Development and Characterization of Celecoxib Solid Self-nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (S-SNEDDS) Prepared Using Novel Cellulose-Based Microparticles as Adsorptive Carriers
Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (SNEDDS) represent an interesting platform for improving the oral bioavailability of poorly soluble lipophilic drugs. While Liquid-SNEDDS (L-SNEDDS) effectively solubilize the drug in vivo, they have several drawbacks, including poor storage stability. Solid-SNEDDS (S-SNEDDS) combine the advantages of L-SNEDDS with those of solid dosage forms, particularly stability. The aim of the present study was to convert celecoxib L-SNEDDS into S-SNEDDS without altering their release behavior.
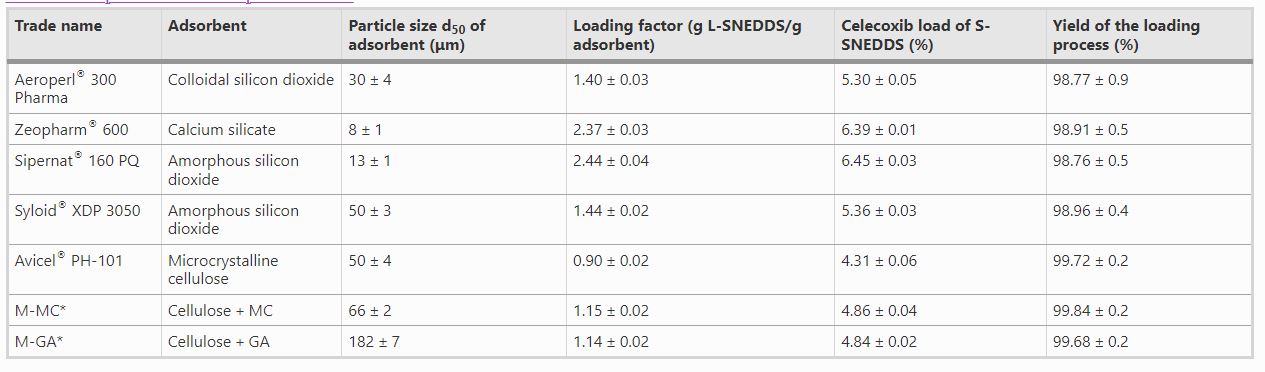
Various commercially available adsorptive carrier materials were investigated, as well as novel cellulose-based microparticles prepared by spray drying from an aqueous dispersion containing Diacel® 10 and methyl cellulose or gum arabic as a binder prior to their use. Particle size and morphology of the carrier materials were screened by scanning electron microscopy and their effects on the loading capacity for L-SNEDDS were investigated, and comparative in vitro dissolution studies of celecoxib L-SNEDDS and the different S-SNEDDS were performed immediately after preparation and after 3 months of storage. Among the adsorptive carrier materials, the novel cellulose-based microparticles were found to be the most suitable for the preparation of celecoxib S-SNEDDS from L-SNEDDS, enabling the preparation of a solid, stable formulation while preserving the in vitro release performance of the L-SNEDDS formulation.
Download the research paper as PDF: Development and Characterization of Celecoxib Solid Self-nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery Systems Prepared Using Novel Cellulose-Based Microparticles as Adsorptive Carriers
Materials
Celecoxib was obtained from Aarti Drugs Ltd. (Mumbai, India). Methyl cellulose, polyoxyethylene (80) sorbitan monooleate (Tween® 80), and d-α-tocopherol polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (d-TPGS) were purchased from Sigma Aldrich Chemie GmbH (Steinheim, Germany). Gelucire® 44/14 was kindly donated by Gattefossé S.A.S (Saint Priest, France). Miglyol® 812 was purchased from Caesar & Loretz GmbH (Hilden, Germany). Aeroperl® 300 Pharma, Zeopharm® 600, and Sipernat® 160 PQ were in-house products of Evonik Resource Efficiency GmbH (Hanau, Germany). Syloid® XDP 3050 was kindly donated by W. R. Grace & Co.-Conn. (Worms, Germany). Avicel® PH-101 was obtained from Dow Chemical Company (Schwalbach am Taunus, Germany) and Diacel® 10 was purchased from CFF GmbH & Co. KG (Gehren, Germany). Gum arabic was obtained from Norevo GmbH (Hamburg, Germany). All other chemicals and solvents were of analytical grade and purchased commercially.
Schmied, FP., Bernhardt, A., Baudron, V. et al. Development and Characterization of Celecoxib Solid Self-nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (S-SNEDDS) Prepared Using Novel Cellulose-Based Microparticles as Adsorptive Carriers. AAPS PharmSciTech 23, 213 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-022-02347-0

