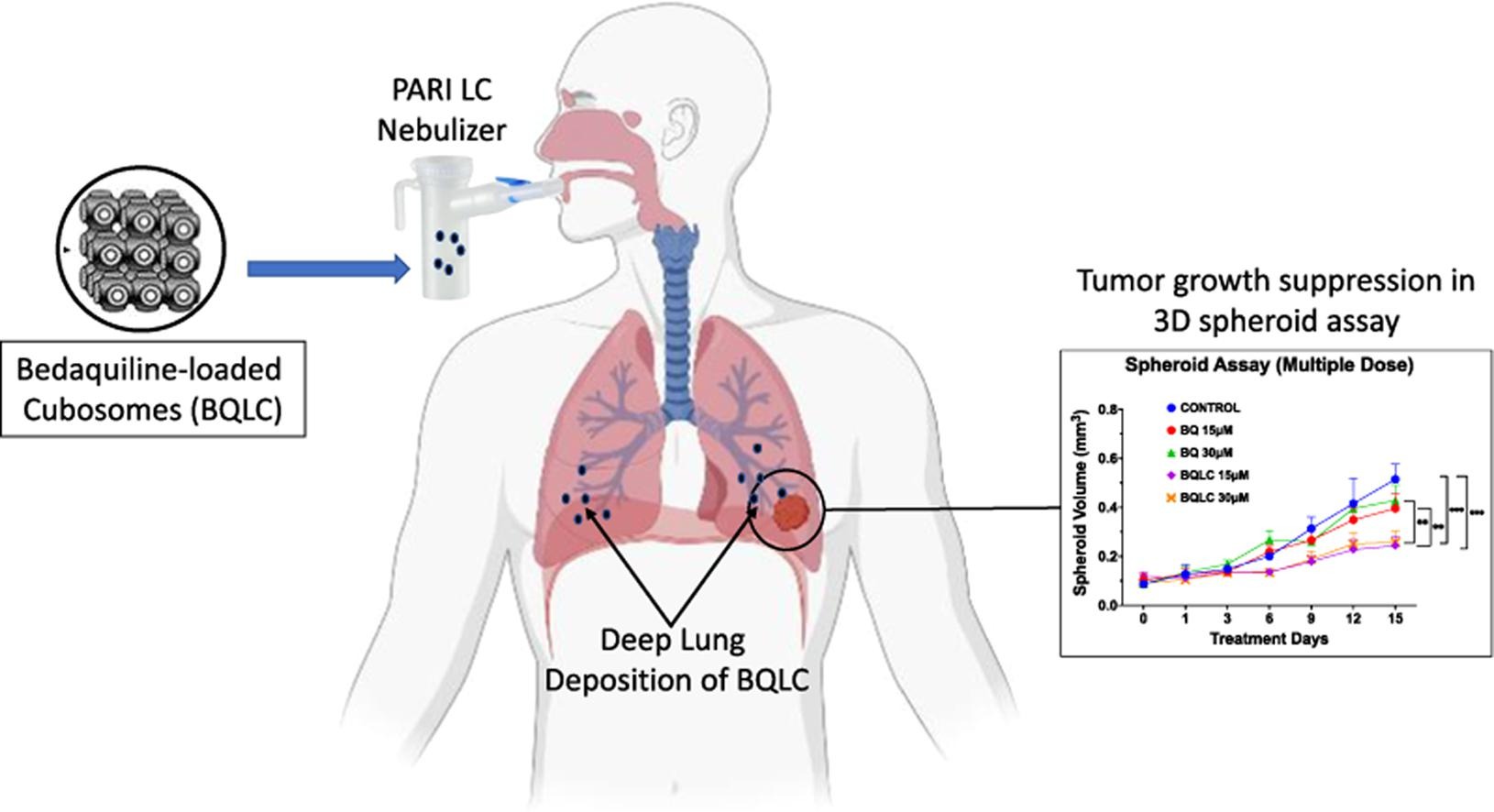
- • Bedaquiline-loaded cubosomes (BQLC) displayed excellent particle size, zeta potential, and aerosolization behavior suitable for NSCLC treatment.
- • BQLCs were efficiently internalized by lung cancer cells and decreased IC50 by 3-fold compared to free bedaquiline.
- • BQLCs significantly inhibited colony formation and cancer metastasis in vitro.
- • In A549 3D spheroids, BQLCs significantly inhibited tumor growth compared to free BQ.
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the leading cause of cancer deaths globally. Treatment-related adverse effects and development of drug resistance limit the available treatment options for most patients. Therefore, newer drug candidates and drug delivery systems that have limited adverse effects with significant anti-cancer efficacy are needed. For NSCLC treatment, delivering drugs via inhalation is highly beneficial as it requires lower doses and limits systemic toxicity. Bedaquiline (BQ), an FDA-approved anti-tuberculosis drug has previously shown excellent anti-cancer efficacy. However, poor aqueous solubility limits its delivery via the lungs.
In this project, we developed inhalable BQ-loaded cubosome (BQLC) nanocarriers against NSCLC. The BQLC were prepared using a solvent evaporation technique with the cubosomal nanocarriers exhibiting a particle size of 150.2 ± 5.1 nm, zeta potential of (+) 35.4 ± 2.3 mV, and encapsulation efficiency of 51.85 ± 4.83%. The solid-state characterization (DSC and XRD) confirmed drug encapsulation and in an amorphous form within the cubosomes. The BQLC nanocarriers showed excellent aerodynamic properties after nebulization (MMAD of 4.21 ± 0.53 µm and FPF > 75%).
The BQLC displayed enhanced cellular internalization and cytotoxicity with a ~ 3-fold reduction in IC50 compared to free BQ in NSCLC (A549) cells, after 48 h treatment. The BQLC suppressed cell proliferation via apoptotic pathway, further inhibited colony formation, and cancer metastasis in vitro. Additionally, 3D-tumor simulation studies established the anti-cancer efficacy of cubosomal nanocarriers as compared to free BQ. This is the first study exploring the potential of cubosomes as inhalation therapy of repurposed drug, BQ and the results suggest that BQLC may be a promising NSCLC therapy due to excellent aerosolization performance and enhanced anti-cancer activity.
Suyash M. Patil, Shruti S. Sawant, Nitesh K. Kunda,
Inhalable bedaquiline-loaded cubosomes for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC),
International Journal of Pharmaceutics, Volume 607, 2021, 121046, ISSN 0378-5173,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.121046.

