Continuous Manufacturing of Highly Drug Loaded Matrix Pellets by ProCell® Technology
This poster by Glatt Pharmaceutical Services was presented at the PBP World Meeting 2024:
Introduction
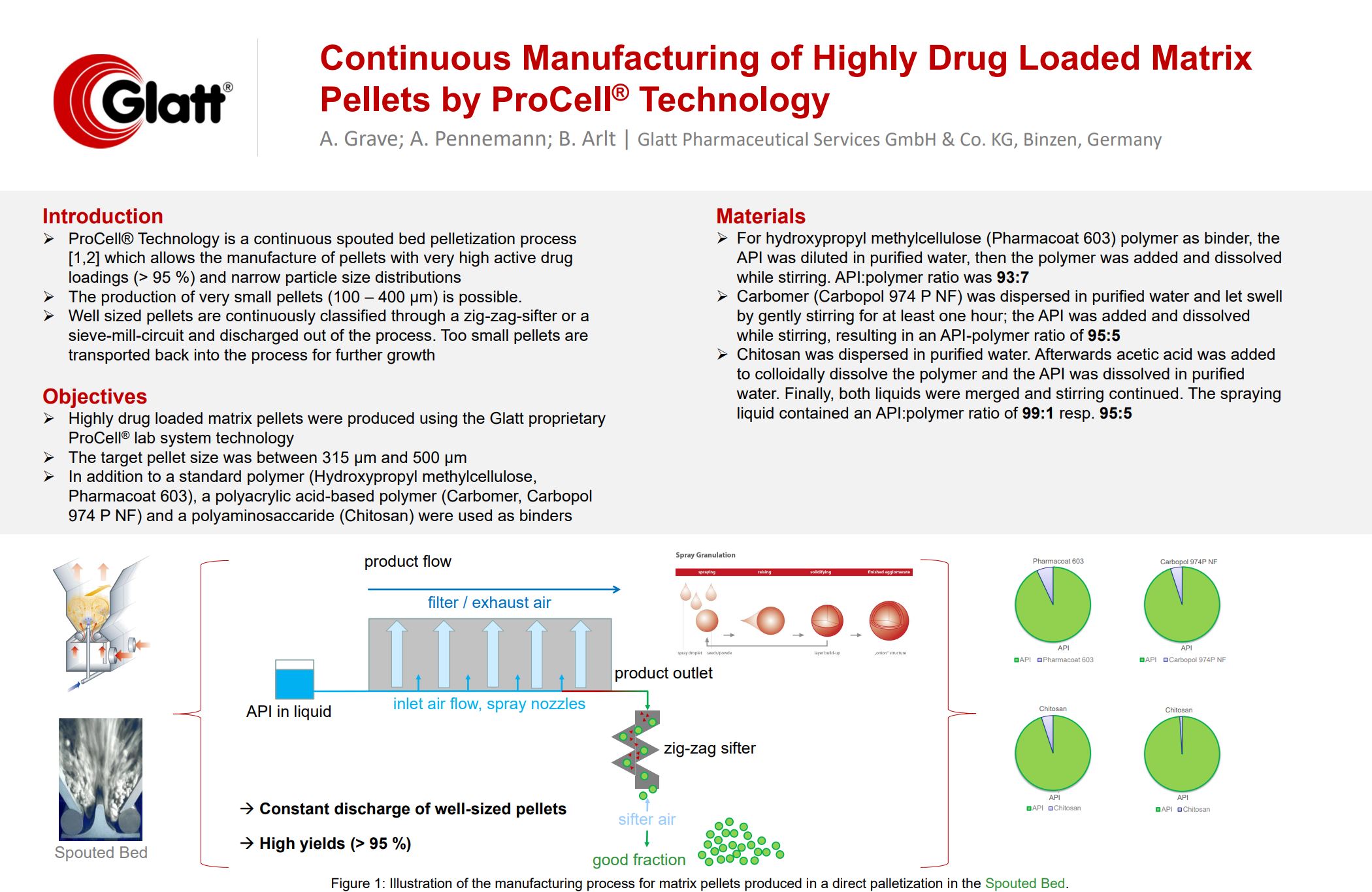
- ProCell® Technology is a continuous spouted bed pelletization process [1,2] which allows the manufacture of pellets with very high active drug loadings (> 95 %) and narrow particle size distributions
- The production of very small pellets (100 – 400 µm) is possible.
- Well sized pellets are continuously classified through a zig-zag-sifter or a sieve-mill-circuit and discharged out of the process. Too small pellets are transported back into the process for further growth
Objectives
- Highly drug loaded matrix pellets were produced using the Glatt proprietary ProCell® lab system technology
- The target pellet size was between 315 µm and 500 µm
- In addition to a standard polymer (Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, Pharmacoat 603), a polyacrylic acid-based polymer (Carbomer, Carbopol 974 P NF) and a polyaminosaccaride (Chitosan) were used as binders
Materials
- For hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (Pharmacoat 603) polymer as binder, the API was diluted in purified water, then the polymer was added and dissolved while stirring. API:polymer ratio was 93:7
- Carbomer (Carbopol 974 P NF) was dispersed in purified water and let swell by gently stirring for at least one hour; the API was added and dissolved while stirring, resulting in an API-polymer ratio of 95:5
- Chitosan was dispersed in purified water. Afterwards acetic acid was added to colloidally dissolve the polymer and the API was dissolved in purified water. Finally, both liquids were merged and stirring continued. The spraying liquid contained an API:polymer ratio of 99:1 resp. 95:5
Characterization of matrix pellets
Results
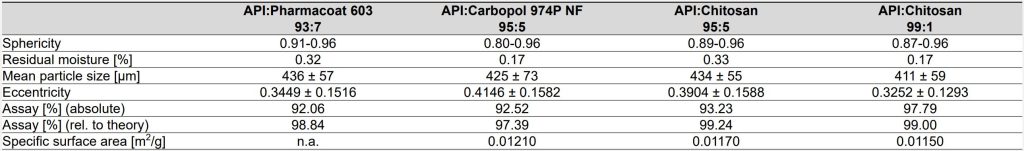
- Pellets with the target particle size between 315 and 500 µm were produced
- Round pellets with a narrow size distribution were obtained [Fig. 2, Table 1]
- Assay values of up to 98 % were analyzed. All pellet types show fast dissolution in pH 6.8
Conclusion
- The ProCell® Technology is a suitable technology for the development and manufacture of highly drug loaded pellets
- The manufacture of pellets with different polymers and API-to-polymer ratios is possible, resulting in high drug loads and immediate release dissolution profiles for all tested polymers
- Narrow particle size distributions and round pellets can be obtained
See the full poster on “Continuous Manufacturing of Highly Drug Loaded Matrix Pellets by ProCell® Technology” here
(click the picture to enlarge the poster)
Source: A. Grave; A. Pennemann; B. Arlt | Glatt Pharmaceutical Services GmbH & Co. KG, Binzen, Germany,
Poster “Continuous Manufacturing of Highly Drug Loaded Matrix Pellets by ProCell® Technology”
Read also the interesting articles on Glatt here:
- Drying liquids – Selecting the best technology for nutraceuticals
- Exploring new ways to produce cosmetic pigments – Interview with Merck and Glatt about the cooperation and the project
- Accessing amorphous solid dispersions for improved Solubility and Bioavailability in paediatric applications

See more posters of the PBP World Meeting 2024: