Phospholipid-Based Delivery Systems – Phospholipids as Excipients in Advanced Veterinary Drugs

Advanced Veterinary Drugs by Using Phospholipids as Excipients
 Phospholipids have been widely used as excipients in human medicine for decades. In veterinary medicine, too, there are various products on the market, which take advantage of the versatile benefits of phospholipids. These natural, biocompatible and non-toxic excipients extracted from, e.g., soybean or egg yolk, show an excellent performance and meet the increasingly stringent regulatory requirements for veterinary products. Phospholipids are multipurpose excipients that can contribute many functions to veterinary formulations. They are suitable for all routes of administration. Besides their technical use as wetting agent, solubiliser, emulsifier, depot former and liposome builder, they can also functionally improve drug products as penetration enhancer, bioavailability enhancer, moisturizer and texturizer. Furthermore, they are physiologically occurring components and therefore irrelevant for residue testing in milk and meat. Phospholipids are odorless or have a characteristic, slightly nutlike odor and a bland taste while synthetic emulsifiers mostly have a bitter taste. They are even able to suppress bitter taste without affecting other taste qualities and therefore perfectly suitable for taste-sensitive animals like cats. When administered by injection, phospholipids are known to have an excellent safety profile, without any risk of inducing allergic reactions or anaphylactic shocks, unlike other, potentially harmful, synthetic detergents.
Phospholipids have been widely used as excipients in human medicine for decades. In veterinary medicine, too, there are various products on the market, which take advantage of the versatile benefits of phospholipids. These natural, biocompatible and non-toxic excipients extracted from, e.g., soybean or egg yolk, show an excellent performance and meet the increasingly stringent regulatory requirements for veterinary products. Phospholipids are multipurpose excipients that can contribute many functions to veterinary formulations. They are suitable for all routes of administration. Besides their technical use as wetting agent, solubiliser, emulsifier, depot former and liposome builder, they can also functionally improve drug products as penetration enhancer, bioavailability enhancer, moisturizer and texturizer. Furthermore, they are physiologically occurring components and therefore irrelevant for residue testing in milk and meat. Phospholipids are odorless or have a characteristic, slightly nutlike odor and a bland taste while synthetic emulsifiers mostly have a bitter taste. They are even able to suppress bitter taste without affecting other taste qualities and therefore perfectly suitable for taste-sensitive animals like cats. When administered by injection, phospholipids are known to have an excellent safety profile, without any risk of inducing allergic reactions or anaphylactic shocks, unlike other, potentially harmful, synthetic detergents.
Veterinary Applications of Phospholipids
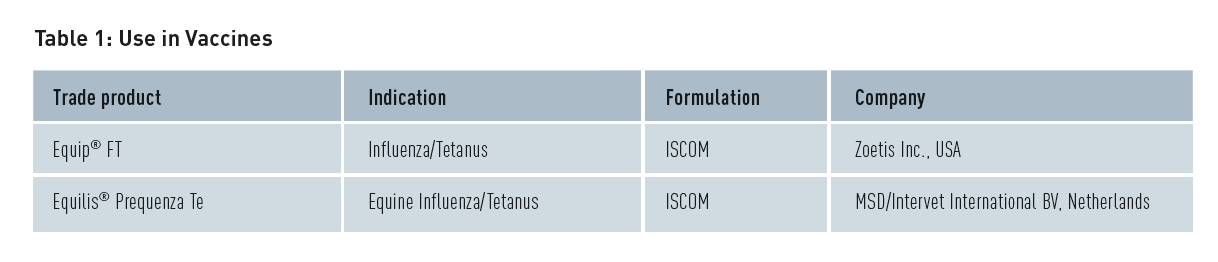
Use in Vaccines
The immunization of animals has been carried out for centuries and is generally accepted as the most cost-effective and sustainable method of controlling infectious veterinary diseases. Phospholipids enable the delivery of immunostimulants and antigens to the target site and trigger the desired immune response. Examples of veterinary vaccines, which use phosphatidylcholine- containing ISCOMs (Immune stimulating complexes) as adjuvant are provided in table 1 below
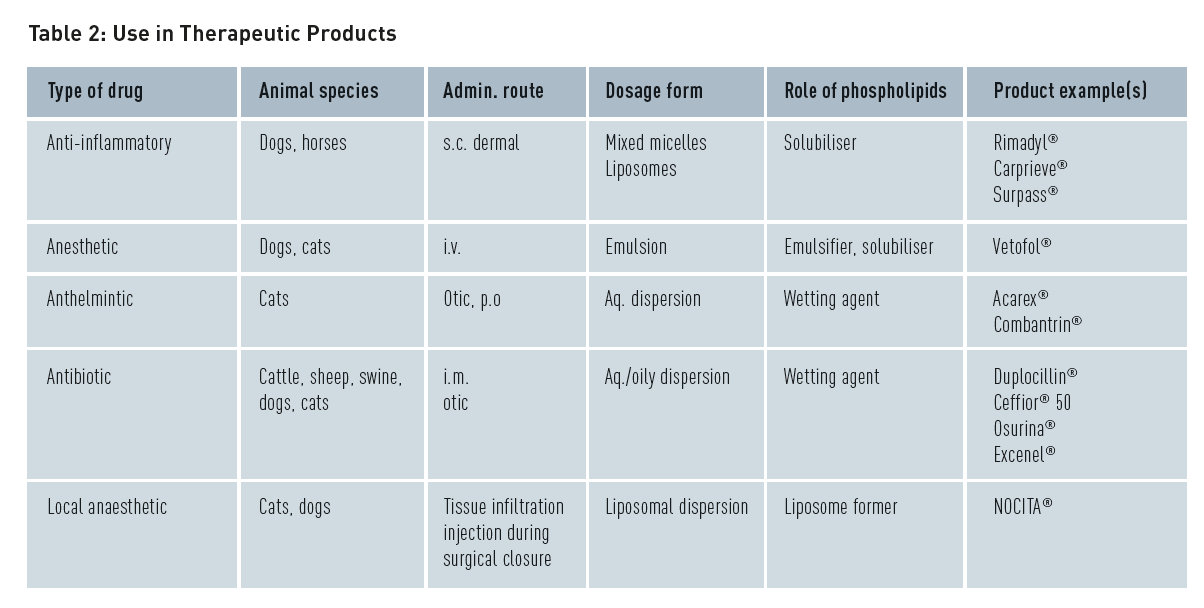
Use in Therapeutic Products
Examples of marketed veterinary therapeutic products – from short to long acting formulations – where phospholipids function as technical aid – are shown in the following table 2.
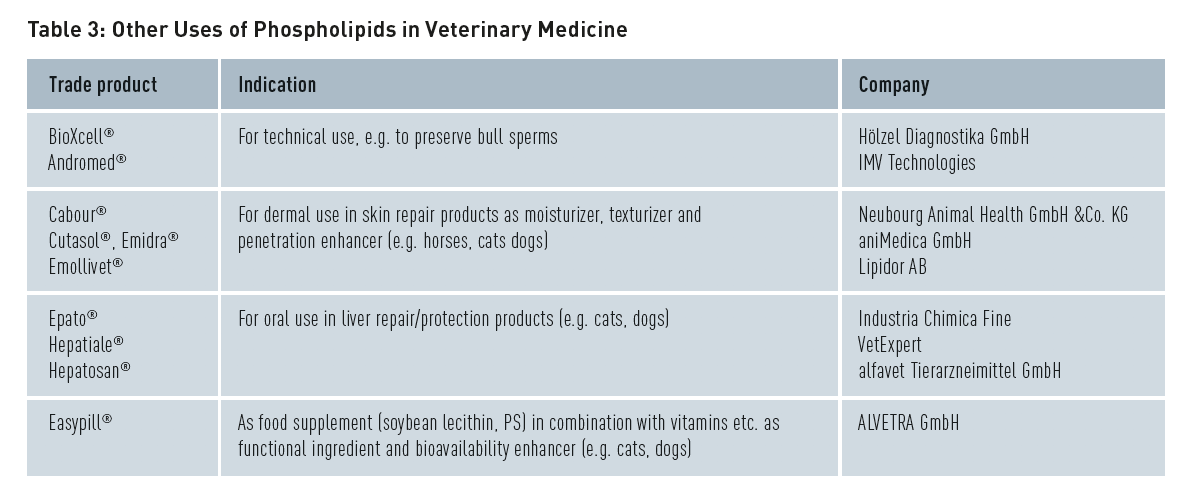
Additional Applications
Future Trends: Depot Formulations
The extended drug delivery of hydrophilic and lipophilic drug substances via the parenteral route has gained increasing importance in the development of pharmaceutical dosage forms. In particular, the animal health industry has generated strong interest in extended drug delivery, e.g. by using injectable depot systems, for both companion and farm animals during the recent years. Such systems show several benefits. The number of treatments can be reduced and drugs can be delivered in a reliable manner. Treatment costs will be decreased, since the number of visits by veterinarians can be minimized. Farmers can reduce the numbers of treatments per season, e.g. for parasite control, to a minimum. Phospholipid-based depot systems are particularly suitable because they are biodegradable, non-toxic and able to release drugs from a couple of days to weeks without remaining residues. More and more injectable depot systems based on phospholipids are being described in the scientific literature.
Please use the form below for more information: