Interactions between multifunctional pharmaceutical excipients and efflux pump for optimal drug transport and bioavailability: An overview
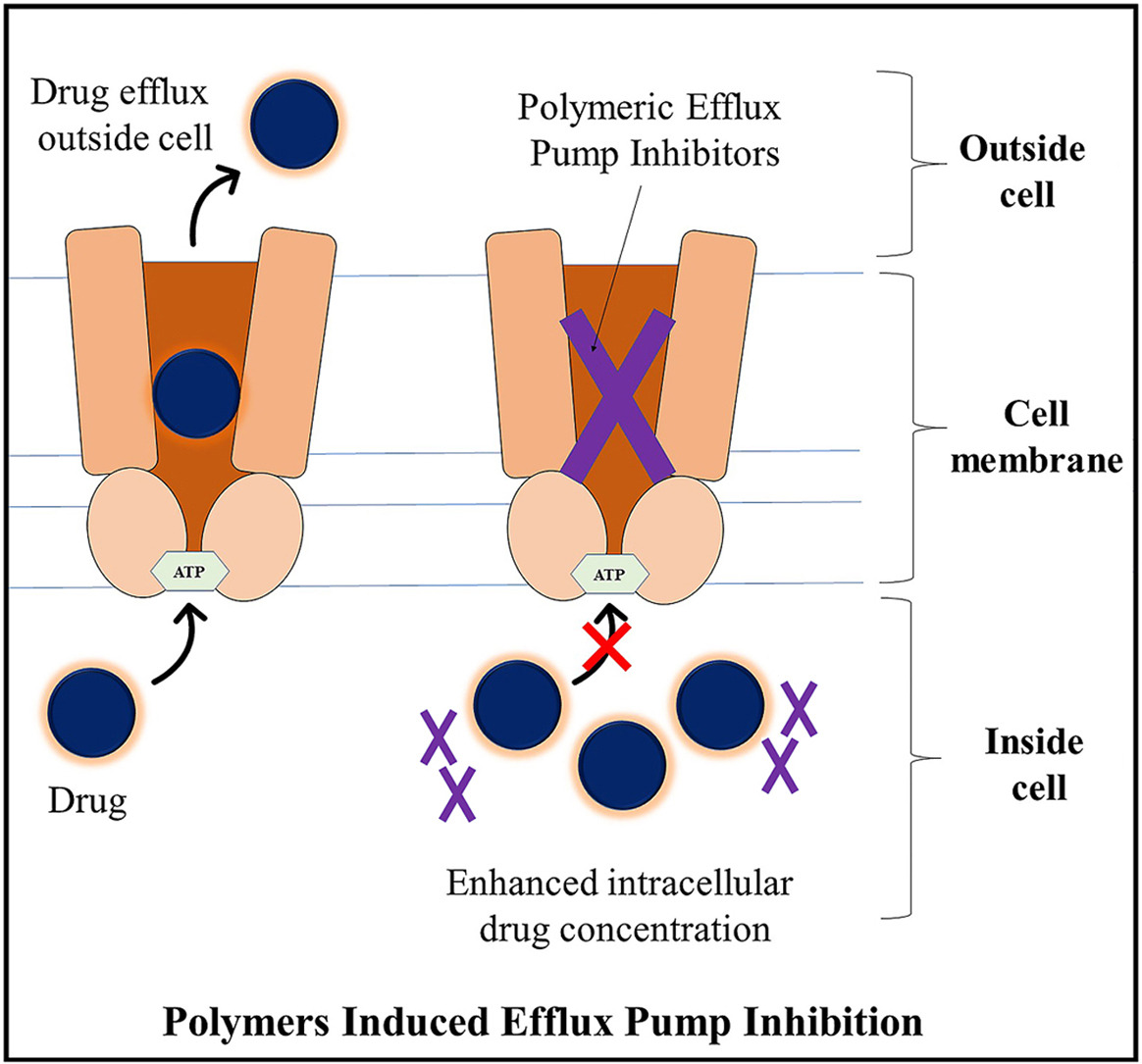
Polymeric excipients ensure the site-specific delivery of the drug at the desired rate for a specified duration to achieve better efficacy. Pharmaceutical excipients were supposed to be pharmacologically inert, and must assure a controlled rate of delivery, an adjustable pharmacokinetic and bio-distribution profile, and improved drug safety. However, the information compiled in the present article demonstrated the significant interaction of pharmaceutical excipients with human physiological entities, such as membrane-spanning proteins (transporters) distributed throughout the body. This may result in altered uptake, intracellular concentration, permeability, distribution, and retention of drugs, expelling them outside the cells.
This potentially affects the safety and efficacy of drugs, especially anti-cancer medicines or those with a narrow therapeutic index. Moreover, inhibition of efflux pumps with polymeric excipients helps in overcoming multidrug resistance and poor bioavailability issues associated with therapeutic pump substrates. Therefore, selecting the most suitable polymeric system is a crucial step in the development of a formulation for desired quality attributes as well as in-vivo drug performance.
Read more here
Vinod L. Gaikwad, Swati G. Sen, Pratik R. Dhake, Interactions between multifunctional pharmaceutical excipients and efflux pump for optimal drug transport and bioavailability: An overview, Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, Volume 94, 2024, 105475, ISSN 1773-2247, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2024.105475.
Read morearticles on Polymers here:
- Biopolymer Packaging Materials in the Pharmaceutical Industry
- Recent advances of electrospray technique for multiparticulate preparation
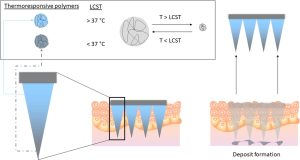
- Leveraging novel innovative thermoresponsive polymers in microneedles for targeted intradermal deposition