Technical evaluation of precisely manufacturing customized microneedle array patches via inkjet drug printing
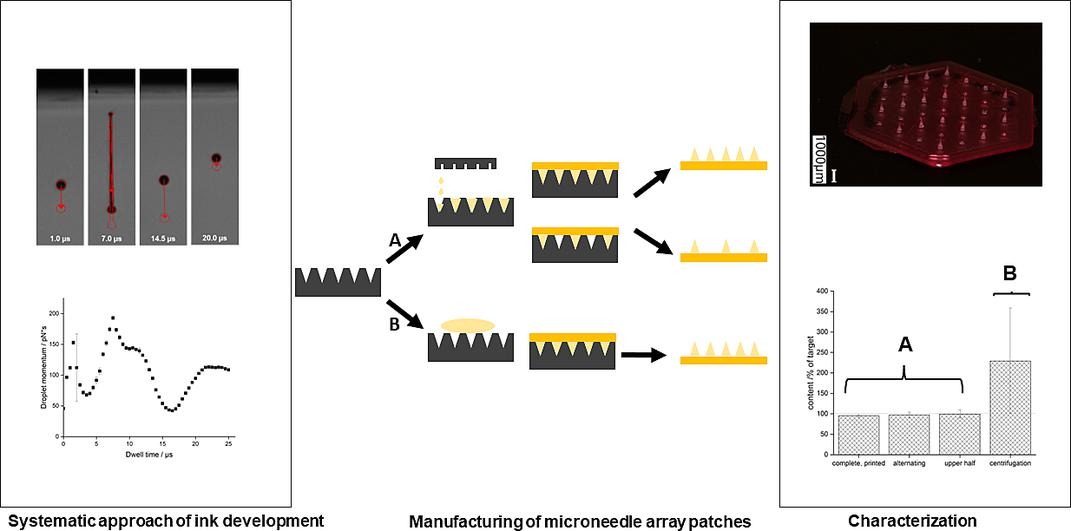
Dissolvable microneedle array patches offer the possibility to deliver active pharmaceutical ingredients bypassing the gastrointestinal tract by piercing the stratum corneum. Usually, microneedles are produced by micromolding but this often results in a waste of active pharmaceutical ingredient. In this study, inkjet printing was investigated as a manufacturing technology for dissolvable microneedle array patches. A suitable ink for the printing process was developed for lisinopril as a peptidomimetic model drug. The printing process was optimized. Povidone was found to be a promising polymer for the precise and smooth production of dissolvable microneedles.
Different patterns of microneedles and blank spaces were successfully printed into one microneedle array patch. It was possible to exactly define the cavities to be filled. The amount of lisinopril was precisely adjusted between 95.14 and 99.26 % of the target dose. The applied method demonstrated the precise dosage opportunities of the inkjet printing methodology for customization and drug waste reduction. Inkjet printing could be used as a precise manufacturing method for personalized microneedle array patches as well as to combine incompatible drug substances in a single patch.
Read more here
Materials
Lisinopril dihydrate was purchased from Zhejiang Huahai Pharmaceutical (Zhejiang, China). Polyvinylpyrrolidone (Povidone, PVP) of different grades (Kollidon® K12, Kollidon® K17, Kollidon® K30) and Amaranth 85 were obtained from BASF (Ludwigshafen, Germany). A low molecular weight hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (hypromellose, HPMC, Pharmacoat® 603) from Shin-Etsu (Tokyo, Japan) was used. Pullulan was purchased from TCI (Tokyo, Japan). Polyethylene glycol (PEG) of different molecular weights.
Lukas C. Lammerding, Jörg Breitkreutz, Technical evaluation of precisely manufacturing customized microneedle array patches via inkjet drug printing, International Journal of Pharmaceutics, Volume 642, 2023, 123173, ISSN 0378-5173, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2023.123173.
Read more on “Overview of Pharmaceutical 3D printing” here:


