Effect of Different Types of Wood Pulp on Hydrolysis Reaction Time and Degree of Polymerization of Microcrystalline Cellulose Powder
Abstract
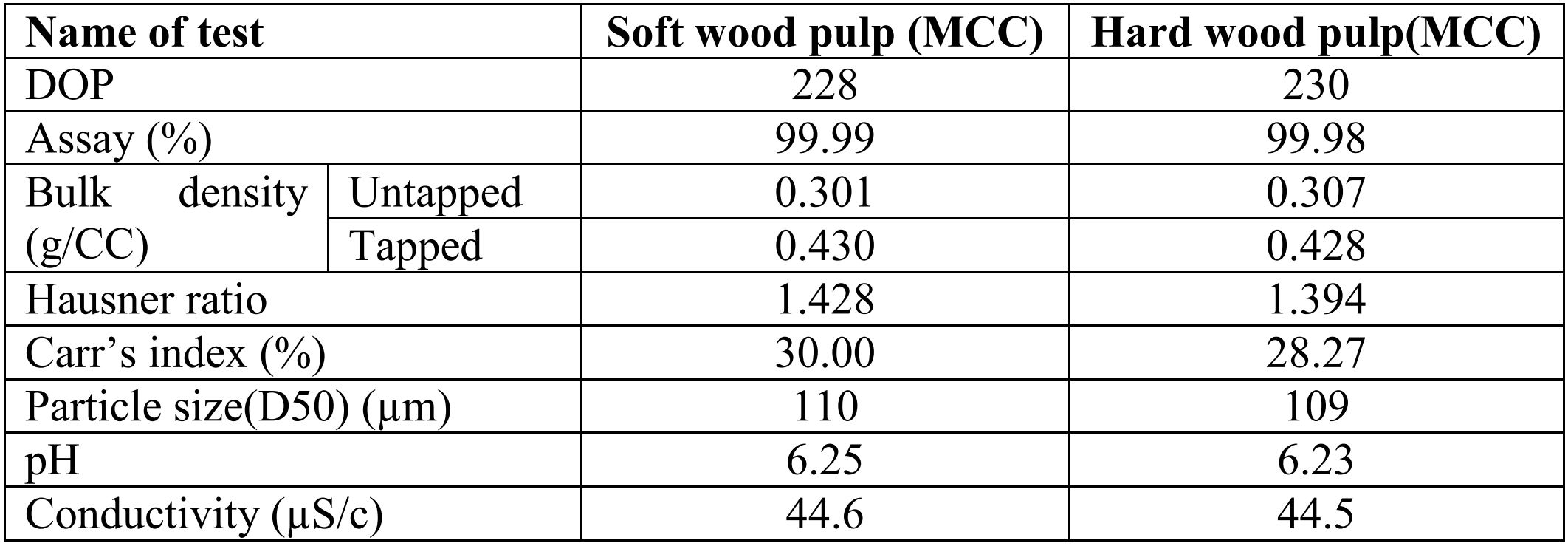
Different types of wood pulps are used to manufacture microcrystalline cellulose. Percentage of alpha cellulose depends on type of wood pulp. Both wood pulp soft and hard wood pulp are usually used to manufacturing microcrystalline cellulose. Though the production process of wood pulp has a major bearing on it’s quality, Soft wood pulp on most occasions has higher alpha cellulose content with excellent finished product quality in terms of yield, physical parameter i.e. bulk density, flowability and chemical parameters i.e. water soluble substances, ether soluble substances, degree of polymerization and residue on ignition. In this paper we examine different wood pulp effect on hydrolysis time and degree of polymerization of finished product microcrystalline cellulose. In this study we used four types of wood pulp and done reaction with same acid concentration, pressure, and temperature only hydrolysis time were different, after drying evaluate degree of polymerization of finished product MCC.
Introduction
Pulp and paper are made from wooden cellulosic fibers. Wood is composed of cellulose, lignin, hemicelluloses and extractives (e.g. resins, fats and pectins). There are three types of cellulose present in the wood pulp, (i) Alpha cellulose (ii) Beta cellulose (iii) Gama cellulose. Generally two types of wood pulp are used to manufacturing MCC (a) Softwood pulp, (b) Hardwood pulp. [1,2] These woods differ considerably in chemical composition i.e. cellulose, hemicelluloses and lignin and structure organization also differ i.e. regions which are more crystalline an amorphous.
[3]
Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) is native form of cellulose. [4] It is isolate from wood pulp by hydrolysis reaction. [5] Hydrolysis reaction is done in the presence of mineral acids and water at controlled temperature and pressure. [6]
In wood pulp, cellulose chains are packed in layers held together by a cross-linkage polymer and strong hydrogen bond. Cellulose consists of liner chain of ß-14-D anhydroglucopyranosyl units. In hydrolysis reaction, high degree of
polymers converts into low degree of polymers. [7] Degree of polymerization(DOP), the number of glucose units present in the cellulose chain) of finished product microcrystalline cellulose depends on source of wood pulp and different parameters of hydrolysis reaction i.e. reaction temperature, reaction pressure, acid concentration used in reaction and reaction time. [8]
Microcrystalline cellulose is used in various fields i.e. Pharmaceuticals industries, Cosmetic industries, Food industries, paint industries and detergent industries. [9] In pharmaceuticals MCC is a perfect excipient for making the formulations. [6] It is one of the most frequently used, to formulate solid dosage forms. It is non-reactive, free-flowing and versatile pharmaceutical excipient. [10] It has strong binding property to bind the pharmaceutical active ingredient, most extensively used filler and has inherent disintegrant properties. [11] In this study we used two types of wood pulp (soft and hard wood pulp) for examine the effect of different types of wood pulps on hydrolysis reaction and effect of hydrolysis time on Degree of polymerization of finished product microcrystalline cellulose.
Download the full article as PDF here Effect of Different Types of Wood Pulp on Hydrolysis Reaction Time and Degree of Polymerization of Microcrystalline Cellulose Powder
Material
Digital weighing balance (Mettler Toledo, Model no-ML802/A01) was used for weighting the sample. Class A graduated measuring cylinder (Electro lab instrument, Model No. ETD1020) was used for checking tapped density of HiCelTM MCC. Hot air oven (Model noPNX-14) was used for testing moisture content. In this study all chemicals were used AR grade.
Source: Sigachi, Effect of Different Types of Wood Pulp on Hydrolysis Reaction Time and Degree of Polymerization of Microcrystalline Cellulose Powder, Article Received on 26 June 2017, Revised on 17 July 2017, Accepted on 07 August 2017, Gaurav Tripathi, Amit Raj Sinha and Monika Tomar, Sigachi®, Industries Private Limited, Dahej SEZ Gujarat, India
Do you need more information or a sample of Sigachi excipients?

