Development and Evaluation of a Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System for Sinapic Acid with Improved Antiviral Efficacy against SARS-CoV-2
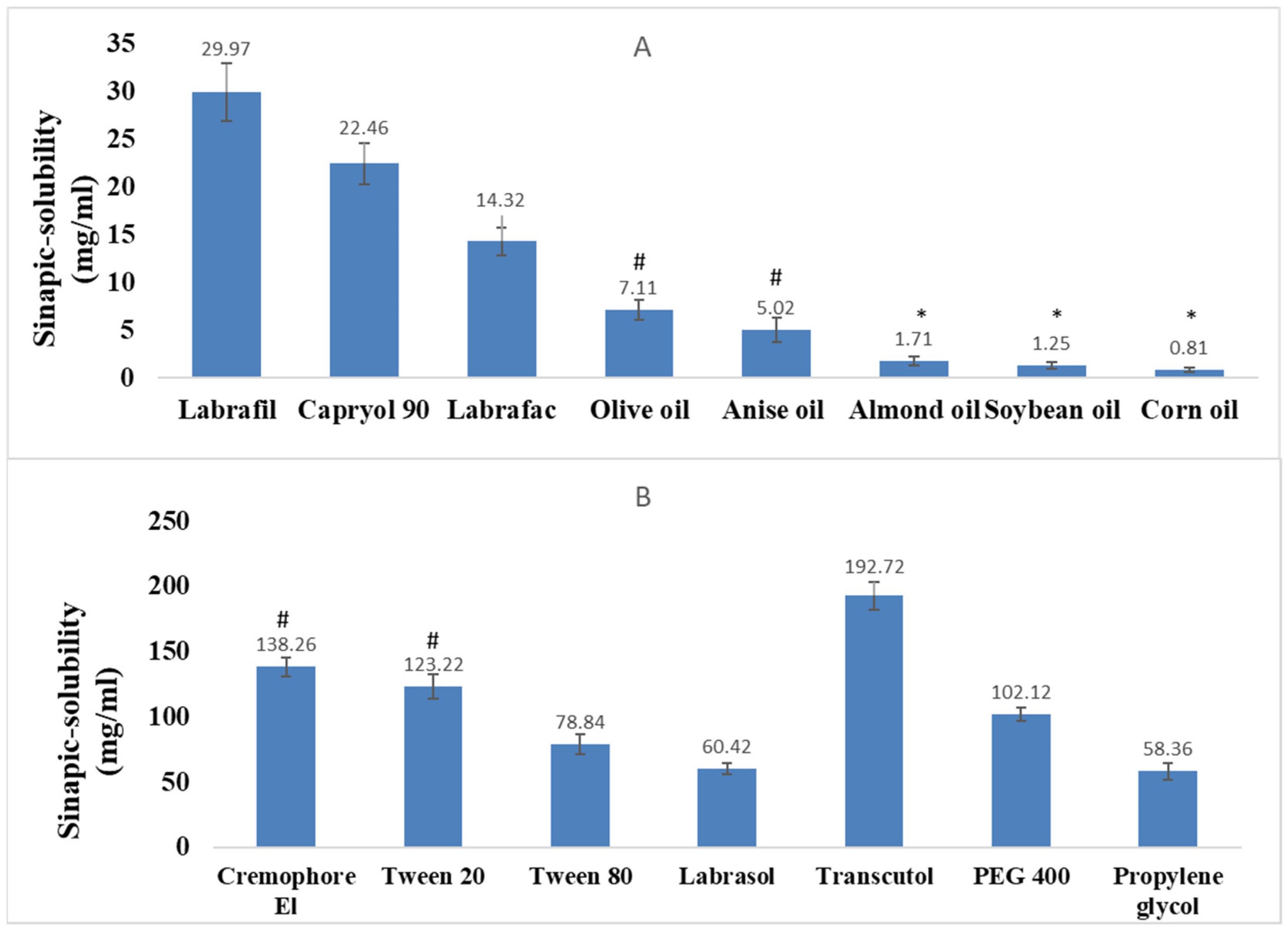
This study aimed to develop a self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (SNE) for sinapic acid (SA) to improve its solubility and antiviral activity. Optimal components for the SA-SNE formulation were selected, including Labrafil as the oil, Cremophor EL as the surfactant, and Transcutol as the co-surfactant. The formulation was optimized using surface response design, and the optimized SA-SNE formulation exhibited a small globule size of 83.6 nm, high solubility up to 127.1 ± 3.3, and a 100% transmittance. In vitro release studies demonstrated rapid and high SA release from the formulation. Pharmacokinetic analysis showed improved bioavailability by 2.43 times, and the optimized SA-SNE formulation exhibited potent antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2. The developed SA-SNE formulation can enhance SA’s therapeutic efficacy by improving its solubility, bioavailability, and antiviral activity. Further in silico, modeling, and Gaussian accelerated molecular dynamics (GaMD)-based studies revealed that SA could interact with and inhibit the viral main protease (Mpro). This research contributes to developing effective drug delivery systems for poorly soluble drugs like SA, opening new possibilities for their application via nebulization in SARS-CoV-2 therapy.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Screening of Components for SA-SNE Development
Download the full study as PDF here: Development and Evaluation of a Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System for Sinapic Acid with Improved Antiviral Efficacy against SARS-CoV-2
or read it here
Alhadrami, H.A.; El-Din, A.S.G.S.; Hassan, H.M.; Sayed, A.M.; Alhadrami, A.H.; Rateb, M.E.; Naguib, D.M. Development and Evaluation of a Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System for Sinapic Acid with Improved Antiviral Efficacy against SARS-CoV-2. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2531. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15112531

