Phospholipids – Nature’s Versatile All-Rounders Showing Excellent Tolerability
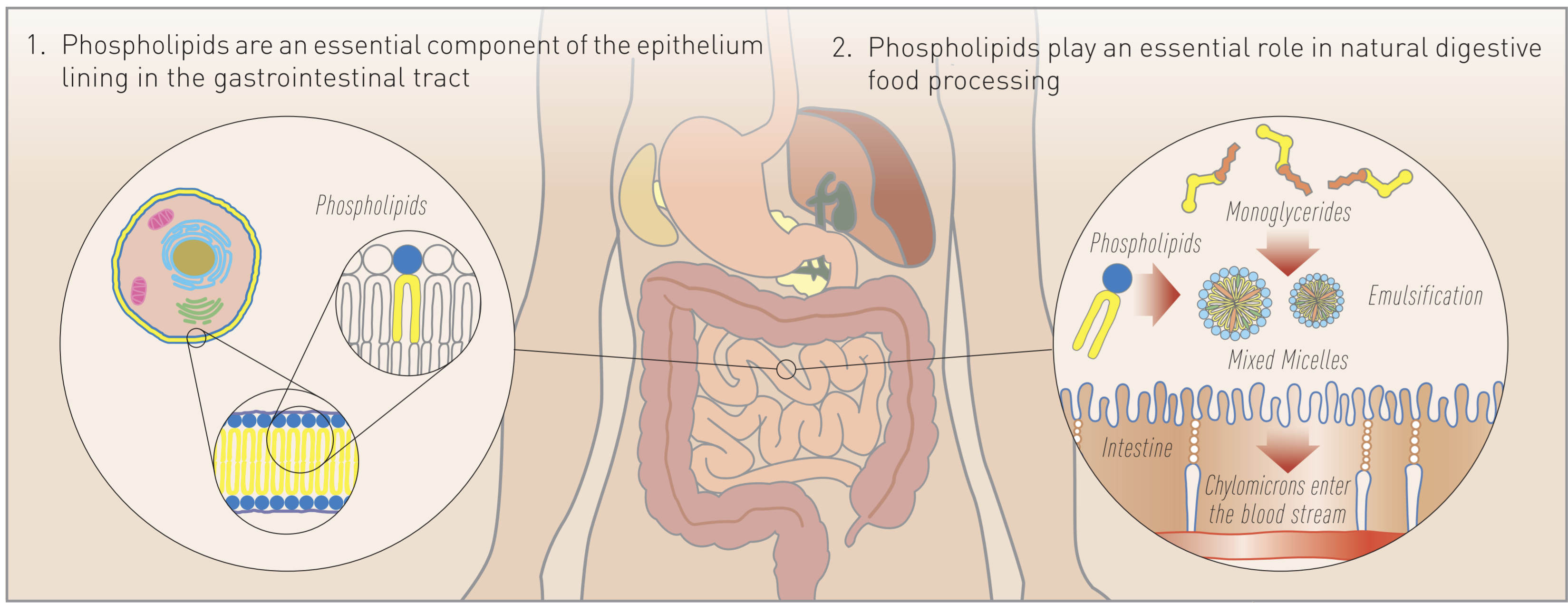
Phospholipids (PLs) are essential building blocks of all biological membranes exhibiting a huge variety of functions. They play an essential role in the natural digestive process of food and are excreted as component of bile by the liver. Bile emulsifies fatty food components which enhances their oral absorption. In addition, phospholipids are an essential component of the epithelium lining in the gastrointestinal tract.[1] The most prominent phospholipid used in health nutrition products is phosphatidylcholine which acts as a valuable dietetic source of polyunsaturated fatty acids and choline.
Phospholipids – Unique Components
- Multifunctional alternative to e.g., synthetic food emulsifiers
- Natural products produced from renewable sources by eco-friendly processes
Applications
- Technical use as emulsifier and liposome former
- Delivery system of nutrients for better absorption [2]
Positive Physiological Aspects
- Liver regeneration [3]
- Cardiovascular health, i.a. due to cholesterol lowering effect [4]
- Prevention of atherosclerosis [5]
- Anti-inflammatory properties [6]
Regulatory
- GRAS status assigned by the FDA [7]
- Allowed as food additive E 322
- No ADI and no safety concerns concluded by the EFSA [8]
The Great Benefits of Phospholipids

“Since Phospholipids are endogenous, they are biocompatible, fully absorbed after ingestion and physiologically metabolisable”
Lipoid provides various nature-derived phospholipids from non-GMO soybean and sunflower seeds as well as innovative delivery systems based on these completely biocompatible substances. For detailed information about our broad portfolio please ask for our product catalogue.
 Download the full brochure from Lipoid as a PDF here
Download the full brochure from Lipoid as a PDF here
Interested in a sample or more information? Contact us now:
References
[1] Braun, A., Stremmel, W., et al., The role of phospholipids within the intestinal mucosal barrier. Zeitschrift für Gastroenterologie 49 (10), A11 (2011).
[2] Van Hoogevest, P., Review – An update on the use of oral phospholipid excipients. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 108, 1 – 12 (2017).
[3] Gundermann, K.-J., Gundermann, S., et al., Essential phospholopids in fatty liver: a scientific update. Clinical and Experimental Gastroenterology 9, 105 – 117 (2016).
[4] Sahebkar, A., Fat lowers fat: Purified phospholipids as emerging therapies for dyslipidemia. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1831 (4), 887 – 893 (2013).
[5] Wojcicki, J., Pawlik, A., et al., Clinical evaluation of lecithin as lipid-lowering agent. Phytotherapy Research 9(8), 597 – 599 (1995).
[6] Stremmel W., Hanemann, A., et al., Phosphatidylcholine (lecithin) and the mucus layer: evidence of therapeutic efficacy in ulcerative colitis? Digestive Diseases 28 (3), 490 – 496 (2010).
[7] U.S. Food and Drug Administration, 21CFR184.1400 revised as of April 1 (2013).
[8] Re-evaluation of lecithins (E 322) as a food additive. EFSA Panel on Food Additives and Nutrient Sources added to Food (ANS). EFSA Journal 15 (4), 4742 (2017).

