Preparation of delayed-release multiparticulate formulations of diclofenac sodium and evaluation of their dissolution characteristics using biorelevant dissolution methods
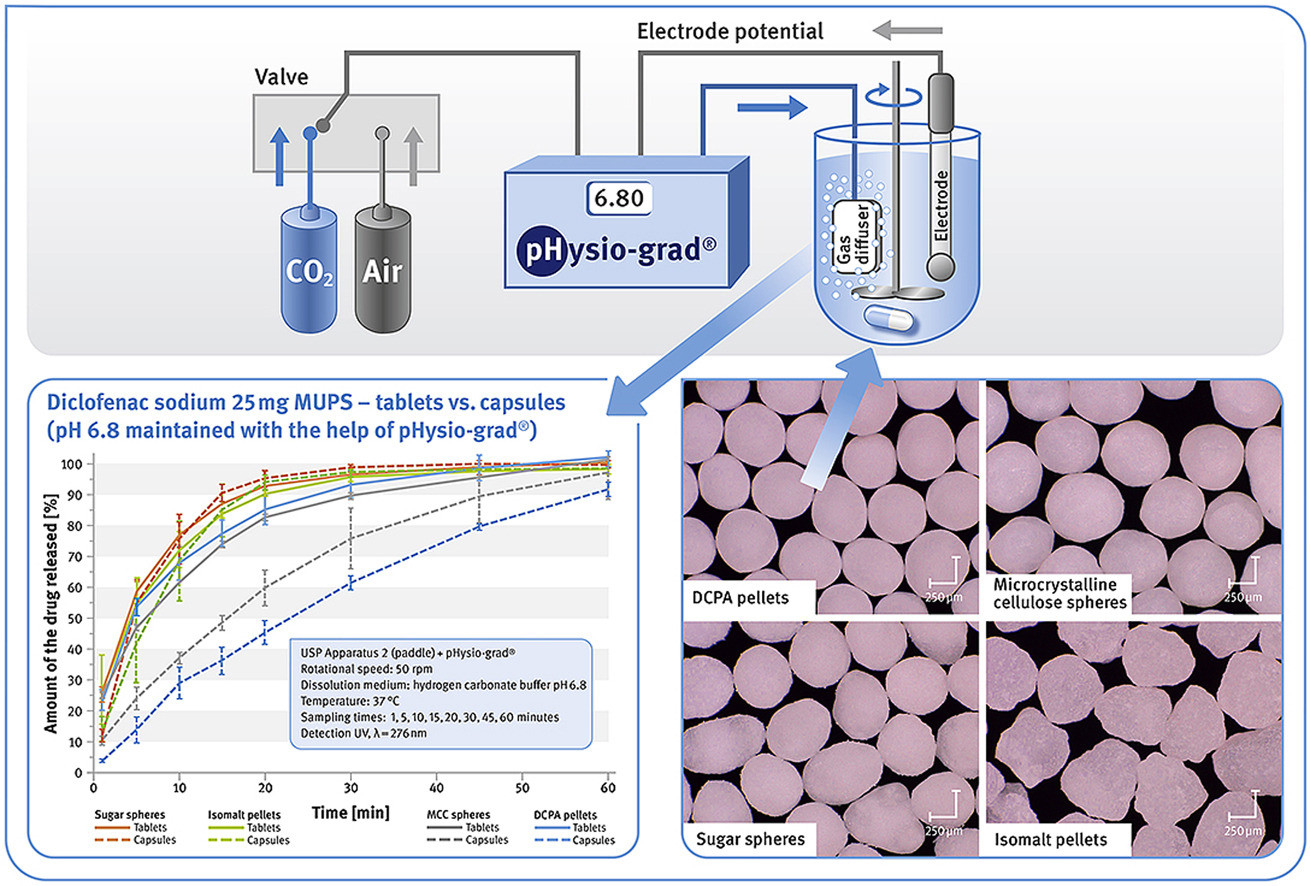
Diclofenac sodium was used as a model drug for preparation of delayed-release (DR) multiparticulates, which were further processed into solid oral dosage forms such as capsules and tablets. Multiple unit pellets systems (MUPS) were prepared from different types of starter pellets (inert cores) including microcrystalline cellulose pellets, sugar spheres, isomalt pellets and novel calcium phosphate-based pellets. The study results showed that the material of the inert cores affected both mechanical properties of the drug-loaded pellets and the dissolution characteristic of the model drug. Biorelevant dissolution method carried out with the help of a pHysio-grad device allowed thorough examination of the developed formulations in the environment mimicking pH conditions along gastrointestinal tract. This method revealed significant differences between the formulations and their sensitivity to variable hydrodynamic conditions.
Download the full research as PDF: Preparation of delayed-release multiparticulate formulations of diclofenac sodium and evaluation of their dissolution characteristics using biorelevant dissolution methods
Author links open overlay panelDaniel Zakowiecki, Maja Szczepanska, Tobias Hess, Krzysztof Cal, Barbara Mikolaszek, Jadwiga Paszkowska, Marcela Wiater, Dagmara Hoc, Grzegorz Garbacz
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, Available online 18 August 2020, 101986
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2020.101986
Keywords: Multiple Unit Pellets Systems, calcium phosphate-based pellets, diclofenac sodium, starter pellets, pHysio-grad
Excipients: calcium phosphate-based (DCPA) pellets – PharSQ® Spheres CM, microcrystalline cellulose pellets – 126 VIVAPUR® MCC Spheres 500, Microcrystalline cellulose 129 VIVAPUR® 200

