Self-Nano-Emulsifying Drug-Delivery Systems: A Limelight on the Development, Advancements and Opportunities in Improving Oral Absorption
Abstract
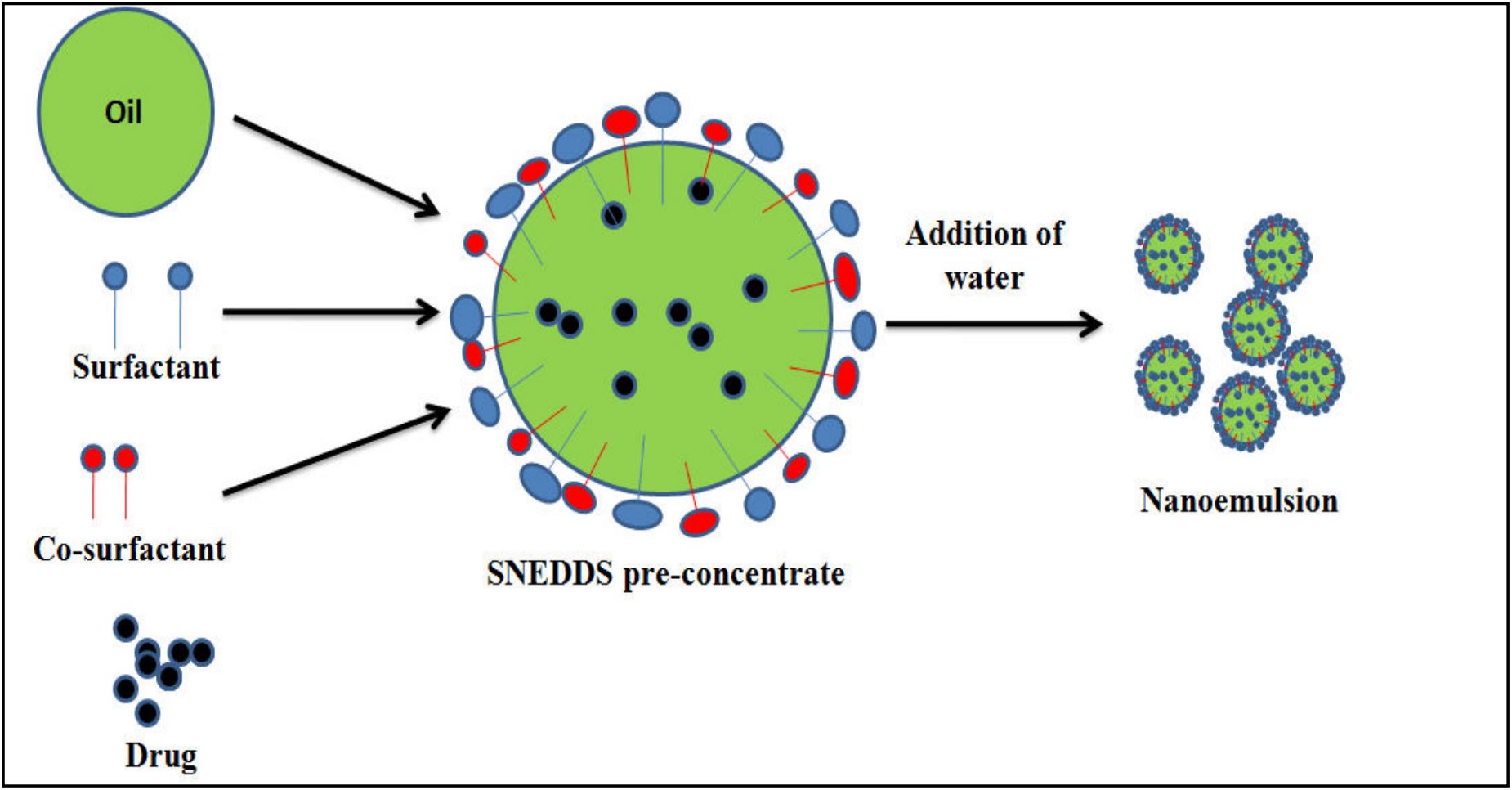
Orally administered medication solubility is a key concern for the pharmaceutical business; about 35-40% of newly introduced pharmaceuticals have less aqueous solubility, resulting in deprived dissolution and limited bio-availability. Employment of lipid-oriented drug release methods like self-nano-emulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS), its use to progress drug solubility, permeability, & bio-availability has been extensively reported in literature. A SNEDDS is made up of an oil component, a surfactant & a co-surface active agent. SNEDDS are intended for a broad variety of applications because of their small droplets, high solubility, large interfacial region, low steadiness, transparent or semi-transparent appearance, and extraordinary kinetic reliability. Multiple orthogonal approaches are necessary for SNEDDS characterization in order to thoroughly organize SNEDDS manufacturing, strength, & biological release. The characterization of SNEDDSs includes multiple orthogonal methods required to fully control SNEDDS manufacture, stability, and biological fate. Encapsulating a drug in SNEDDSs can lead to increased
solubilization, stability in the gastro-intestinal tract, and absorption, resulting in enhanced bio-availability. To improve efficacy and patient conformity, a supersaturated, mucus permeating, and tailored SNEDDS can be produced. The
self-emulsification method has proven effective in oral medication delivery.
(Remark Pharma Excipients: The rest of the article was deleted on request of the author)
Source: Self-Nano-Emulsifying Drug-Delivery Systems: A Limelight on the Development, Advancements and Opportunities in Improving Oral Absorption, Vyshali Parigela 1 & A Vijayalakshmi, SCOPE journal ,Volume 14 Number 01 March 2024

