Effect of feed frame on lubricant sensitivity during upscaling from a compaction simulator to a rotary tablet press
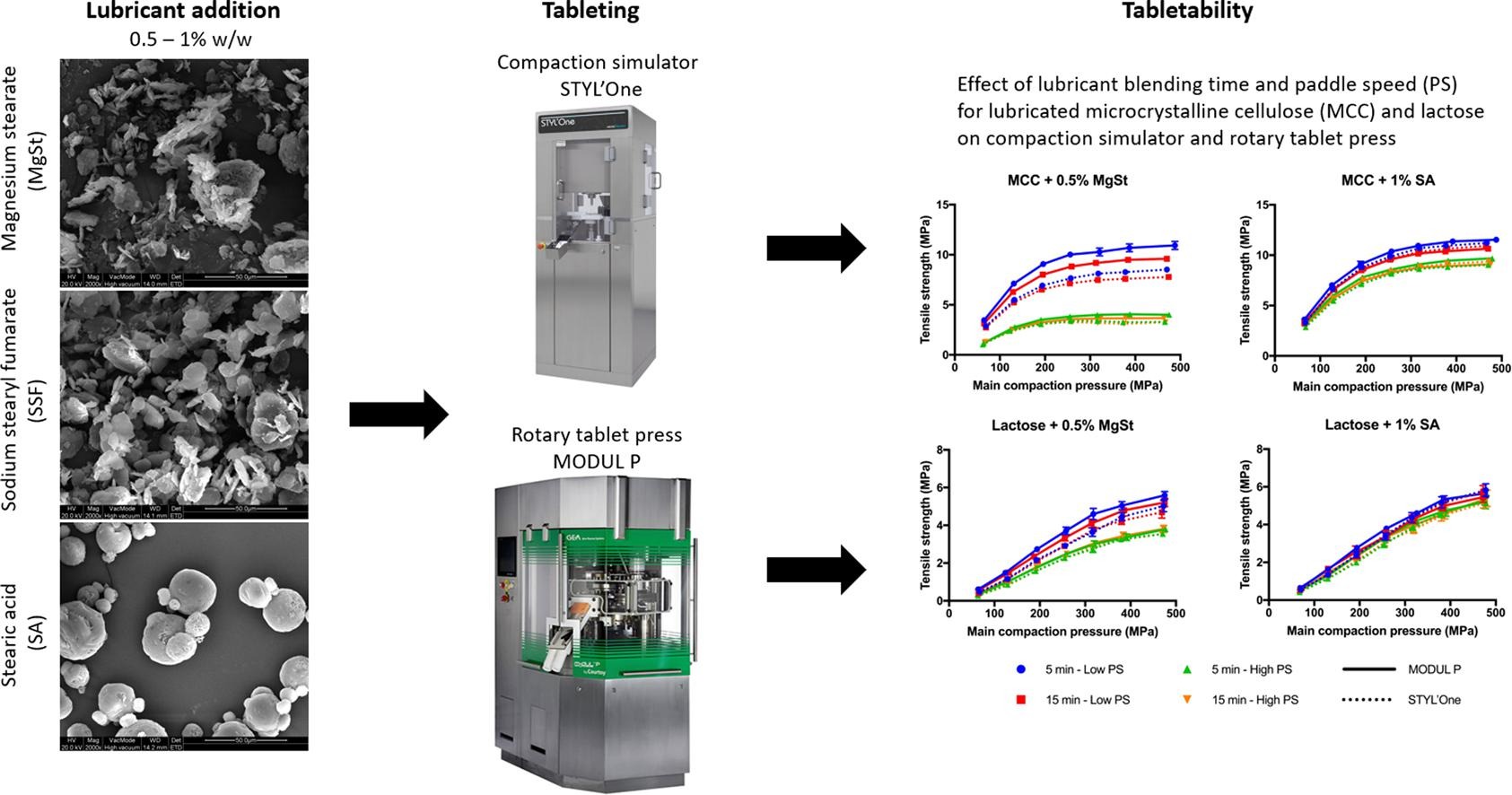
Internal lubrication can be associated with reduced tabletability. Deformation mechanism, lubricant type, lubricant blending time and paddle speed (PS) of the forced feeder are known to be influenceable factors. This study investigated the effect of lubricant blending time and PS of forced feeders on the tensile strength of lubricated microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) and lactose tablets. Magnesium stearate(MgSt), sodium stearyl fumarate (SSF) and stearic acid (SA) were used as lubricants.
Tablets were produced on a compaction simulator and a rotary tablet press to investigate lubricant sensitivity during upscaling. Lubricant sensitivity was found higher for MCC compared to lactose which was attributed to the higher plasticity of MCC. The reduction in tensile strength upon lubricant addition followed the order: MgSt > SSF > SA; which could be linked to particle size, specific surface area and particle shape of the lubricants. Although differences in tensile strength were observed between the lubricant types, comparable ejection forces were obtained.
The impact of PS on tensile strength was higher compared to lubricant blending time for both tableting machines. A good correlation of tensile strength and lubricant sensitivity between the compaction simulator and rotary tablet press was observed based on the calculation of paddle passes (NPP).
About this article: Cedrine de Backere, Thomas De Beer, Chris Vervaet, Valérie Vanhoorne,
Effect of feed frame on lubricant sensitivity during upscaling from a compaction simulator to a rotary tablet press,
International Journal of Pharmaceutics, Volume 616, 2022, 121562, ISSN 0378-5173, ttps://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.121562. (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378517322001168)
Materials
Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC, Avicel® PH102, DuPont Pharma, Wilmington, DE, USA), spray dried lactose monohydrate (SuperTab® 11SD, DFE Pharma, Goch, Germany), anhydrous dibasic calcium phosphate (DCP, Emcompress® AN, JRS Pharma, Rosenberg, Germany), partially pregelatinized starch (Starch 1500®, Colorcon, Harleysville, PA, USA), mannitol (Pearlitol® 200 SD, Roquette Frères, Lestrem, France) were used as model compounds exhibiting different compaction properties, from fragmentation to plastic/ductile and elastic deformation. Magnesium stearate (MgSt, Ligamed® MF-2-V, Peter Greven, Bad Münstereifel, Germany), sodium stearyl fumarate (SSF, Pruv®, JRS Pharma, Rosenberg, Germany) and stearic acid 95 (SA, Stellipress micro 95, Stéarinerie Dubois Pharma, Boulogne Billancourt, France) were used as lubricants. Temperature (21.0 ± 2.0 °C) and relative humidity (45 ± 5%) were logged during material storage, blend preparation and tableting experiments.
Read more on Sodium Stearyl Fumarate as a pharmaceutical excipient here:


