How to ensure a successful tablet coating formulation development by using polyvinyl alcohol and HPMC in combination with calcium carbonate as a titanium dioxide alternative
Purpose
- Recent ban of titanium dioxide (TiO2; E171) for the use in food and nutritional supplements (European Commission). The regulation includes a commitment to review the necessity of titanium dioxide as a white colorant in medicinal products1.
- It is challenging to find a suitable alternative for TiO2 because of its high opacity.
- As an approved white drug colorant in the EU, calcium carbonate is of interest as a potential alternative to TiO2 in the coating process.
Objectives
- Evaluate a suitable alternative pigment to TiO2 for tablet coating.
- Deep assessment of calcium carbonate in terms of its opacifying potential as well as the impact on required process conditions.
- Recommended formulations with a comparable covering effect need to be identified.
Methods
Colored tablet cores were manufactured using a rotary tablet press (FETTE 1200i) at 74 rpm; compression force: 10 kN; height: 5.0 mm; tablet diameter: 11 mm; targeted tablet weight: 500 mg. A simplified core formulation with red iron oxide as pigment was used: 98.0% mannitol +0.5% iron oxide +1.5% magnesium stearate. The coating with Parteck® COAT EMPROVE® ESSENTIAL (Polyvinyl alcohol, Merck) was performed using a rotating drum coater type LDCS from Vector Freund Corporation. To identify a relevant coloring of the core tablets, different concentrations of iron oxide were tested and determined by color measurements. The ratio of mannitol was adapted in respect of the amount of iron oxide to simulate a suitable coloring.

Color measurements were performed by using Konica Minolta Spectrophotometer CM-700d. At a level of 0.5% iron oxide a suitable coloration of tablet cores was achieved to simulate potential colored drug substances and to evaluate the covering properties of calcium carbonate in comparison to titanium dioxide.
Results
Based on the results it was found that CaCO3 represents a viable alternative to TiO2 by increasing the solid content in the coating dispersion without any negative effect on the viscosity or feasibility of the coating process in general. Although the effectiveness and efficiency to TiO2 is not directly comparable, the covering effect of CaCO3 can be enhanced by adapting the solid content of CaCO3.
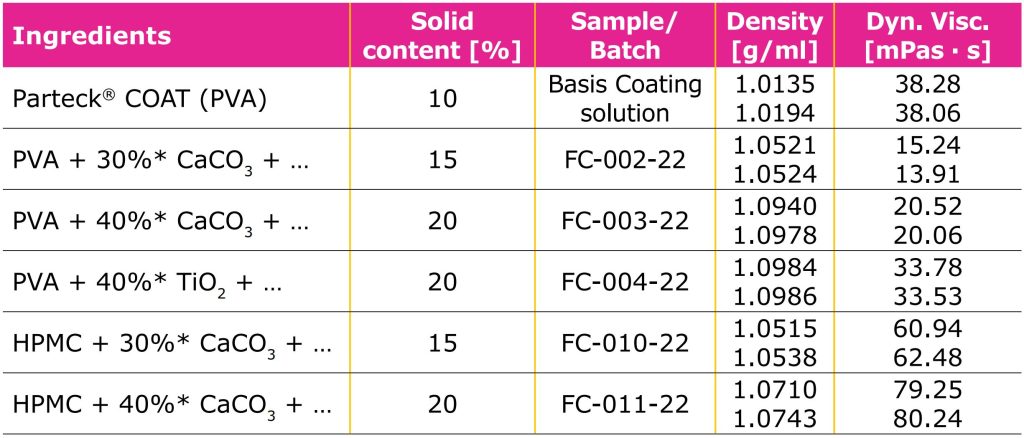
Characterization of different coating solutions at 25 °C; *In relation to the total solid content in the coating dispersion; ingredients include 10% talcum and 20% plasticizer; the amount of polymer was adapted to the individual formulation.
Coating liquid
It was observed that the addition of pigments can affect the viscosity of the spraying liquid. Calcium carbonate has low influence on viscosity in comparison to basic coating solution whereas for titanium dioxide an increase of viscosity is observed. This effect is even more pronounced when using HPMC based polymers (see Table 1).
Film coated tablets
Trials with calcium carbonate
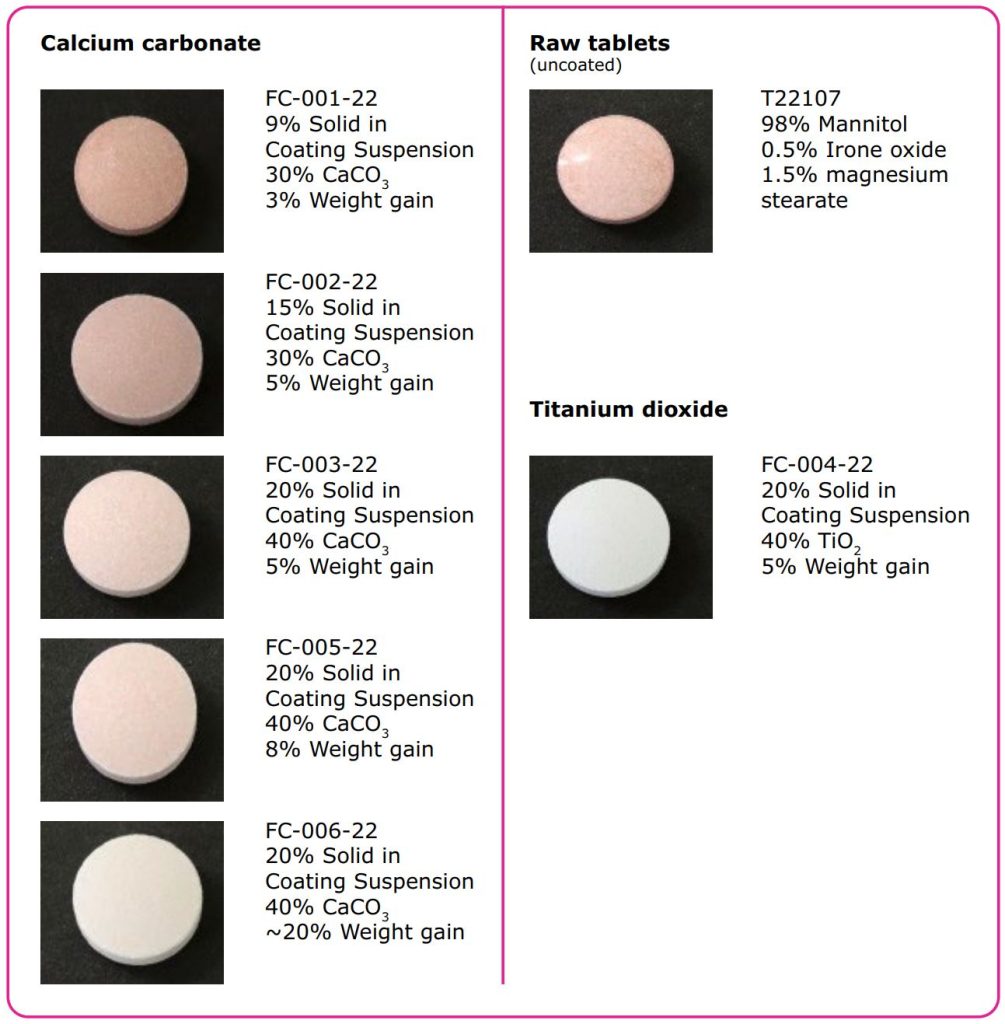
- Constant & homogenous coating process was achieved.
- Higher solid content and weight gain lead to a better covering of colored core tablets.
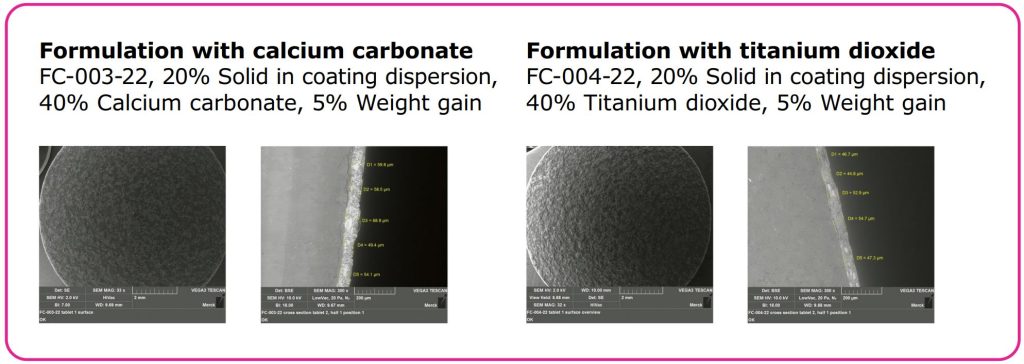
- Higher coating thickness is achieved at same process conditions compared to TiO2 (see Figure 2).
Trials with titanium dioxide
- Requires higher speed and more time for homogenization of coating suspension with 30% w/w solid content.
- Higher solid content leads to material settling in coating pipe and spray gun blocking tendency.
- Lower coating thickness (see Figure 2).
Conclusions
- The replacement of titanium dioxide by calcium carbonate has an interesting potential for future coating applications. In combination with polyvinyl alcohol low viscosities of the spraying liquid can be maintained even at high solid contents which can enable a high process efficiency.
- This effect can potentially balance the required weight gains required to achieve the targeted covering effect of the core tablet surface.
- It could be demonstrated that iron oxide can be integrated in core-tablets to simulate stronger colored drug substances. Color measurements confirm the tendency that with higher calcium carbonate content the red coloring (parameter a) is further reduced indicating a stronger covering effect caused by higher opacity which is also confirmed by increasing L values (see Figure 4).
See the full poster on “How to ensure a successful tablet coating as a titanium dioxide alternative” here
(click the picture to download the poster)
Source: Merck poster “How to ensure a successful tablet coating as a titanium dioxide alternative”
Do you need more information or a sample of excipients by Merck?