Nanostructured lipidic carriers for dual drug delivery in the management of psoriasis: Systematic optimization, dermatokinetic and preclinical evaluation
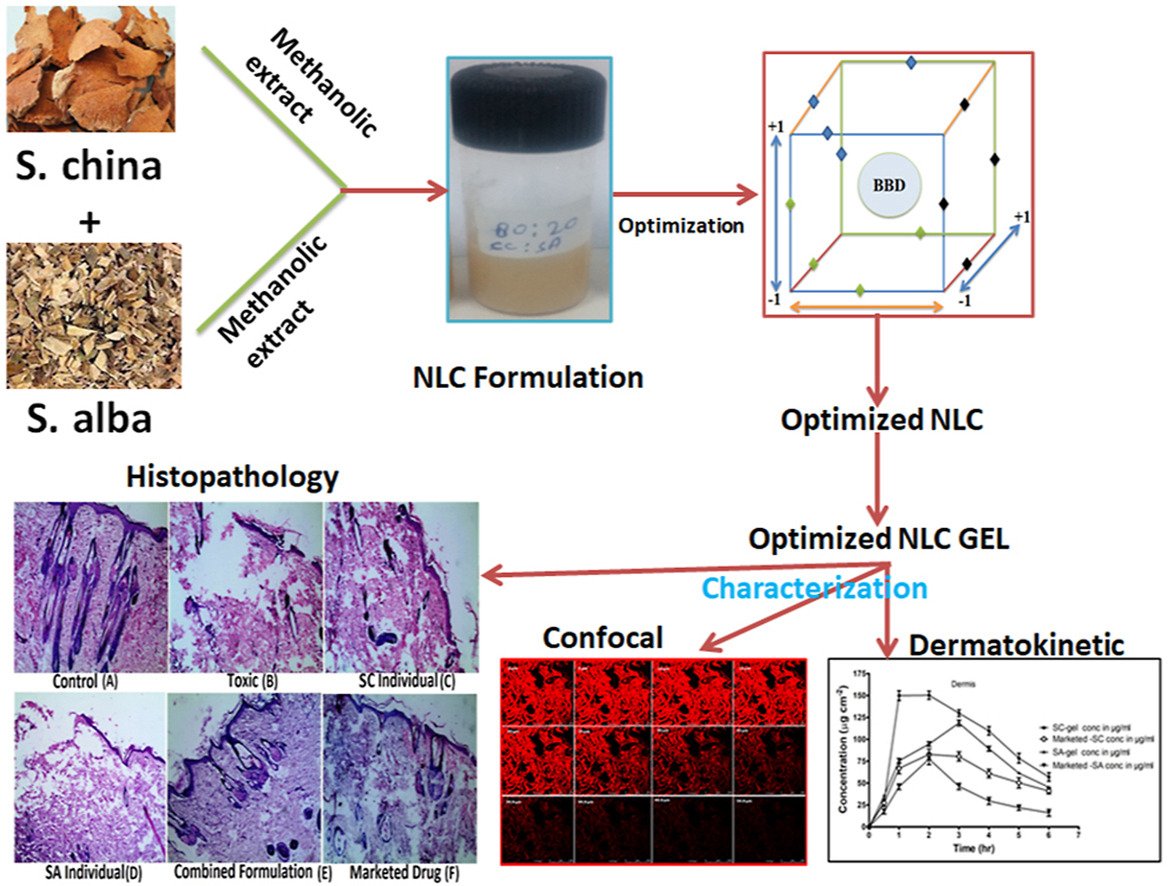
In the present study, we selected two potential herbal drugs (Smilax china and Salix alba) and developed nano lipidic carriers (NLC) gel for safe and effective topical therapy against psoriasis. Optimization of formulation of NLCs was performed using Box-Behnken design by selecting three input variables viz. lipid concentration, surfactant concentration and sonication time at three levels; and evaluated for the average particle size, polydispersity and %encapsulation as the response parameters.
Highlights
• The study involved development of Smilax china and Salix alba NLCs to achieve enhance bioavailability of both the drugs.• NLCs were optimized by factorial design to obtain minimum possible size in nano range and high encapsulation.
• Optimized NLCs showed enhanced in vivo antipsoriatic activity on BALB/c mice model as compared to the marketed formulation.
• Histopathology study showed safe nature of the NLCs with no change in skin architecture during antipsoriatic activity.
The outcomes of the present study showed that optimized dual drug-loaded NLCs had low average particle size (150.20 ± 3.57 nm) and polydispersity (0.301 ± 0.01) and high entrapment (86.32 ± 2.78% w/w). TEM imaging of the optimized formulation showed spherical vesicles. The drug release and dermal transport studies revealed sustained drug release (57.55 ± 5.38%) and enhanced dermal flux (3.88 μg/cm2/h), respectively. Thermo-analytical studies of NLCs showed fluidized state of the membrane of mice skin for smooth penetration of drugs. Confocal study revealed uniform distribution and deeper layer penetration of the optimized NLC gel system as compared to hydroalcoholic solution. Further, dermatokinetic study showed improved penetration of drug-loaded NLC gel in mice skin than the marketed formulation. The score obtained from skin irritation study revealed non-irritancy of the developed system. Further, in the developed psoriatic model, PASI score established decline in all the parameters as compared to the toxic control group, as well as better efficacy than the marketed formulation. Hence, the obtained results construe that developed NLCs as potential carriers for the effective and safe topical delivery of herbal drugs. More on nanostructured lipidic carriers for psoriasis treatment

