Novel Combination Proliposomes Containing Tobramycin and Clarithromycin Effective against Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilms
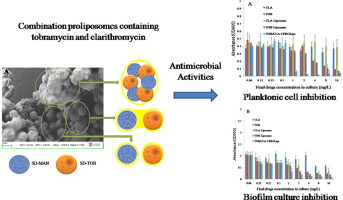
Tobramycin (TOB) and clarithromycin (CLA) can potentially be used synergistically for the treatment of respiratory infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) in cystic fibrosis (CF) patients. This study aimed to develop a novel combination proliposome formulation (TOB/CLA-CPROLips) containing both hydrophilic TOB and hydrophobic CLA via a core-carrier approach. The combination proliposomes were produced by spray drying a suspension comprising spray-driedmannitol (SD-MAN, 0.45 %) and spray-dried tobramycin (SD-TOB, 0.05 %) particles suspended in an ethanolic lipid solution of CLA (0.05 %). The lipid layer coated on the surface of the dry proliposome particles conferred moisture protection and sustained drug release properties in comparison to the pure drugs. The optimized TOB/CLA-CPROLips formulation was stable after 3 months of storage at 60 % relative humidity (RH) and 25 °C. The combination drug proliposomes showed a synergistic antimicrobial activity against planktonic cells and biofilm cultures of P. aeruginosa. In conclusion, the core-carrier method coupled with spray-drying provided a novel approach for the preparation of combination antibiotics proliposomes.

