Influence of commonly used excipients on the chemical degradation of enalapril maleate in its solid state: The role of condensed water
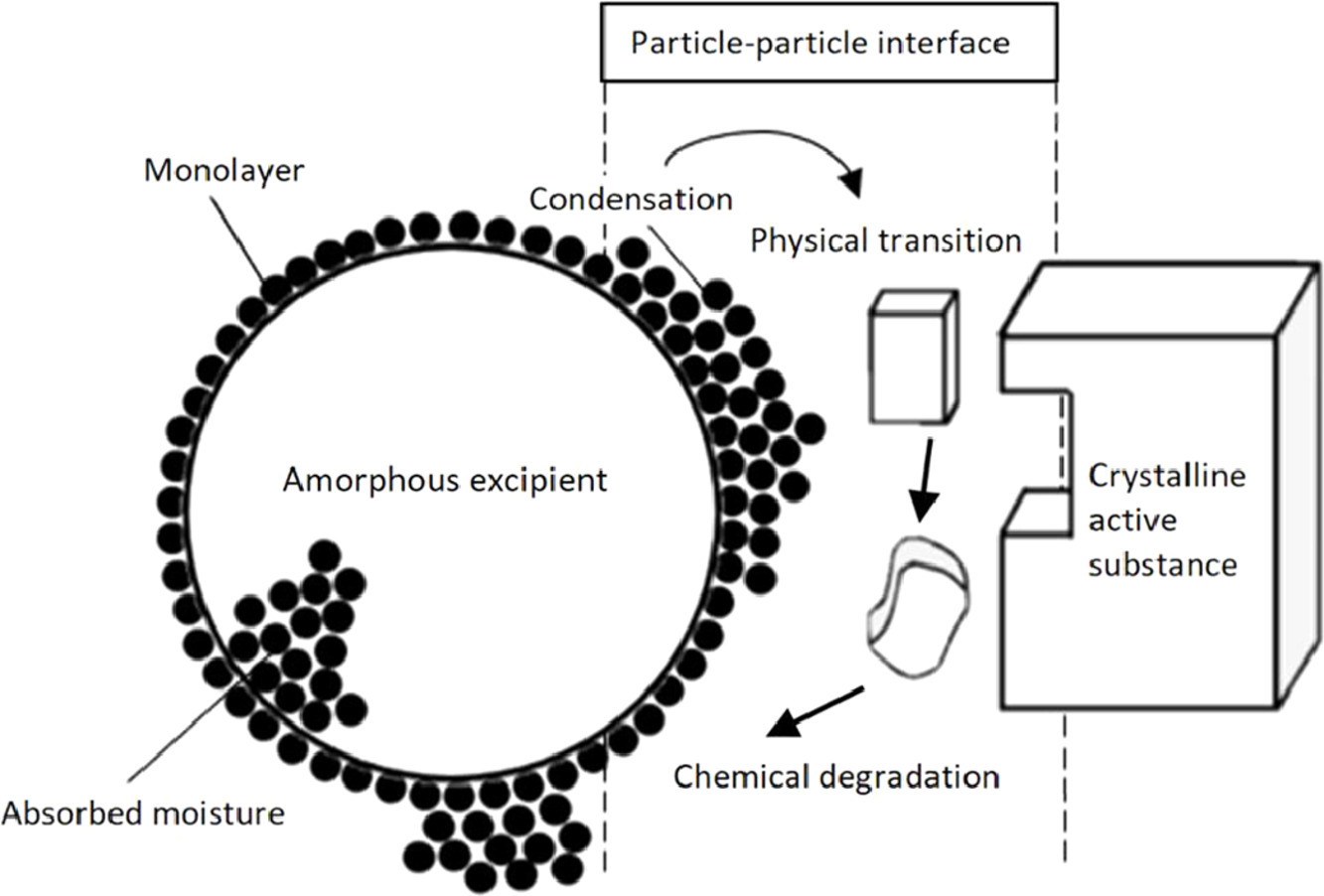
The physicochemical stability of enalapril maleate was investigated in the presence of fourteen different excipients divided into four different classes. The extent of a drug-excipient interaction was investigated by following the chemical stability using HPLC. It was found that there is a certain order in the stability of enalapril maleate. Enalapril maleate remained most stable in the presence of: disaccharides > celluloses > starches > superdisintegrants. The amount of degradation can be related to the excipient characteristics. A material with a higher water sorption capacity and lower crystallinity presents a more reactive particle surface. It was revealed that the condensation layer deposited on the surface of the excipient is responsible for the degradation of enalapril maleate. A confirmation was found by changing the surface of the excipient and influencing the environmental humidity that allowed a variable build-up of the condensation layer. For this particle-particle interaction, the microenvironmental pH only presents a minor effect as it was found to not be a determining factor for degradation. Moreover, there appears to be a firm relationship between the degradation of enalapril maleate and the water sorption-activity of excipients.
About this article: Merel Rachel Bout, Herman Vromans, Influence of commonly used excipients on the chemical degradation of enalapril maleate in its solid state: The role of condensed water, European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Volume 171, 2022, 106121, ISSN 0928-0987, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2022.106121.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0928098722000069)
Table 1. A: Overview of all used materials for experiments.
| Divided class | Materials | Brand name, supplier, country |
|---|---|---|
| Enalapril maleate | Enalapril maleate, Zhejiang Huahai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., China | |
| Disaccharides | Lactose monohydrate | Pharmatose 200 M, DFE Pharma, Germany |
| Spray-dried lactose | Supertab® 11SD, DFE Pharma, Germany | |
| Anhydrous lactose | Supertab® 21AN, DFE Pharma, Germany | |
| Celluloses | Microcrystalline cellulose | Vivapur® 101, JRS Pharma, Germany |
| Silicified microcrystalline cellulose | PROSOLV® SMCC 90, JRS Pharma, Germany | |
| Starches | Potato starch | Native starch – potato based, Roquette, France |
| Corn starch | Meritena® Pharma 141, Tereos, France | |
| Pregelatinized starch | C*Gel-Instant® 12,018, Cargill, United States | |
| Partially pregelatinized starch | Starch 1500®, Colorcon, United States | |
| Amylopectin | Amylopectin from maize, Sigma-Aldrich, The Netherlands | |
| Super-disintegrants | Sodium starch glycolate | Primojel® type A, DFE Pharma, Germany |
| Sodium starch glycolate | Glycolys® type A, Roquette, France | |
| Croscarmellose sodium | Ac-di-sol® SD-711, DuPont, United States | |
| Crospovidone | Kollidon® CL, BASF, Germany | |
| Silicon dioxide | ZEOFREE® 5162, Evonik Silica, Finland |

