Soluplus® as Promising Polymer for Topical Film Forming Solid Solutions of Betamethasone Dipropionate (BDP)
This poster was presented at the PBP World Meeting 2024 in Vienna:
BACKGROUND & INTRODUCTION
Topical film-forming solutions (FFSs) represent an innovative form of sustained release dermatological dosage forms. They can be applied to the skin as solutions, gels or sprays. After evaporation of the volatile solvent, the polymer contained in the formulation forms a solid film [1]. FFSs possess several advantages, especially for the treatment of localized lesions such as warts, keloids, hypertrophic scars, or non-melanoma skin cancers. They can be applied precisely and once solidified, ensure that accidental contamination is avoided, and a prolonged release is achieved. As previously demonstrated for a non-pharma grade polymer, they can also provide marked enhancement of solubility and skin penetration, especially if the resulting film represents a true molecularly dispersed solid solution [2]. In the present study, it was investigated if such a pronounced solubility enhancement is also possible with the novel, pharma-grade polymer Soluplus® which has shown itself to be an effective absorption enhancer of poorly soluble actives in peroral drug delivery [3].
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Formulation design and physical characterization
- Formulations were prepared by dissolving Soluplus® in a mixture of 95:5 (w/w) ethanol/water with a polymer concentration of 10%.
- The resulting films were transparent and showed very good adherence to skin (Fig. 2-a). The elasticity of the films could be further improved by addition of plasticizers such as triethyl citrate or propylene glycol.
DSC characterization
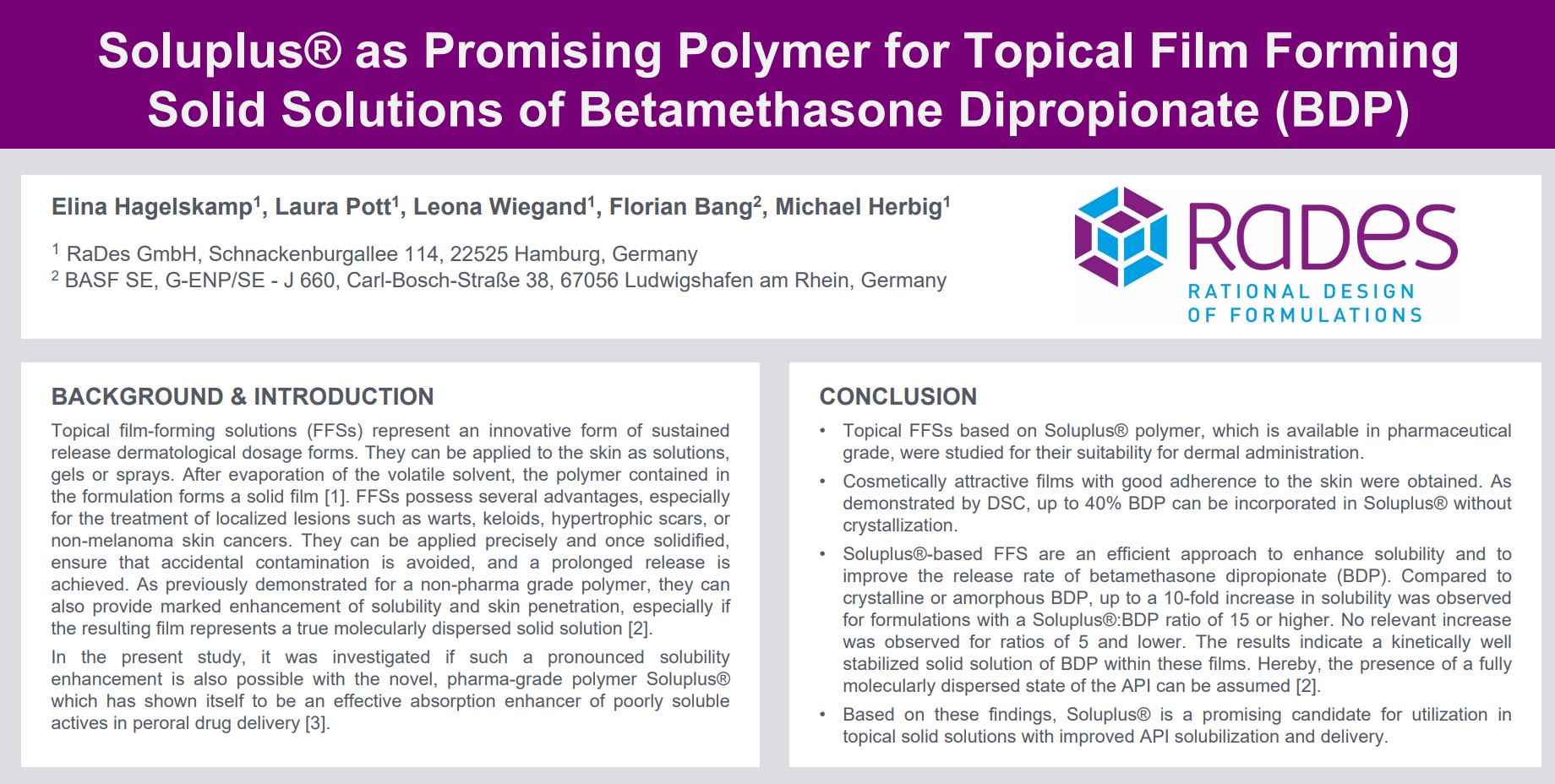
- BDP showed a melting point at 179.8°C with an enthalpy of 74 J/g.
- No melting events were observed in Soluplus® films from 1% up to 40% BDP content, indicating the absence of crystalline material.
Release study setup

- A customized setup was developed for the release study of the in situ generated film. Thereby, FFS or the corresponding negative control (Soluplus®-free BDP solution) was applied to the bottom of a vial, and the ethanol content was allowed to evaporate (approx. 1-2 h). The vial was then mounted freely suspended over a stirred 20 mM citrate buffer solution at pH=5.0, ensuring that the film or BDP layer of the negative control was completely covered by the acceptor medium and was not in direct contact with the stirring bar. Samples of 300 µL, drawn every 5 minutes over the course of 1 hour, were centrifuged for 1 min at 25000 rcf, diluted with MeOH (1:1) and analyzed by UPLC-UV. The sampled solution was directly replaced with fresh acceptor media.
Release of BDP from the residual film
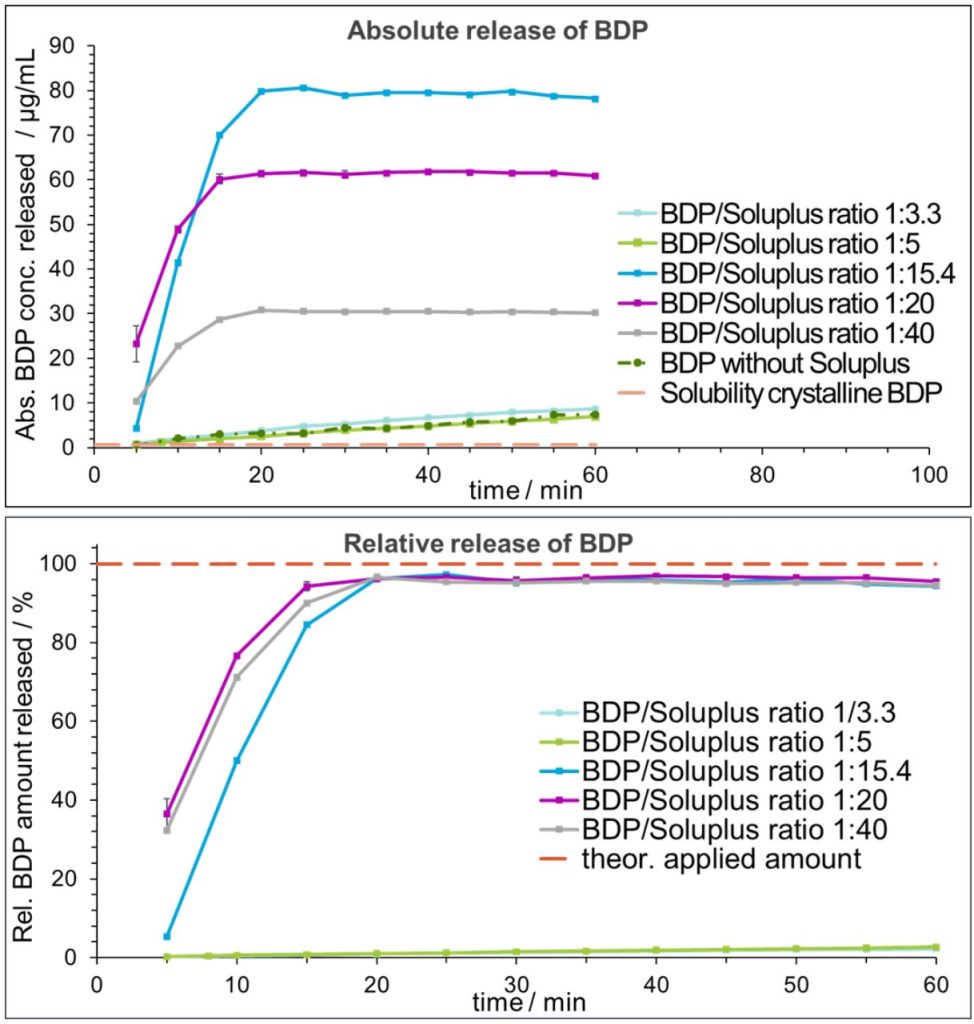
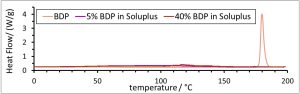
- Mixtures with polymer excess ratios ≤ 5, showed a continuous increase with a maximum concentration of approx. 7 µg/mL, comparable to the negative control. In contrast, for polymer excess ratios ≥ 15.4, a plateau at approx. 98% of the BDP
amount applied was reached after 15-20 min and maintained throughout the experiment. Remarkably, the solubility was hereby improved by a factor of up to 10 compared to the polymer-free reference. - Moreover, kinetic stabilization of the dissolved BDP was demonstrated in a prolonged release experiment of the 1:10 film over 24 hours (data not shown).
- Overall, the observed phenomena are consistent with solid solution characteristics and strongly indicate a molecularly dispersed state of BDP in films with BDP-to-Soluplus® ratios ≥ 15.4
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials
Betamethasone dipropionate (BDP) was used in Pharm. Eur. quality. Soluplus® (polyvinyl caprolactam-polyvinyl acetate-polyethylene glycol graft co-polymer) was kindly provided by BASF SE, Germany.
Methods
DSC measurements were performed on a TA Instruments Discovery DSC250 with a heating rate of 10°C/min. The BDP determination of the release study was performed using a Waters Acquity UPLC system equipped with a photodiode array detector and Empower 2 software. A gradient of water and acetonitrile, both containing 0.1% FA, was used: from 50/50 to 20/80 in 1.50 min, then isocratic at 50/50 for 1.50 min. A Waters Acquity UPLC BEH C18 column (1.7 μm, 2.1 x 50 mm) was used at 60°C, with a flow rate of 0.6 ml/min and an injection volume of 2 μL. The detection wavelength was set to 239 nm.
CONCLUSION
- Topical FFSs based on Soluplus® polymer, which is available in pharmaceutical grade, were studied for their suitability for dermal administration.
- Cosmetically attractive films with good adherence to the skin were obtained. As demonstrated by DSC, up to 40% BDP can be incorporated in Soluplus® without crystallization.
- Soluplus®-based FFS are an efficient approach to enhance solubility and to improve the release rate of betamethasone dipropionate (BDP). Compared to crystalline or amorphous BDP, up to a 10-fold increase in solubility was observed for formulations with a Soluplus®:BDP ratio of 15 or higher. No relevant increase was observed for ratios of 5 and lower. The results indicate a kinetically well stabilized solid solution of BDP within these films. Hereby, the presence of a fully molecularly dispersed state of the API can be assumed [2].
- Based on these findings, Soluplus® is a promising candidate for utilization in topical solid solutions with improved API solubilization and delivery.
See the full poster on “Soluplus® as Promising Polymer” here
(click the picture to download the poster)
Source: Elina Hagelskamp, Laura Pott, Leona Wiegand, Florian Bang, Michael Herbig, poster “Soluplus® as Promising Polymer”, PBP 14th World Meeting, 18 – 21 March 2024, Vienna
Do you want to see more posters of the PBP World Meeting 2024 in Vienna?


