The Effect of Freeze-Drying on Mucoadhesion and Transport of Acrylated Chitosan Nanoparticles
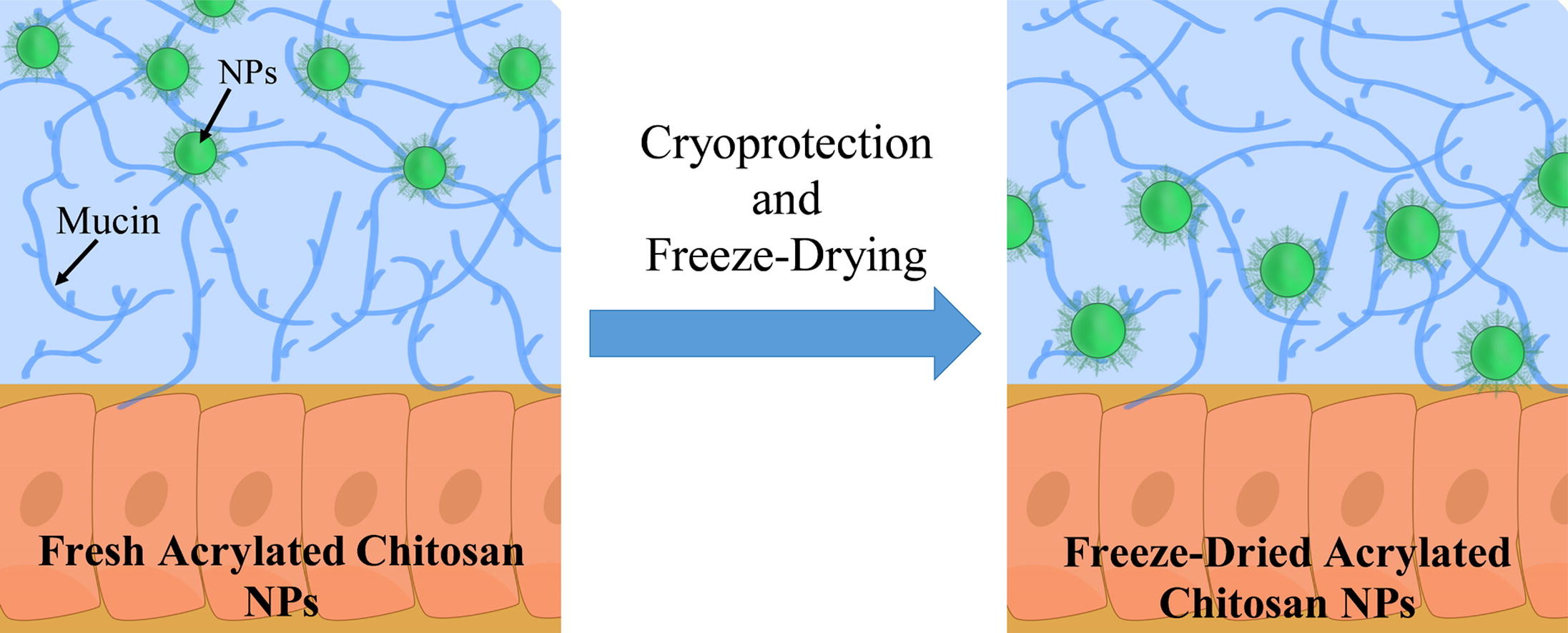
Nanoparticle-based mucosal drug delivery is a promising method to increase the residence time of a drug in the mucosa.
It is known that the stability of polysaccharide-based nanoparticles in aqueous solutions is limited, due to hydrolysis; hence the long-term stability of a formulation is usually improved by freeze-drying. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of cryoprotection and freeze-drying on the physical and chemical properties of mucoadhesive acrylated chitosan (ACS) nanoparticles including the potential of these carriers to deliver drugs.
The results showed that the most effective cryoprotection was achieved using sucrose. The incorporation of a hydrophilic macromolecular drug, dextran sulfate, increased the nanoparticle size and decreased the zeta potential for both fresh and freeze-dried nanoparticle formulations.
In addition, the freeze-dried nanoparticles presented penetration across a mucus gel layer and the flow through technique revealed that short term mucoadhesive properties were not impaired. ACS nanoparticles were able to deliver a model drug across a mucin gel layer but could not improve drug penetration through the triple co-culture cell model that was used in order to mimic the small intestine epithelium.
See the research
Author links open overlay panelShakedEliyahu, AndreiaAlmeida, MariaHelena Macedo, Josédas Neves, BrunoSarmento, HavazeletBianco-Peled
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118739

