Anionic and Ampholytic High-Amylose Starch Derivatives as Excipients for Pharmaceutical and Biopharmaceutical Applications: Structure-Properties Correlations
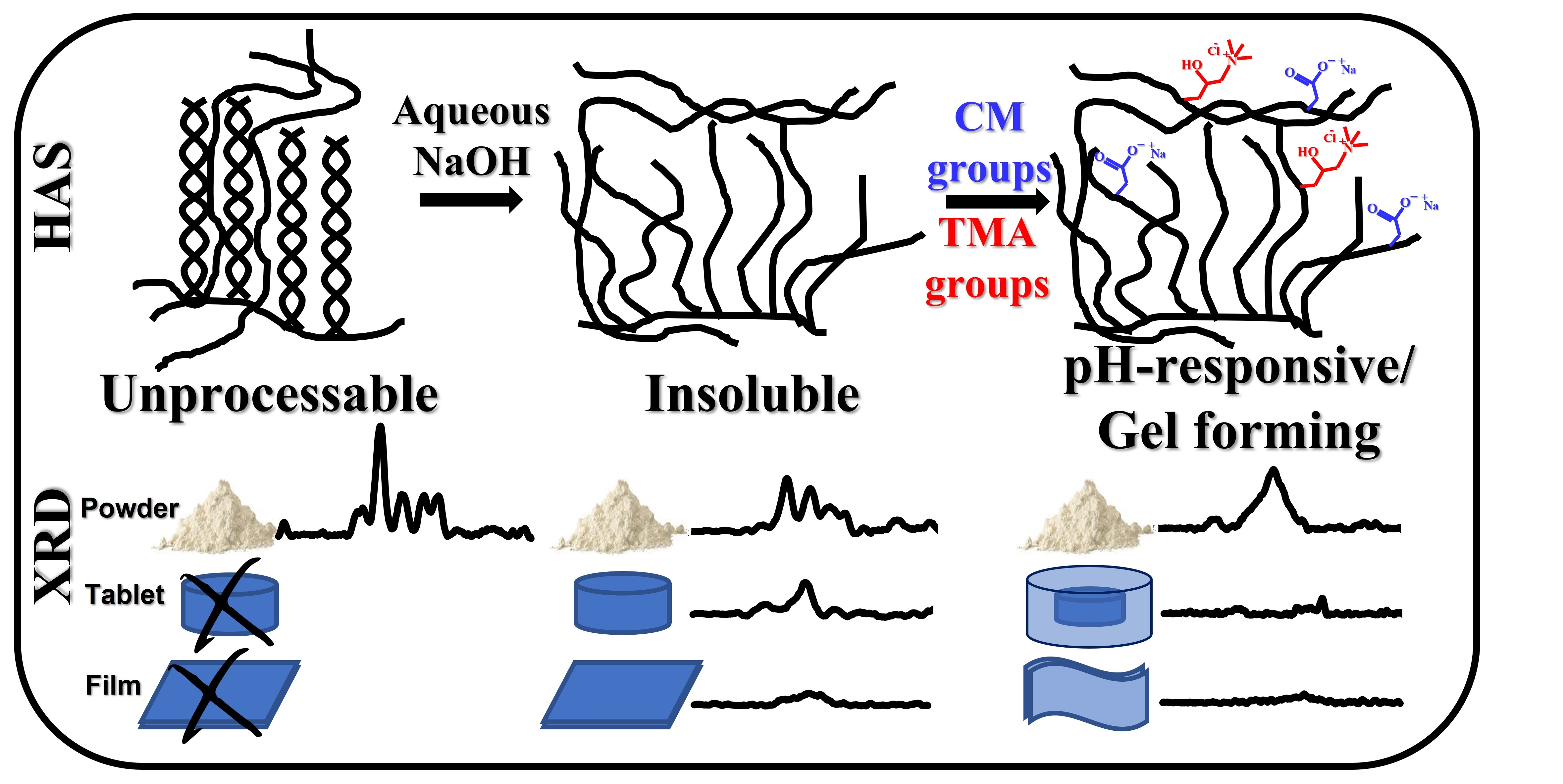
Many chemical modifications of starch are realized in organic (mostly methanol) phase, allowing high degrees of substitution (DS). Some of these materials are used as disintegrants. To expand the usage of starch derivative biopolymers as drug delivery system, various starch derivatives obtained in aqueous phase were evaluated with the aim to identify materials and procedures which would generate multifunctional excipients providing gastro-protection for controlled drug delivery. Chemical, structural and thermal characteristics of anionic and ampholytic High Amylose Starch (HAS) derivatives under powder (P), tablet (T) and film (F) forms were evaluated by X-ray Diffraction (XRD),
Fourier Transformed Infrared (FTIR) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) methods and correlated with the behavior of tablets and films in simulated gastric and intestinal media. At low DS, the HAS carboxymethylation (CMHAS) in aqueous phase, generated tablets and films that were insoluble at ambient conditions. The CMHAS filmogenic solutions, with a lower viscosity, were easier to cast and gave smooth films without the use of plasticizer. Correlations were found between structural parameters and the properties of starch excipients. Compared to other starch modification procedures, the aqueous modification of HAS generated tunable multifunctional excipients that may be recommended for tablets and functional coatings for colon-targeted formulations.
Download the full article here Anionic and Ampholytic High-Amylose Starch Derivatives as Excipients for Pharmaceutical and Biopharmaceutical Applications_Structure-Properties Correlations
or read it here
Reagents
Hylon VII® (~70% amylose), Melojel® (~28% amylose) and PenPure60® native potato starch were generous gifts from Ingredion (Westchester, IL, USA). Potato amylose (100%) and potato amylopectin (100%) were purchased from BDH Biochemicals (Chemical Division, Toronto, CA, USA). Vivastar® was a gift from JRS Pharma (Patterson, NY, USA). Chloroethylamine hydrochloride (CEA), glycidyl trimethylammonium chloride (GTMAC), sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) with a MW of 90,000 g/mol, sodium monochloroacetate (SMCA), sodium trimetaphosphate (STMP) and other chemicals were all reagent grade and used as received from Millipore Sigma (Burlington, MA, USA). Pancreatin from porcine pancreas (8× concentrated) was purchased from Millipore Sigma. The proposed time to simulate gastric transit is 2 h in simulated gastric (SGF) followed by simulated intestinal fluid (SIF) The SGF was made with 7 mL HCl (37% w/w) and 2 g NaCl for 1 L (as described by the USP-43, NF 38 [37]). The SIF was prepared with 6.8 g monobasic potassium phosphate in 750 mL distilled water and 77 mL 0.2 N NaOH and adjusted to pH 6.8 with 0.2 N NaOH as described by the USP-43, NF 38 [37].
Labelle, M.-A.; Ispas-Szabo, P.; Tajer, S.; Xiao, Y.; Barbeau, B.; Mateescu, M.A. Anionic and Ampholytic High-Amylose Starch Derivatives as Excipients for Pharmaceutical and Biopharmaceutical Applications: Structure-Properties Correlations. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030834

