Introduction of Shellac as a pharmaceutical excipient
Shellac as a pharmaceutical Excipient
Shellac is a natural resin that is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry as a coating material for tablets and capsules. It is derived from the secretions of the female lac insect, which feeds on certain trees in Southeast Asia and India. Shellac has been used for centuries in a variety of applications, including as a varnish, food glaze, and adhesive. In the pharmaceutical industry, shellac is highly valued for its ability to provide a protective coating for drugs that are sensitive to moisture, light, or air.

Description of Shellac by drugs.com – Excipient (pharmacologically inactive substance)
“Shellac is composed of hydroxyaliphatic acids and alicyclic acids. Shellac has been used in the pharmaceutical industry as a tablet coating, often for enteric coating on tablets. In the cosmetics industry, shellac has been used in mascara, hair spray, nail polish and eyeliner. Traditionally, shellac has been used in the furniture industry as a wood or paint sealant.
The median lethal dose for shellac has been found to be more than 5 grams per kilogram, many more times than what the average consumer might be exposed. Toxicity studies in animals have shown no adverse effects from oral, dermal, ocular or respiratory tract exposure to formulations containing up to 6 percent shellac. Mutagenicity, irritation, sensitization and photosensitization were not seen in clinical analysis of cosmetic formulations containing up to 6 percent shellac. However, reports from 2011 note cases of allergic contact dermatitis in the eye area of those who used certain cosmetics, such as mascara.”
Manufacturing Process for Pharmaceutical Grade Shellac
The process of manufacturing pharmaceutical grade shellac begins with the collection of resin from the female lac insect. The collected resin is then washed and purified using a series of solvents to remove any impurities. The purified shellac is then processed to remove any remaining solvent and dried into a powder. The final product is then milled to the desired particle size and packaged for use in pharmaceutical applications.
Use in Pharma
Shellac is used extensively in the pharmaceutical industry as a coating material for tablets and capsules. The coating protects the drug from environmental factors such as moisture, light, and air, which can degrade the drug’s potency. Shellac also helps to mask the taste and odor of drugs, making them more palatable for patients.
Another key use of shellac is as a primary polymer base for printing inks used in pharmaceuticals, dietary supplements and foods. An esterified version of shellac is also used for these printing inks. The adhesion properties of shellac work well in these applications on everything from sugar and film coated tablets to all types of capsules.
Dave Schoneker, Black Diamond Regulatory Consulting, LLC
USP-NF and EP Monographs for Shellac
The United States Pharmacopeia-National Formulary (USP-NF) and the European Pharmacopoeia (EP) both have monographs for shellac. The monographs describe the specifications for pharmaceutical grade shellac, including its physical and chemical properties, as well as the tests that must be performed to ensure the quality and purity of the product.
PhEur: Shellac
USP/NF: Shellac
JP/JPE: Purified Shellac and White Shellac
INCI: Shellac
EINECS: 232-549-9
E-Number: 904
CAS Number: 9000-59-3
Products containing Shellac on pharmaexcipients.com
| Product | Company |
| BonuLac® | Biogrund GmbH |
| Sepifilm™ SN | Seppic |
What is the use of shellac in nutraceuticals, food and cosmetics?
In addition to its use in the pharmaceutical industry, shellac is also used in nutraceuticals, food, and cosmetics.
Nutraceuticals
Shellac is used as a coating material for nutraceuticals, such as vitamins and dietary supplements. The coating helps to protect the active ingredients from degradation caused by exposure to moisture, light, and air. It can also improve the appearance of the product and make it easier to swallow.
Food
Shellac is used as a glaze and coating material in the food industry. It is commonly used to coat candies, chocolate, and other confectionery products, providing a glossy and protective coating. It can also be used to coat fruits and vegetables, helping to preserve their freshness and appearance.
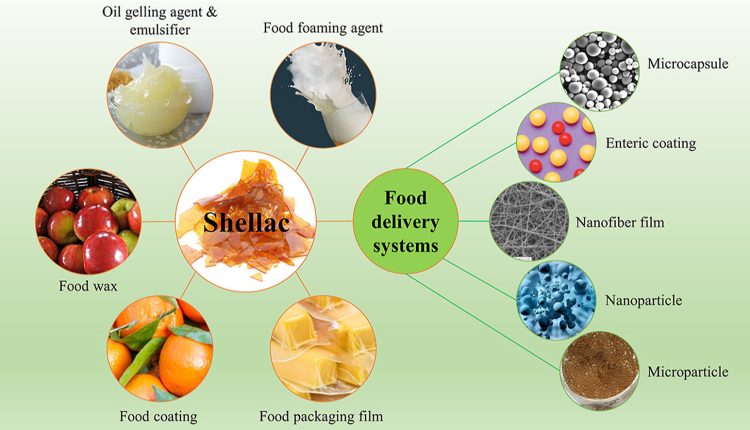
Usage of Shellac
- Food wax
- Food coating
- Food packaging film
- Food foaming agent
- Oil gelling agent & emulsifer
- Microcapsule
- Enteric coating
- Nanofiber film
- Nanoparticle
- Microparticle
Cosmetics
Shellac is used as a film-forming agent in cosmetics, such as nail polishes and hair sprays. It can improve the durability and shine of these products, as well as provide a protective barrier against external factors. Additionally, shellac is a common ingredient in hair styling products, where it is used to help hold hair in place.
In all these industries, the use of shellac is subject to regulations and guidelines to ensure that it is safe for human consumption and use. The source and quality of the shellac used in these industries may also be regulated to ensure that it meets specific standards.


