Nanoamorphous drug products – Design and development
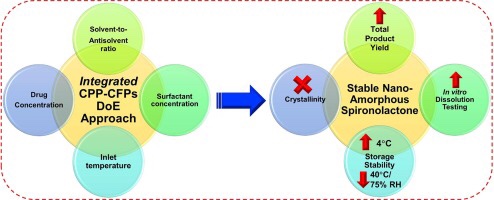
Most of the recent drug compounds coming out of the drug discovery pipeline are labile (multiple polymorphs), and need to be developed into robust marketed oral drug formulations. There are only 22 oral macroamorphous drug products approved by FDA and till date none approved oral nanoamorphous drug products. However, there are several oral nanoamorphous drug formulations (including both labile and non-labile drugs) being researched and a few of these are in the clinical trials. Due to the labile nature of these drug compounds, there is a need to utilize a controlled strategy for design and development of robust nanoamorphous drug formulations in order to prevent any physicochemical instability. The present research focuses on the use of a novel integrated critical process parameters and critical formulation parameters (iCPP-CFPs) DoE approach for the design and development of stable nanoamorphous spironolactone (BCS class II compound with eight polymorphic forms). There are possibilities of the interconversion of these polymorphic forms during processing (manufacturing nanoamorphous particles) and during storage. In the present study, polymorphic transitions (amorphous to crystalline and anhydrous to hydrate) were carefully monitored via orthogonal solid-state characterization tools. Significant polymorphic transitions were observed in the formulations stored at 40 °C/75% RH over six months, however the formulations stored at 4 °C were stable. The significant iCPP-CFPs (solvent-to-antisolvent ratio, drug concentration and inlet temperature of the spray dryer) were critically investigated for their influence on different CQAs (critical quality attributes). Solvent-to-antisolvent ratio and inlet temperature were identified to be the significant iCPP-CFPs. Particle size and total product yield were identified to be the significant CQAs. Lab-scale manufacturing of the spray dried nanoamorphous spironolactone resulted in a remarkably high total product yield (82.4 ± 3.91% w/w) with a uniform and homogenous particle size (244.2 ± 23.32 nm). Furthermore, the physicochemical attributes and the drug release criteria of the nanoamorphous spironolactone were compared with two marketed products (spironolactone tablets, USP 100 mg (Pfizer and Mylan)) and other in-house formulations. In addition, nanoamorphous spironolactone showed a significantly superior kinetic solubility/dissolution rate (10-fold) with a longer supersaturation time (∼6h) compared to the in-house formulations.

