Spray drying of API nanosuspensions: Importance of drying temperature, type and content of matrix former and particle size for successful formulation and process development
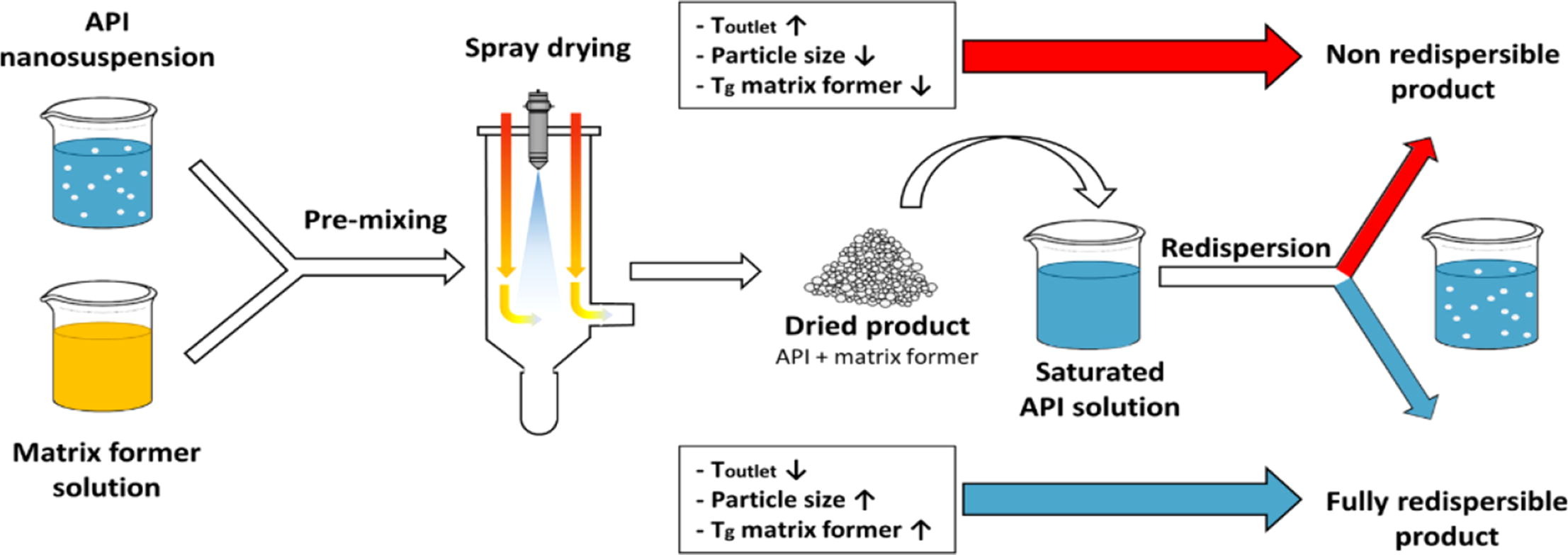
Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) nanosuspensions from naproxen (Nap) and itraconazole (Itra) stabilized with Kollidon®VA64 (KVA) and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) were produced in two different size classes each by wet media milling. These API nanosuspensions were spray dried with lactose, trehalose and sucrose as matrix formers in different proportions and at different drying temperatures (Toutlet). Toutlet as well as the API content significantly influenced the redispersibility of the API nanoparticles.
It could be shown that these two parameters are related to each other, with an increasing API content leading to a decreasing maximum applicable Toutlet (Tcritical). Drying above Tcritical always led to an alteration of the size characteristics of the API nanoparticles and thus to a non-redispersible product with respect to the defined quality criteria. For each proportion of API to matrix former, a Tcritical could be found. Tcritical showed a linear relation to the API content. The linear regression of this relation was defined as process boundary. The y-intercept of the process boundary correlated well with the glass transition temperature (Tg) of the pure matrix former used for spray drying.
The two APIs under investigation led to virtually identical behaviour if other parameters were kept constant. The particle size of the initial nanosuspension had an important influence. Nanosuspensions with comparatively small particle sizes led to a significantly stronger decrease of the process boundaries compared to the use of larger particle sizes. The maximum API content that leads to a redispersible product is thus decisively determined by Toulet of the spray dryer, Tg as well as the proportion of the matrix former and by the particle size of the API nanoparticles used. Continue on Spray drying of API nanosuspensions
Keywords: Spray drying, drug nanosuspensions, poorly water-soluble drugs, critical drying temperature, itraconazolenaproxen, particle size, glass transition temperaturere, dispersibility, reconstitution; Granulac 200, Kollidon®VA64
Stefan Czyz, Martin Wewers, Jan Henrik Finke, Arno Kwade, Bernard van Eerdenbrugh, Michael Juhnke, Heike Bunjes, Spray drying of API nanosuspensions: Importance of drying temperature, type and content of matrix former and particle size for successful formulation and process development, European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, Volume 152, 2020, Pages 63-71, ISSN 0939-6411, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2020.04.021.

