Comparison of Preservatives Used in Various Therapeutic Applications
CONSIDERATIONS FOR USE OF PRESERVATIVES IN TOPICAL, ORAL, OPHTHALMIC, TRANSMUCOSAL, INJECTABLE, INHALATION, AND OTIC APPLICATIONS
A variety of preservatives can be used in therapeutic applications such as topical, oral, transmucosal, inhalation, and otic, as well as injectables. These excipients help to increase the shelf life of products and prevent microbial growth. When selecting a preservative for formulation, a number of factors should be considered as each has its own advantages and disadvantages depending on the application.
This article outlines considerations when using the following excipients as preservatives:
- Benzalkonium chloride
- Benzyl alcohol
- Parabens
- Benzoic acid and sodium benzoate
BENZALKONIUM CHLORIDE
Considerations for Use of Benzalkonium Chloride as a Preservative
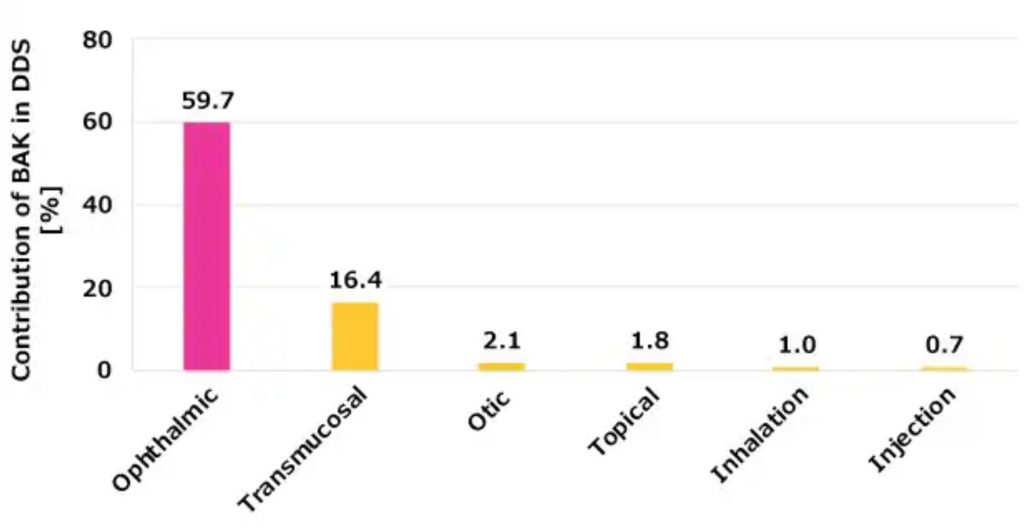
Benzalkonium chloride is frequently used as a preservative due to its wide anti-microbial and broad pH range activity. Of the more than 700 formulations currently on the market that contain benzalkonium chloride, 60% of the formulations are ophthalmic, followed by transmucosal, otic, topical, and inhalation indications (Figure 1).1
Global Market Overview (Total Products: 769)
Figure 1. Benzalkonium chloride is used as a preservative in a variety of applications.
Benzalkonium chloride is not a single moiety; it is available as a combination of C12 and C14 carbon chains. For higher anti-microbial efficacy, the pharmacopeias recommend ≥ 40% w/w C12 and ≥ 20% w/w C14 homologues. High batch-to-batch consistency of benzalkonium chloride is essential for reproducible preservative efficacy activity and can vary among suppliers.
SUMMARY OF BENZALKONIUM CHLORIDE ATTRIBUTES
Table 1 summarizes several attributes of benzalkonium chloride.
Synergy with Other Preservatives
Benzalkonium chloride can be used in combination with EDTA and other preservatives including benzyl alcohol and boric acid. Benzalkonium chloride plus sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) has been shown to attenuate the irritation potential of SDS in transdermal patches.
Incompatibilities of Benzalkonium Chloride
Because benzalkonium chloride is cationic in nature, it is normally incompatible with other cationic surfactants and phospholipids. Benzalkonium chloride is adsorbed onto hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) and thus presents challenges for preservative efficacy assays.
It is also incompatible with acidic active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) because it causes precipitation. Basic amino acids such as histidine, arginine, lysine, as well as tromethamine or meglumine, can be used with acidic APIs to form a complex with API and enable benzalkonium chloride to be used for preservative action.
Microbial Activity of Benzalkonium Chloride
Benzalkonium chloride offers microbial activity against yeast, bacteria, and mold. It is ineffective against some strains of pseudomonas aeruginosa but a combination of benzalkonium chloride with EDTA can increase efficacy.
Safety
Benzalkonium chloride should not be used in inhalation products such as those for asthma as it can induce bronchospasms.
Compatibility of Benzalkonium Chloride with Membrane Filters
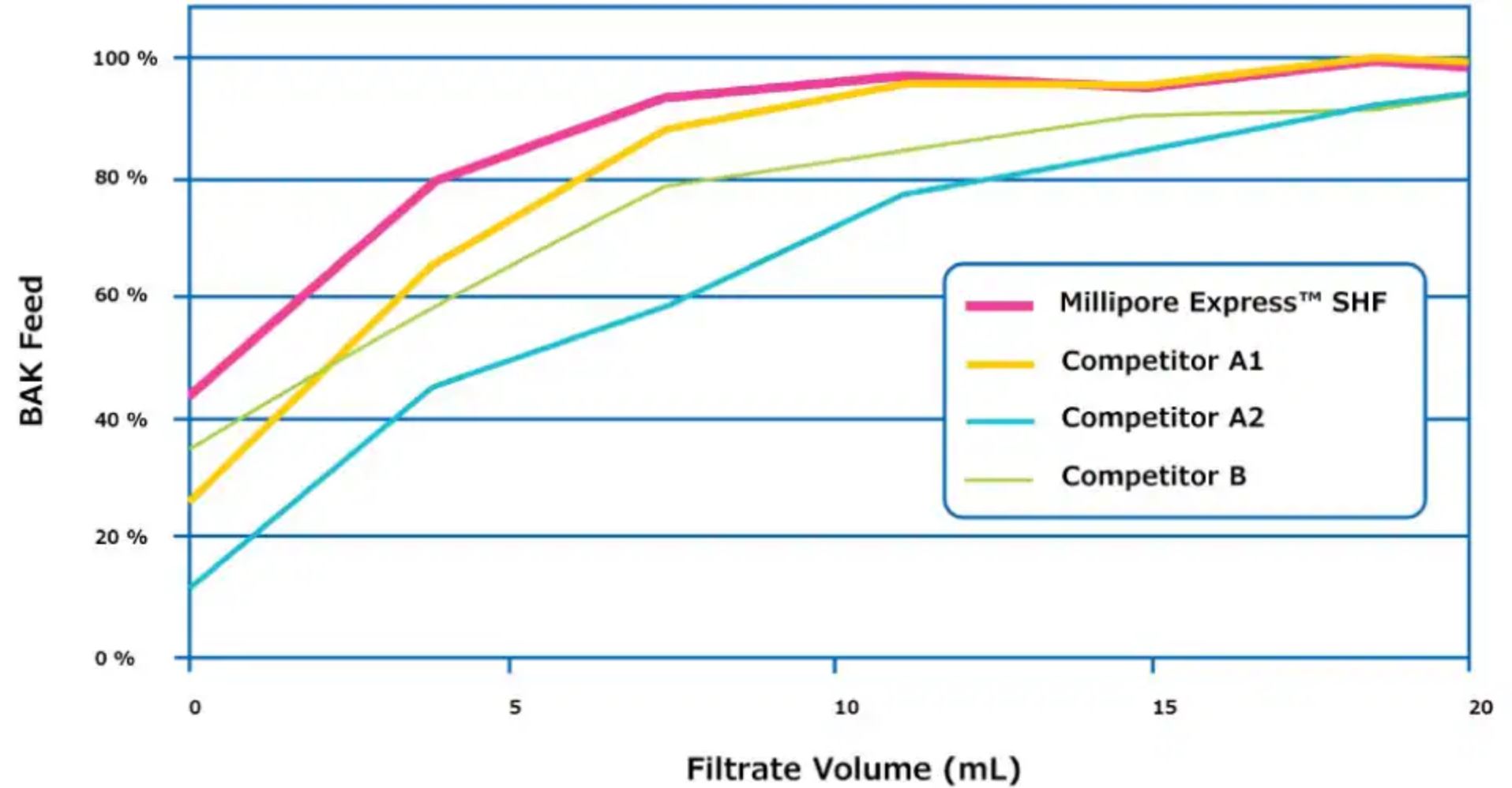
Many preservatives bind or are adsorbed by membrane filters which causes a loss of the appropriate amount of preservatives in the final product. Benzalkonium chloride has this tendency which affects the preservative assay, yield of the process, and increases the flush volume. To avoid this problem, a polyethylenesulfone (PES) filter should be used. As shown in Figure 2, test results with a 0.01 % benzalkonium chloride solution showed the lowest binding and lowest preservative loss in the final product. For most competitive membranes, product losses were more than double that of the Millipore Express® SHF membrane.
Pharmacopeia Compliance
Impurities in benzalkonium chloride such as benzyl chloride can react with the API. Use of a compendial grade of benzalkonium chloride where the limit of impurities is less than 0.05 % reduces the risk of interactions with the API.
BENZYL ALCOHOL
Considerations for Use of Benzyl Alcohol as a Preservative
Benzyl alcohol is a preservative used in more than 500 formulations including injections, topical, oral, and otic applications (Figure 3).1 It is also used as a stabilizer and because of its anesthetic properties, it is sometimes used to reduce pain on injection.9 While this preservative has numerous applications, it should not be used in neonates and used with caution in children older than four weeks.10
Read more here
Source: Merck, website: Comparison of Preservatives Used in Various Therapeutic Applications (sigmaaldrich.com)

