Co-Dispersion Delivery Systems with Solubilizing Carriers Improving the Solubility and Permeability of Cannabinoids (Cannabidiol, Cannabidiolic Acid, and Cannabichromene) from Cannabis sativa (Henola Variety) Inflorescences
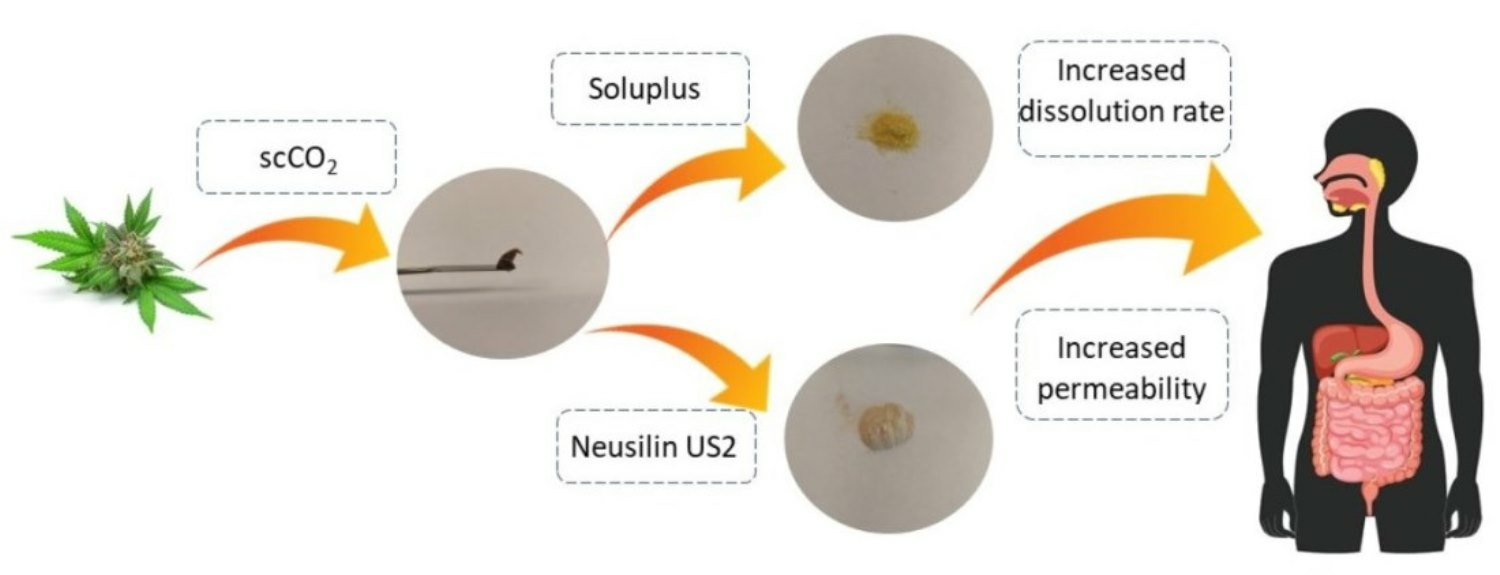
Cannabinoids: cannabidiol (CBD), cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), and cannabichromene (CBC) are lipophilic compounds with limited water solubility, resulting in challenges related to their bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy upon oral administration. To overcome these limitations, we developed co-dispersion cannabinoid delivery systems with the biopolymer polyvinyl caprolactam-polyvinyl acetate-polyethylene glycol (Soluplus) and magnesium aluminometasilicate (Neusilin US2) to improve solubility and permeability. Recognizing the potential therapeutic benefits arising from the entourage effect, we decided to work with an extract instead of isolated cannabinoids. Cannabis sativa inflorescences (Henola variety) with a confirming neuroprotective activity were subjected to dynamic supercritical CO2 (scCO2) extraction and next they were combined with carriers (1:1 mass ratio) to prepare the co-dispersion cannabinoid delivery systems (HiE). In vitro dissolution studies were conducted to evaluate the solubility of CBD, CBDA, and CBC in various media (pH 1.2, 6.8, fasted, and fed state simulated intestinal fluid). The HiE-Soluplus delivery systems consistently demonstrated the highest dissolution rate of cannabinoids. Additionally, HiE-Soluplus exhibited the highest permeability coefficients for cannabinoids in gastrointestinal tract conditions than it was during the permeability studies using model PAMPA GIT. All three cannabinoids exhibited promising blood-brain barrier (BBB) permeability (Papp higher than 4.0 × 10−6 cm/s), suggesting their potential to effectively cross into the central nervous system. The improved solubility and permeability of cannabinoids from the HiE-Soluplus delivery system hold promise for enhancement in their bioavailability.
Download the full article as PDF here Co-Dispersion Delivery Systems with Solubilizing Carriers Improving the Solubility and Permeability of Cannabinoids (Cannabidiol, Cannabidiolic Acid, and Cannabichromene) from Cannabis sativa (Henola Variety) Inflorescences
or read it here
Materials
Cannabis sativa plant material, Białobrzeskie, Tygra, Henola varieties, was donated from the Experimental Station for the Cultivar Testing in Chrząstowo, belonging to the Research Centre for Cultivar Testing in Słupia Wielka. The agricultural details are presented in Supplementary Materials. The plant material for the study was collected after hemp plants reached the maturation phase, i.e., from the moment of seed formation to the first seed. Immediately after collection, two samples of 500 g each were separated and dried to an absolutely dry mass. The entire drying period lasted twenty hours. The temperature in the oven was maintained at no higher than 50 °C for the first 6 hours and the oven temperature was maintained at 105 °C for the remaining 14 h of drying.
Food-grade CO2 was provided by Air Liquide Polska (Cracow, Poland). Soluplus® (polyvinyl caprolactam-polyvinyl acetate-polyethylene glycol graft copolymer), was supplied by BASF SE (Ludwigshafen, Germany). Neusilin US2 (magnesium aluminometasilicate) was kindly provided by Fuji Chemical Industry (Minato, Tokyo). Cannabinoid standards (CBD–CAS: 13956-29-1, CBDA–CAS: 1244-58-2, and CBC–CAS: 20675-51-8) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Poznan, Poland). Trifluoroacetic acid and acetonitrile (high-performance liquid chromatography [HPLC] grade) were provided by Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). The chemicals 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl, iron (III) chloride hexahydrate, 2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid), neocuproine, 2,4,6-Tri(2-pyridyl)-s-triazine, trolox, Trizma® Base, Trizma® hydrochloride, butyrylcholine iodide, acetylcholine iodide, acetylcholinesterase, butyrylcholinesterase, 5,5-dithiobis-2-nitrobenzoic acid, tyrosinase, galantamine, azelaic acid were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Schnelldorf, Germany). Sodium chloride, sodium dihydrogen phosphate, sodium hydrogen phosphate, and dimethyl sulfoxide were obtained from Avantor Performance Materials (Gliwice, Poland). Ammonium acetate, an analytical weighed amount of HCl, 1 N, and methanol were supplied by Chempur (Piekary Śląskie, Poland). Cupric chloride dihydrate, acetic acid (99.5%), and ethanol (96%) were supplied by POCH (Gliwice, Poland). Prisma HT, GIT, BBB lipid solution, an acceptor sink buffer, and a brain sink buffer were supplied by Pion Inc. (Forest Row, East Sussex, UK). High-quality pure water was prepared using a Direct-Q 3 UV purification system (Millipore, Molsheim, France; model Exil SA 67120). FaSSIF and FeSSIF were purchased from Biorelevant (London, UK).
Source: Stasiłowicz-Krzemień, A.; Szulc, P.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. Co-Dispersion Delivery Systems with Solubilizing Carriers Improving the Solubility and Permeability of Cannabinoids (Cannabidiol, Cannabidiolic Acid, and Cannabichromene) from Cannabis sativa (Henola Variety) Inflorescences. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2280. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15092280
Read more over The Role of Excipients in CBD Products here:


