Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as a Gene Delivery Platform for Cancer Therapy
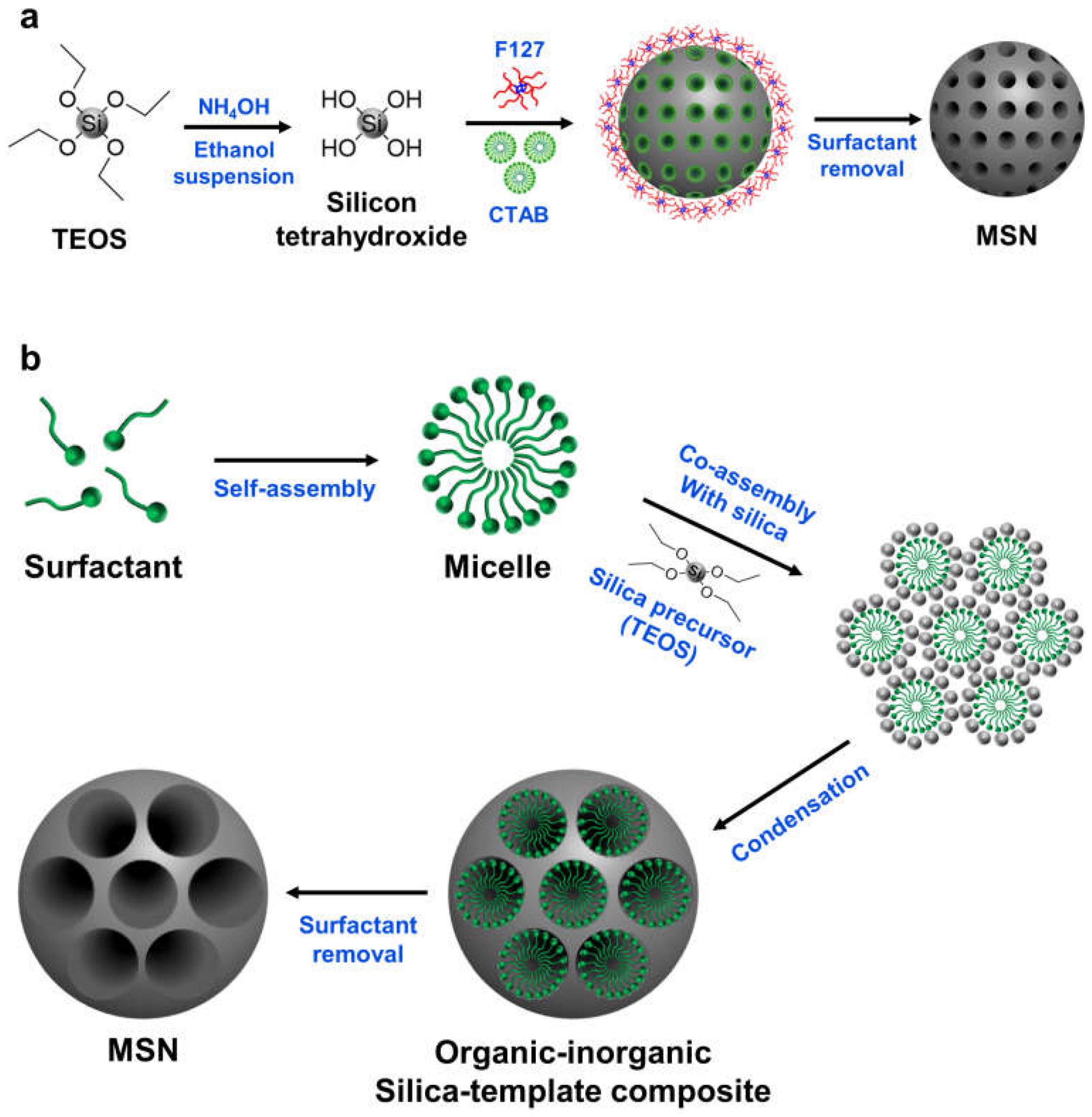
Cancer remains a major global health challenge. Traditional chemotherapy often results in side effects and drug resistance, necessitating the development of alternative treatment strategies such as gene therapy. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) offer many advantages as a gene delivery carrier, including high loading capacity, controlled drug release, and easy surface functionalization. MSNs are biodegradable and biocompatible, making them promising candidates for drug delivery applications. Recent studies demonstrating the use of MSNs for the delivery of therapeutic nucleic acids to cancer cells have been reviewed, along with their potential as a tool for cancer therapy. The major challenges and future interventions of MSNs as gene delivery carriers for cancer therapy are discussed.
1. Introduction
Download the full review as PDF here: Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as a Gene Delivery Platform for Cancer Therapy
or read it here
Khaliq, N.U.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Yu, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Sung, D.; Kim, H. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as a Gene Delivery Platform for Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1432.
https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15051432

