Central Composite Design-Based Optimization of Lopinavir Vitamin E-TPGS Micelle: In Vitro Characterization and In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Study
Highlights
- • Lopinavir was successfully loaded into Vitamin E-TPGS micelles.
- • Micelle were prepared by thin film hydration technique.
- • Polymer concentration and rotational speed are key parameters in micelle preparation.
- • Aqueous solubility of Lopinavir was enhanced by 2.6 folds.
- • TPGS micelles enhanced the relative bioavailability of Lopinavir by 3.17 folds.
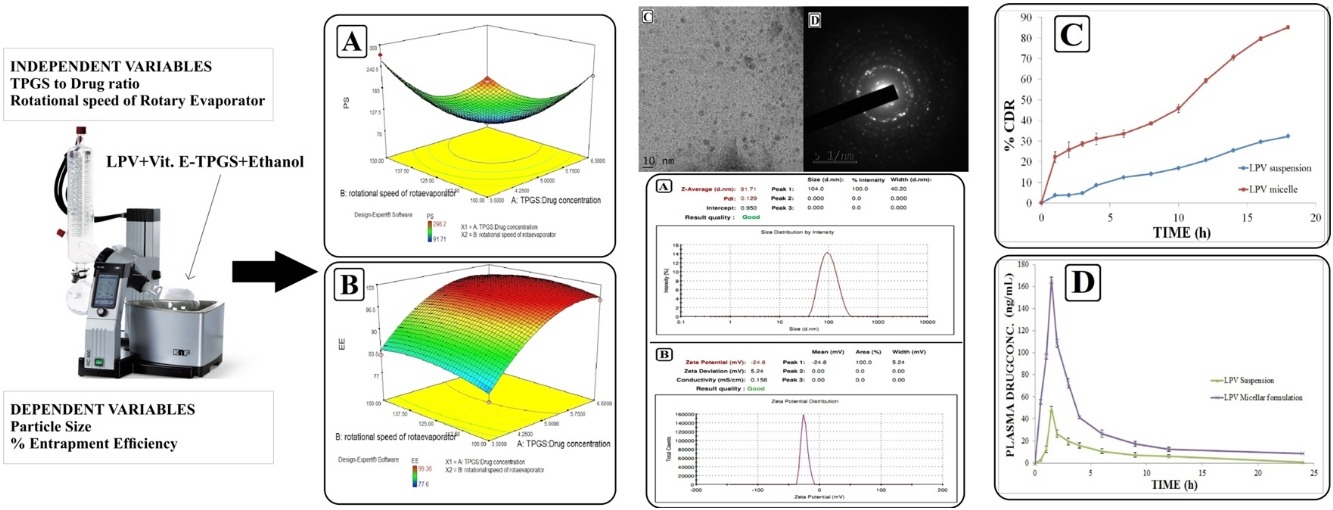
This study was aimed at formulating Lopinavir loaded Vitamin E-TPGS micelles to enhance its oral bioavailability. Lopinavir is an HIV-1 protease inhibitor with low aqueous solubility leading to poor oral bioavailability and thus frequent dosing. Drug loaded micelles were fabricated using thin film hydration technique and optimized by two-factor five-level central composite design. For this purpose independent variables selected were TPGS to drug ratio and rotational speed of rotary evaporator, whereas dependent variables chosen were particle size and % entrapment efficiency. The effect of an independent variable on the dependent variable was studied by generating a quadratic polynomial model. Results of in vitro characterization showed that prepared lopinavir micelles exhibited particle size 91.71 nm, polydispersity index 0.129, zeta potential -24.8 mV, entrapment efficiency 99.36±1.06 % and drug loading 20.83±1.23 %. Results of DSC and P-XRD evaluation revealed that drugs were successfully encapsulated inside the Vitamin E-TPGS micelles. In vitro release studies displayed enhancement in drug dissolution as a result of its loading into micelles. TEM images showed that micelles were spherical. On oral administration of lopinavir micelles; the relative bioavailability was boosted by 3.17 folds compared to lopinavir suspensions. Thus, we can conclude that TPGS based micelles possess the prodigious potential to overcome the challenges of current HAART therapy.
Author links open overlay panelHitendra Shaligram Mahajan, Payal Hasmukhlal Patil
Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.111149
Keywords: Lopinavir, Vitamin E-TPGS, bioavailability enhancement, central composite design

