Formulating Resveratrol and Melatonin Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (SNEDDS) for Ocular Administration Using Design of Experiments
Recent studies have demonstrated that Sirtuin-1 (SIRT-1)-activating molecules exert a protective role in degenerative ocular diseases. However, these molecules hardly reach the back of the eye due to poor solubility in aqueous environments and low bioavailability after topical application on the eye’s surface. Such hindrances, combined with stability issues, call for the need for innovative delivery strategies. Within this context, the development of self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (SNEDDS) for SIRT-1 delivery can represent a promising approach. The aim of the work was to design and optimize SNEDDS for the ocular delivery of two natural SIRT-1 agonists, resveratrol (RSV) and melatonin (MEL), with potential implications for treating diabetic retinopathy.
Pre-formulation studies were performed by a Design of Experiment (DoE) approach to construct the ternary phase diagram. The optimization phase was carried out using Response Surface Methodology (RSM). Four types of SNEDDS consisting of different surfactants (Tween® 80, Tween® 20, Solutol® HS15, and Cremophor® EL) were optimized to achieve the best physico-chemical parameters for ocular application. Stability tests indicated that SNEDDS produced with Tween® 80 was the formulation that best preserved the stability of molecules, and so it was, therefore, selected for further technological studies. The optimized formulation was prepared with Capryol® PGMC, Tween® 80, and Transcutol® P and loaded with RSV or MEL. The SNEDDS were evaluated for other parameters, such as the mean size (found to be ˂50 nm), size homogeneity (PDI < 0.2), emulsion time (around 40 s), transparency, drug content (>90%), mucoadhesion strength, in vitro drug release, pH and osmolarity, stability to dilution, and cloud point. Finally, an in vitro evaluation was performed on a rabbit corneal epithelial cell line (SIRC) to assess their cytocompatibility. The overall results suggest that SNEDDS can be used as promising nanocarriers for the ocular drug delivery of RSV and MEL.
2.1. Materials
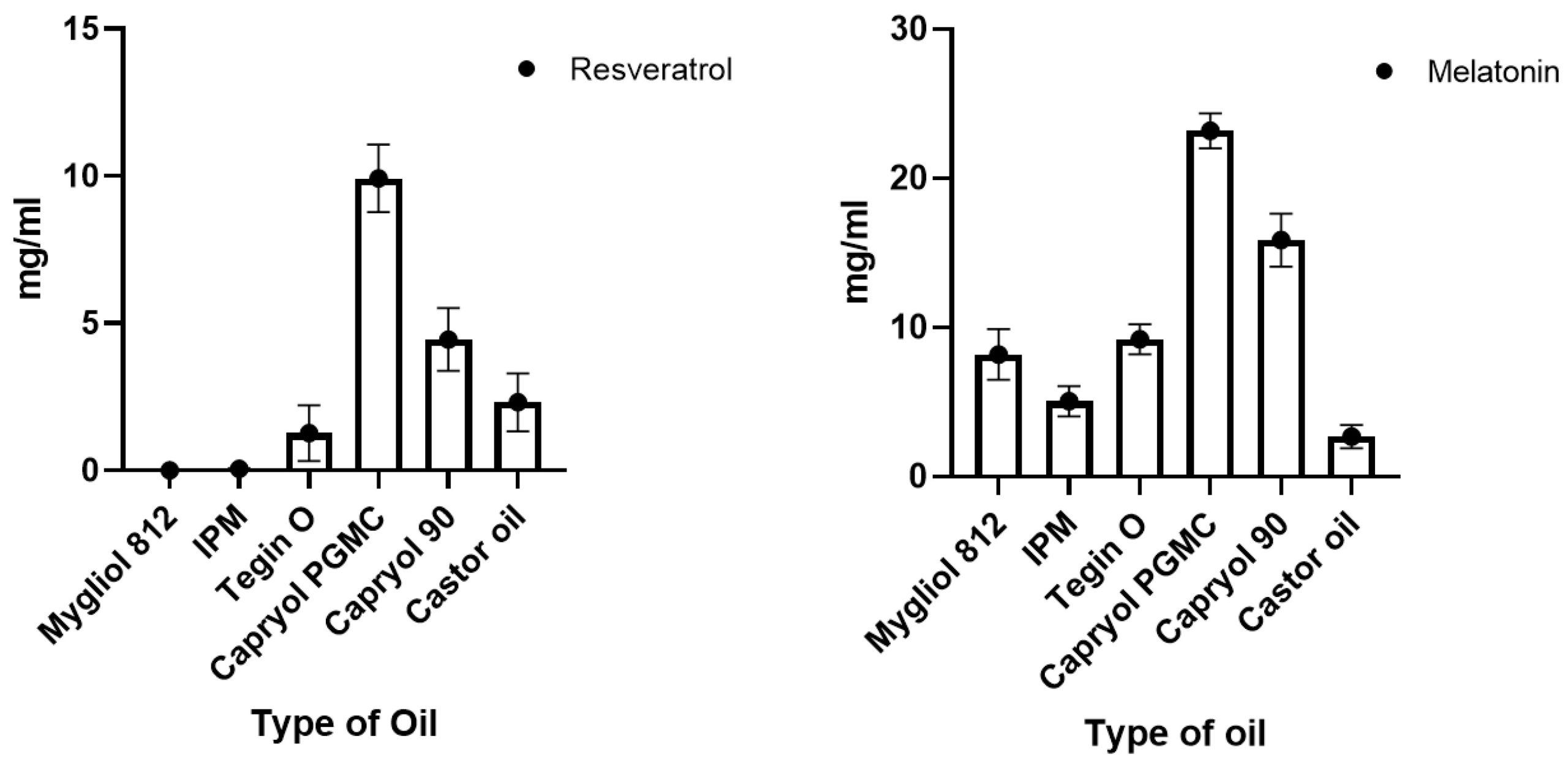
Mygliol® 812 from IOI Oleo GmbH (Witten, Germany), isopropylmyristate (IPM) from A.C.E.F (Fiorenzuola d’Arda, Italy), Tegin® O (glyceryl oleate), Capryol® PGMC (Propylene glycol mono and dicaprylate NF), and Capryol® 90 (propylene glycol monocaprylate NF) donated by Gattefossé SAS (Saint-Priest, France), castor oil from Sigma (Schnelldorf, Germany) were initially tested to assess the solubility of the model drugs in different oily vehicles. For the preparation of the SNEDDS, the following surfactants were used: Tween® 80 (polysorbate 80), Tween® 20 (polysorbate 20), and Cremophor® EL (castor oil polyoxyethylene ether) were purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany); Solutol® HS15 (Kolliphor® HS15, polyethylene glycol (15)-hydroxystearate) was gifted by BASF (Ludwigshafen am Rhein, Germany). Transcutol®, (2-(2-ethoxyethoxy)ethanol) gifted by Gattefossé SAS (Saint-Priest, France) was used as the co-surfactant. MEL (purity ≥98% by HPLC) was purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany); RSV [trans-3,4′,5-Trihydroxystilbene; hydroalcoholic extract from Polygonum cuspidatum, Siebold et Zucc., roots; purity 99.0% by HPLC] was produced by Giellepi SpA (Seregno, Italy) and kindly gifted by Labomar SpA (Istrana, Italy). Supplementary Table S1 resumes the physico-chemical properties of the two drugs.
Download the full study as PDF here: Formulating Resveratrol and Melatonin Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (SNEDDS) for Ocular Administration Using Design of Experiments
or read it here
Zingale, E.; Bonaccorso, A.; D’Amico, A.G.; Lombardo, R.; D’Agata, V.; Rautio, J.; Pignatello, R. Formulating Resveratrol and Melatonin Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (SNEDDS) for Ocular Administration Using Design of Experiments. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 125.
https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16010125

