Combination of time-dependent polymer and inulin as a coating for sustained delivery of budesonide pellets aimed for use in IBD treatment
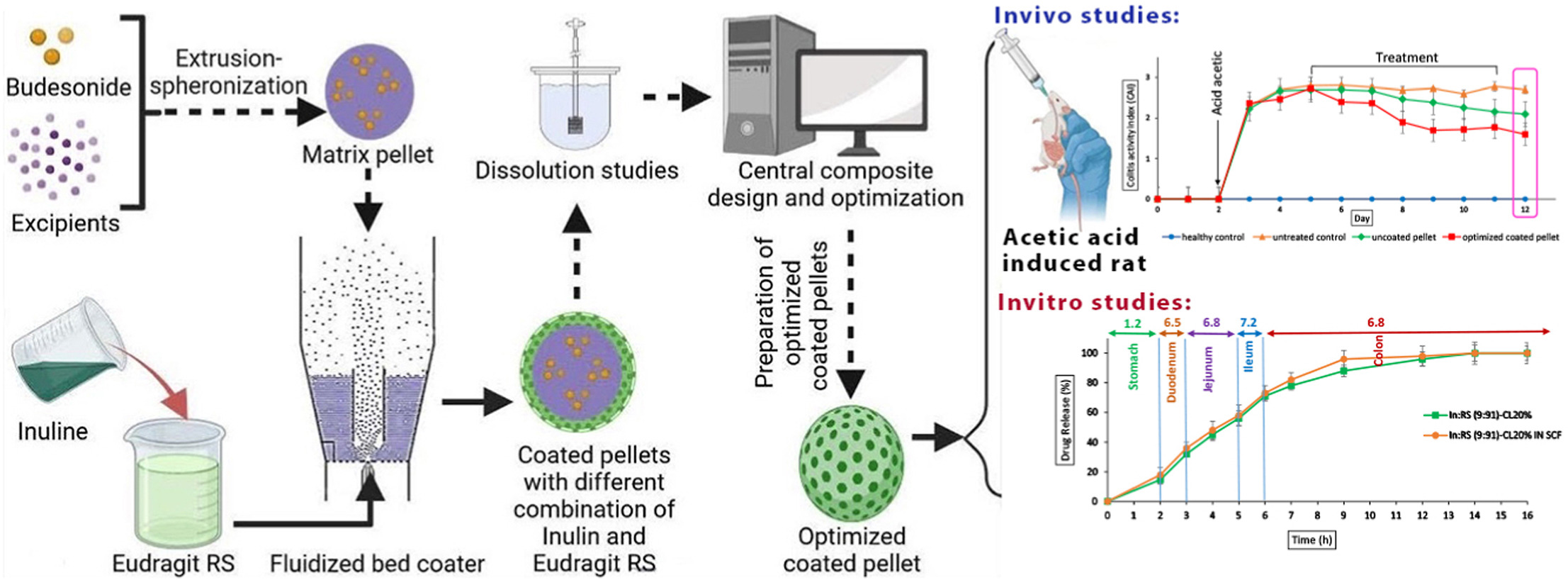
Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, both forms of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), are prevalent conditions. Budesonide, a medication widely recommended as a first-line treatment for Crohn’s disease, necessitates the development of formulations capable of delivering the drug to the intestinal region. Inulin, a highly effective polysaccharide and prebiotic in treating IBD, possesses inadequate film-forming abilities. However, harnessing the beneficial effects of inulin in IBD treatment, researchers designed a single-layer coating using a central composite design (CCD) that combined inulin and eudragit RS. This coating aimed to sustain the release of budesonide pellets, providing targeted therapy for Crohn’s disease.
The study focused on two independent variables: the percentage of inulin and the coating level. The responses evaluated were the release of the drug during a 2-h period at pH 1.2, as well as within three and 10 h at pH 6.8. The release profiles of the coated pellets were examined in media with varying pH levels to determine the optimal coating formulation. Subsequently, the optimized coated pellets underwent continuous mode dissolution testing to assess their release profile. Finally, the impact of the optimized formulation on reducing inflammation was evaluated in rats with experimentally induced colitis. The coating formulation composed of 9% inulin and 91% eudragit RS at a coating level of 20% displayed a complete and pH-independent release profile.
Approximately 85% of the drug was gradually released throughout the small and large intestines. The presence of inulin in the coating formulation rendered it susceptible to microbial degradation, resulting in an increased drug release rate in the colonic medium containing rat cecal content. In vivo results demonstrated the favorable therapeutic effects of this delivery system in treating inflammation in rats. The controlled release of the drug throughout the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) contributed to its efficacy in mitigating inflammation.
Download the full article as PDF here Combination of time-dependent polymer and inulin as a coating for sustained delivery of budesonide pellets aimed for use in IBD treatment
or read it here
Materials
Budesonide (Jaber Ebne Hayyan, Tehran, Iran), Avicel PH 102, Lactose monohydrate, triethyl citrate (TEC) and talc (Merck Company, Frankfurt, Germany), polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP K30) (Rahavard Tamin, Tehran, Iran), inulin (high molecular weight) (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, USA) isopropyl alcohol (Dr. Mojallaly, Tehran, Iran), sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) (Scharlau,Barcelona, Spain) and eudragit RS 30D (Evonik Industries, AG Hanau, Germany) were utilized in this study. Other reagents and solvents utilized in this study were of analytical grade.
Fatemeh Soltani, Hossein Kamali, Abbas Akhgari, Mahboobeh Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar, Hadi Afrasiabi Garekani, Ali Nokhodchi, Fatemeh Sadeghi, Combination of time-dependent polymer and inulin as a coating for sustained delivery of budesonide pellets aimed for use in IBD treatment, Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 2023, 104927, ISSN 1773-2247, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2023.104927.
Read more on Introduction to Talc as a pharmaceutical excipient here:


