Topical nanocarriers for management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A review
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic autoimmune disease manifested by chronic joint inflammation leading to severe disability and premature mortality. With a global prevalence of about 0.3%–1% RA is 3–5 times more prevalent in women than in men. There is no known cure for RA; the ultimate goal for treatment of RA is to provide symptomatic relief. The treatment regimen for RA involves frequent drug administration and high doses of NSAIDs such as indomethacin, diclofenac, ibuprofen, celecoxib, etorcoxib.
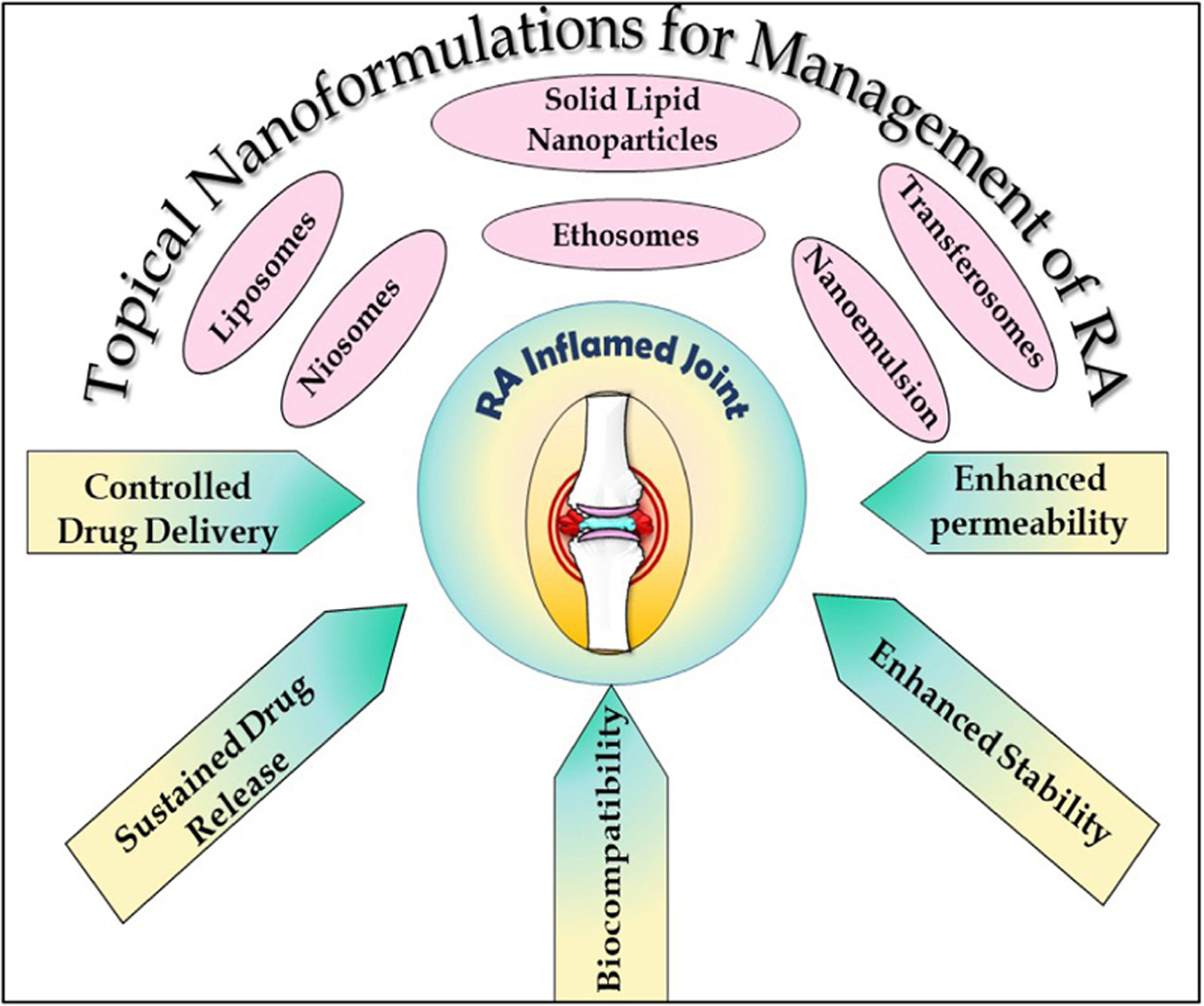
These potent drugs often have off target effects which drastically decreases patient compliance. Moreover, conventional non-steroidal anti-inflammatory have many formulation challenges like low solubility and permeability, poor bioavailability, degradation by gastrointestinal enzymes, food interactions and toxicity. To overcome these barriers, researchers have turned to topical route of drug administration, which has superior patience compliance and they also bypass the first past effect experienced with conventional oral administration. Furthermore, to enhance the permeation of drug through the layers of the skin and reach the site of inflammation, nanosized carriers have been designed such as liposomes, nanoemulsions, niosomes, ethosomes, solid lipid nanoparticles and transferosomes.
These drug delivery systems are non-toxic and have high drug encapsulation efficiency and they also provide sustained release of drug. This review discusses the effect of formulation composition on the physiochemical properties of these nanocarriers in terms of particle size, surface charge, drug entrapment and also drug release profile thus providing a landscape of topically used nanoformulations for symptomatic treatment of RA.
Download the full article as a PDF here or read it here
Article information: Chando Anita, Momin Munira, Quadros Mural, Lalka Shaily. Topical nanocarriers for management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A review, Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, Volume 141, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111880.

