Development of Bedaquiline Loaded SNEDDS Using Quality by Design (QbD) Approach to Improve Biopharmaceutical Attributes for the Management of Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis (MDR-TB)
Background:
The ever-growing emergence of antibiotic resistance associated with tuberculosis (TB) has become a global challenge. In 2012, USFDA has given expedited approval to bedaquiline (BDQ), as a new treatment for drug-resistant TB in adults when no other viable options are available. BDQ is a diarylquinoline derivative and exhibits targeted action on mycobacterium tuberculosis but due to poor solubility desired therapeutic action is not achieved.
Objective:
To develop a QbD-based self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system of Bedaquiline using various oils, surfactants, and co-surfactants.
Methods:
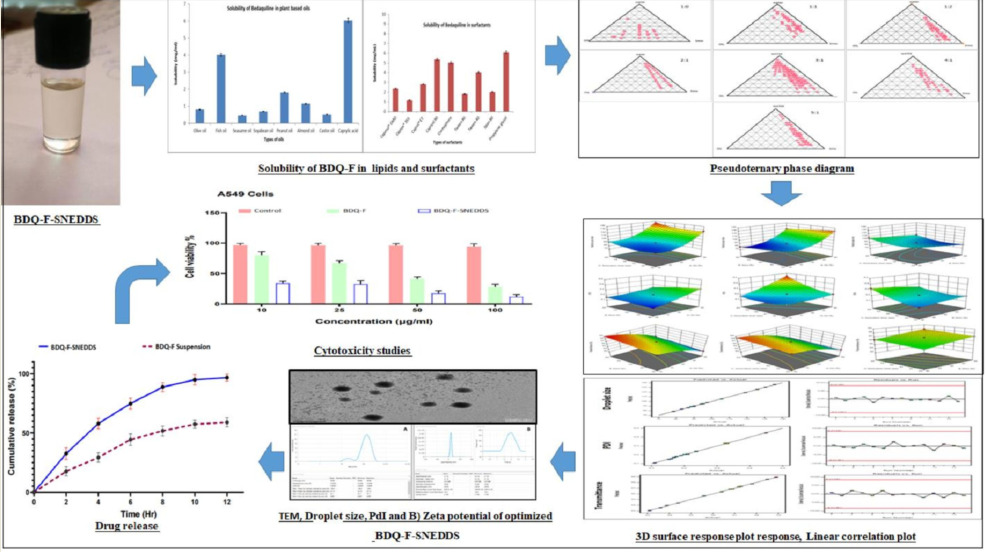
The quality target product profile (QTPP) and critical quality attributes (CQAs) were identified with a patient-centric approach which facilitated the selection of critical material attributes (CMAs) during pre-formulation studies and initial risk assessment. Caprylic acid as a lipid, propylene glycol as a surfactant and Transcutol-P as a co-surfactant were selected as CMAs for the formulation of Bedaquiline fumarate SNEDDS. Pseudo-ternary phase diagrams were constructed to determine the optimal ratio of oil and Smix. To optimize the formulation, a Box-Benkhen design (BBD) was used. The optimized formulation (BDQ-F-SNEDSS) was further evaluated for parameters such as droplet size, polydispersity index (PDI), percentage transmittance, dilution studies, stability studies, and cell toxicity through the A549 cell. Results: Optimized BDQ-F-SNEDDS showed well-formed droplets of 98.88±2.1 nm with a zeta potential of 21.16 mV. In vitro, studies showed enhanced drug release with a high degree of stability at 25 ± 2 ºC & 60 ± 5 % and 40 ± 2 ºC & 75± 5 %. Furthermore, BDQ-F-SNEDDS showed promising cell viability in A549 cells indicating BDQ-F-SNEDDS as a safer formulation for oral delivery. Conclusion: Finally, it was concluded that the utilization of a QbD approach in the development of BDQ-F-loaded SNEDDS offers a promising strategy to improve the biopharmaceutical properties of the drug, resulting in potential cost and time savings.
2. Materials
Bedaquiline fumarate (BDQ-F) (99.5% pure) was obtained as a complimentary sample from Omgene Life Sciences Pvt Ltd. The high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) grade solvents, such as Acetonitrile, Methanol, and Ethanol, were procured from Merck Ltd in Mumbai, India. Transcutol-P and Cremophor R EL were acquired from Sigma-Aldrich (Bangalore, India). All other chemicals used in the study were of analytical grade and deionized water was used for all experiments.
Download the Pre-Print as PDF here: Pre-Print – Development of Bedaquiline Loaded SNEDDS Using Quality by Design (QbD) Approach to Improve Biopharmaceutical Attributes for the Management of Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis (MDR-TB)
or read it here
Jahan, R.N.; Solanki, P.; Akhtar, M.S.; Khan, Z.; Ahmad, F.J.; Aqil, M.; Sultana, Y. Development of Bedaquiline Loaded SNEDDS Using Quality by Design (QbD) Approach to Improve Biopharmaceutical Attributes for the Management of Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis (MDR-TB) . Preprints 2023, 2023080906.
https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202308.0906.v1
Read more on the Word Tuberculosis Day here:


