Enteric coating of oral solid dosage forms as a tool to improve drug bioavailability
Enteric coating is a common procedure in the development of oral pharmaceutical dosage forms.
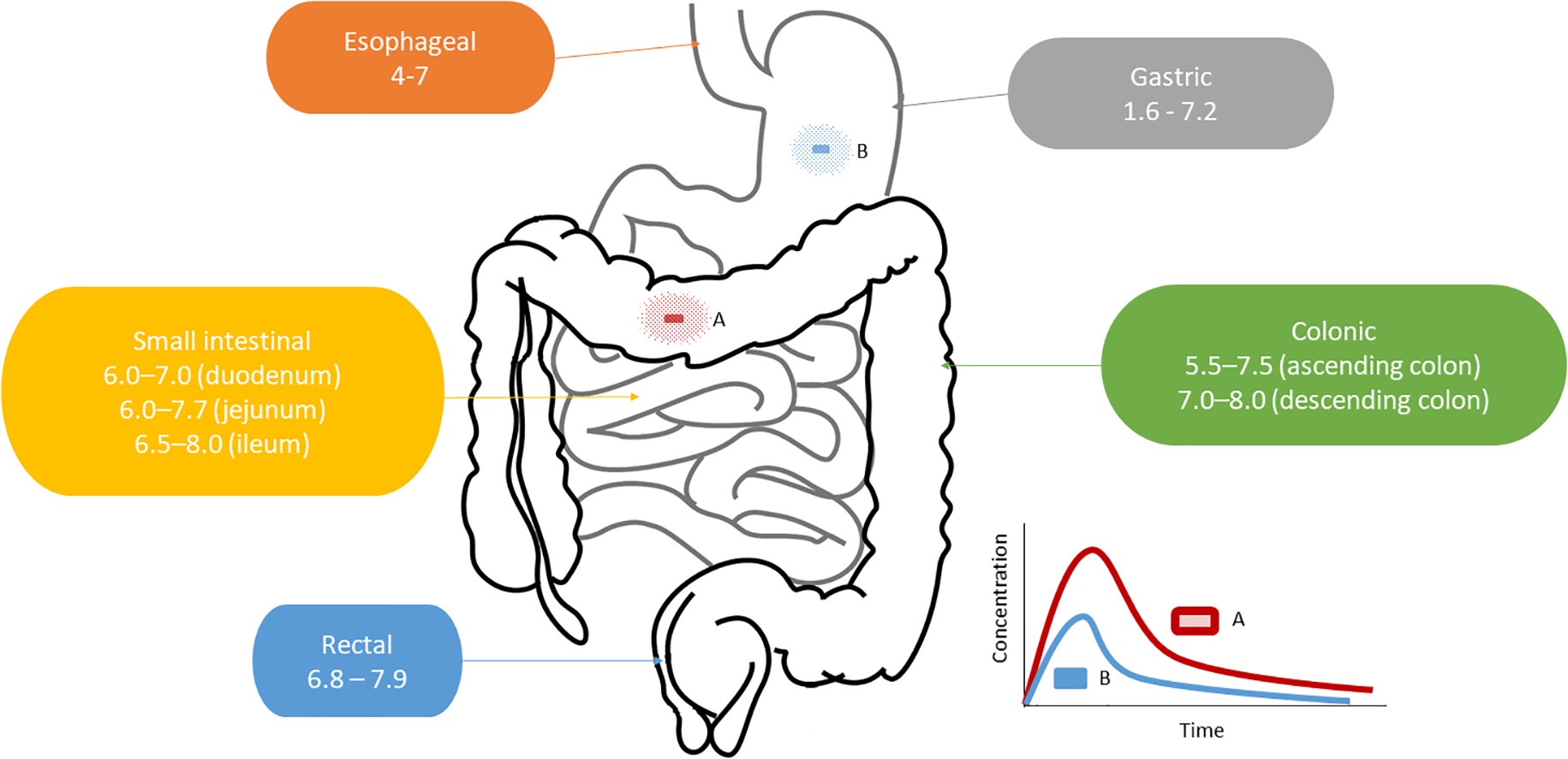
The main advantage of enteric coating is that it protects the drug from acidic pH and enzymatic degradation in the stomach while protecting it from the undesirable effects of some drugs. There is certain controversy regarding the real influence of enteric coating on the bioavailability of many drugs. Various scientific articles have demonstrated an improvement in the extent of bioavailability of some drugs when enteric coating is used.
In recent years, there have been many studies examining different formulation strategies for monolithic and multiparticulate systems, including different pharmaceutical oral dosage forms and delivery systems based on the combined use of enteric coating and other methods that improve the bioavailability of drugs administered orally.
However, the real bioavailability, serum levels and therapeutic effect of these drugs may be influenced by gastrointestinal pH values, gastrointestinal environment, inter-individual or intra-individual variability in gastric emptying and gastrointestinal transit time, interpatient variability associated with the type of polymer used for enteric coating or other formulation variables.
It deserves special attention to know the real influence of enteric coating on the bioavailability of new oral dosage forms. More on Enteric coating of oral solid dosage forms as a tool to improve drug bioavailability

