Layer by Layer: The Fundamentals of Multi-Layer Tableting
Multi-layer tableting offers a straightforward solution for a variety of challenging formulations. From multi-phasic release systems— to combinations of incompatibles (APIs)—to gastro-retentive tablets, this underutilized method provides efficiency and cost- savings as compared with more popular complex processes.
This article compares multi-layer formulation options to traditional methods, providing a step-by-step guide to the multi-layer tableting process, and offering crucial tips to formulating and manufacturing robust multi-layer tablets. It demonstrates how tooling considerations, excipient selection, layer design, and tamping force adjustment can affect overall tablet robustness as well as layer-to-layer adhesion.
FUNDAMENTALS OF MULTI-LAYER TABLETING
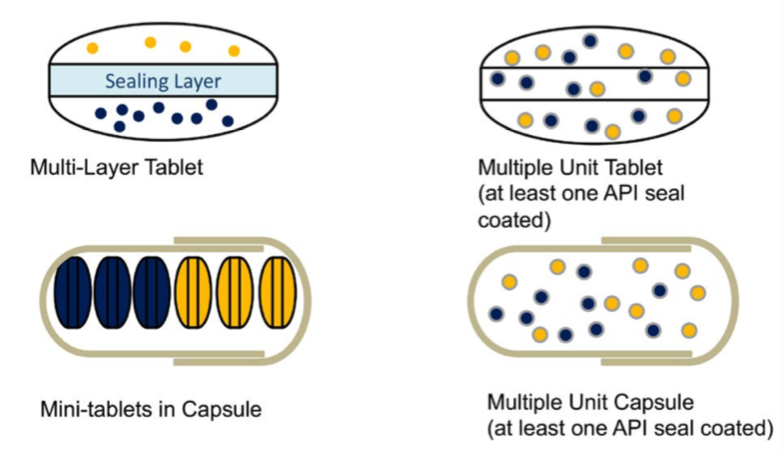
Patient treatments often combine two drugs that have synergistic therapeutic activity, spurring drug developers to be innovative with fixed-dose combinations. Not all compounds are physically and chemically compatible, thus making multi- layer tablets—with APIs in separate layers—extremely useful.
A combination of two or more delivery mechanisms is another reason to use a multi-layer tablet. Ingredients in multi-layered tablets can be delivered at different rates or by different mechanisms, one layer could have a loading dose while the other might provide a sustaining dose of the same medication, or each layer could contain a different sustained-release compound. There are a variety of approaches to formulating these multi-layer tablets.
Download the full article here: Executive Summary The Fundamentals of Multi-layer Tableting
Excutive summary by Gernot Warnke and Tony Carpanzano from JRS Pharma in Pharmaceutical Technology

