Introduction to Talc as a pharmaceutical excipient
Talc as a pharmaceutical Excipient
Talc is a naturally occurring mineral that is commonly used in a wide range of industries, including the pharmaceutical industry. In pharmaceuticals, talc is used as a lubricant and diluent in tablet formulations, as well as a glidant in capsule formulations. It is also used as an excipient in topical and oral suspensions, and as a bulking agent in some powders.

Definition as per “Pharmazeutische Hilfsstoffe” (Peter C. Schmidt – Siegfried Lang)
Talcum, soapstone, soapstone, a selected, powdered, natural, hydrous magnesium silicate (MgSiO3). It has a monoclinic crystal structure. The substance may contain different amounts of minerals, among which chlorite (hydrous aluminum and magnesium silicates), magnesite (magnesium carbonate), calcite (calcium carbonate) and dolomite (calcium and magnesium carbonate) are predominant.
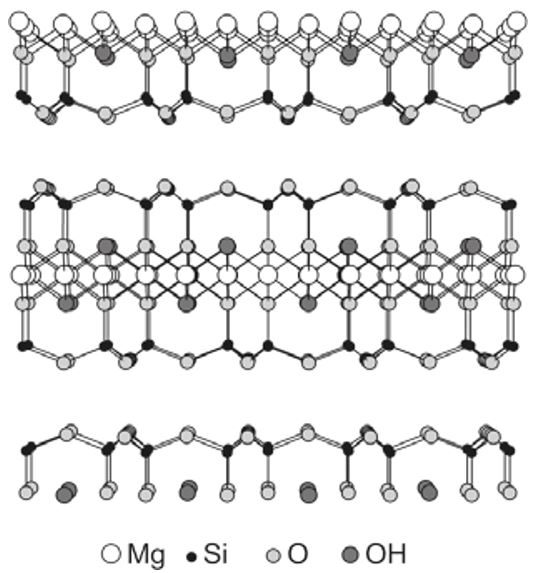
Talc for pharmaceutical purposes must be free of asbestos. Chemical purity 93-98% for high quality talc types. In 85 different types of talc from 15 countries, X-ray diffraction has shown purities between 47 and 93% (Soriano et al. 1996). The chemical composition of the pure substance is Mg3Si4O10(OH)2, Mr 379.3. like hectorite, talc. is a three-layer silicate. The figure shows in the middle the three-layer silicate with the octahedral layer and the central atom magnesium, flanked by two SiO4 tetrahedral layers. The next three-layer silicate level follows at the top and bottom. The individual layers are easily displaceable against each other, which is the reason for the high slip properties of talc.
Sources and Manufacturing Process
Pharmaceutical grade talc is derived from high-quality talc ores that are mined from deposits around the world. The majority of talc used in pharmaceuticals is sourced from mines in the United States, China, and India. The talc ore is then processed to remove impurities and produce a fine, white powder that meets the requirements of the pharmaceutical industry.
The manufacturing process for pharmaceutical grade talc involves several steps, including crushing, grinding, and milling the ore to a fine powder. The talc is then purified through a process of flotation, where the impurities are removed using water and chemicals. The resulting talc powder is then sterilized to ensure it meets the standards required for use in pharmaceuticals.
Use in Pharmaceuticals
Talc is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry due to its unique properties, including its ability to absorb moisture, lubricate, and flow easily. It is commonly used in tablet formulations as a lubricant and diluent, which helps to improve the flow properties of the powder mixture and ensure that the tablets are easily swallowed. Talc is also used as a glidant in capsule formulations to improve the flow of the powder into the capsule.
Talc is used as an excipient in topical and oral suspensions, where it helps to stabilize the suspension and prevent settling. It is also used as a bulking agent in some powders, where it provides a non-reactive and inert filler. Use of talc in different dosage forms:
Tablets
- Lubricant: Talc helps to reduce friction between particles during the tablet compression process, preventing sticking and ensuring smooth tablet release from the die.
- Diluent: Talc serves as a filler, reducing the concentration of active ingredient in the tablet and ensuring consistent tablet size and weight.
- Disintegrant: Talc promotes tablet disintegration by absorbing moisture and swelling, which helps to break down the tablet into smaller particles for faster dissolution.
Capsules
- Glidant: Talc is used as a glidant in capsule formulations to improve the flow of the powder into the capsule shell.
- Lubricant: Talc reduces friction between the capsule shell and the powder, ensuring easy release of the powder from the capsule.
Topical and Oral Suspensions
- Stabilizer: Talc is used as a stabilizer in suspensions, preventing settling of particles by increasing the viscosity of the liquid.
- Bulking Agent: Talc provides bulk to the suspension, improving the appearance and feel of the product.
Powders
- Bulking Agent: Talc provides bulk to powders, ensuring that they fill their containers completely.
- Lubricant: Talc reduces friction between the particles in powders, making them easier to mix and preventing caking or clumping.
USP-NF and EP Monographs for Talc
The United States Pharmacopeia-National Formulary (USP-NF) and European Pharmacopoeia (EP) monographs provide standards for the quality and purity of talc used in pharmaceuticals. The USP-NF monograph for talc requires that it meets certain physical and chemical properties, including a minimum purity of 98%, a maximum limit of 0.5% acid-insoluble substances, and a maximum limit of 3% of particles greater than 75 microns in size. The EP monograph for talc requires a minimum purity of 98% and a maximum limit of 1% acid-insoluble substances.
- CAS Number: 14807-96-6
- INCI: Talc
- EINECS: 238-877 -9
- E-Number: 553b
In conclusion, talc is a commonly used excipient in the pharmaceutical industry due to its unique properties. Talc is a versatile excipient that serves multiple functions in pharmaceutical dosage forms, making it an important component of many formulations.


