Improved Transdermal Delivery of Novel Cannabinoid-Loaded Patches Using Eudragit Matrix
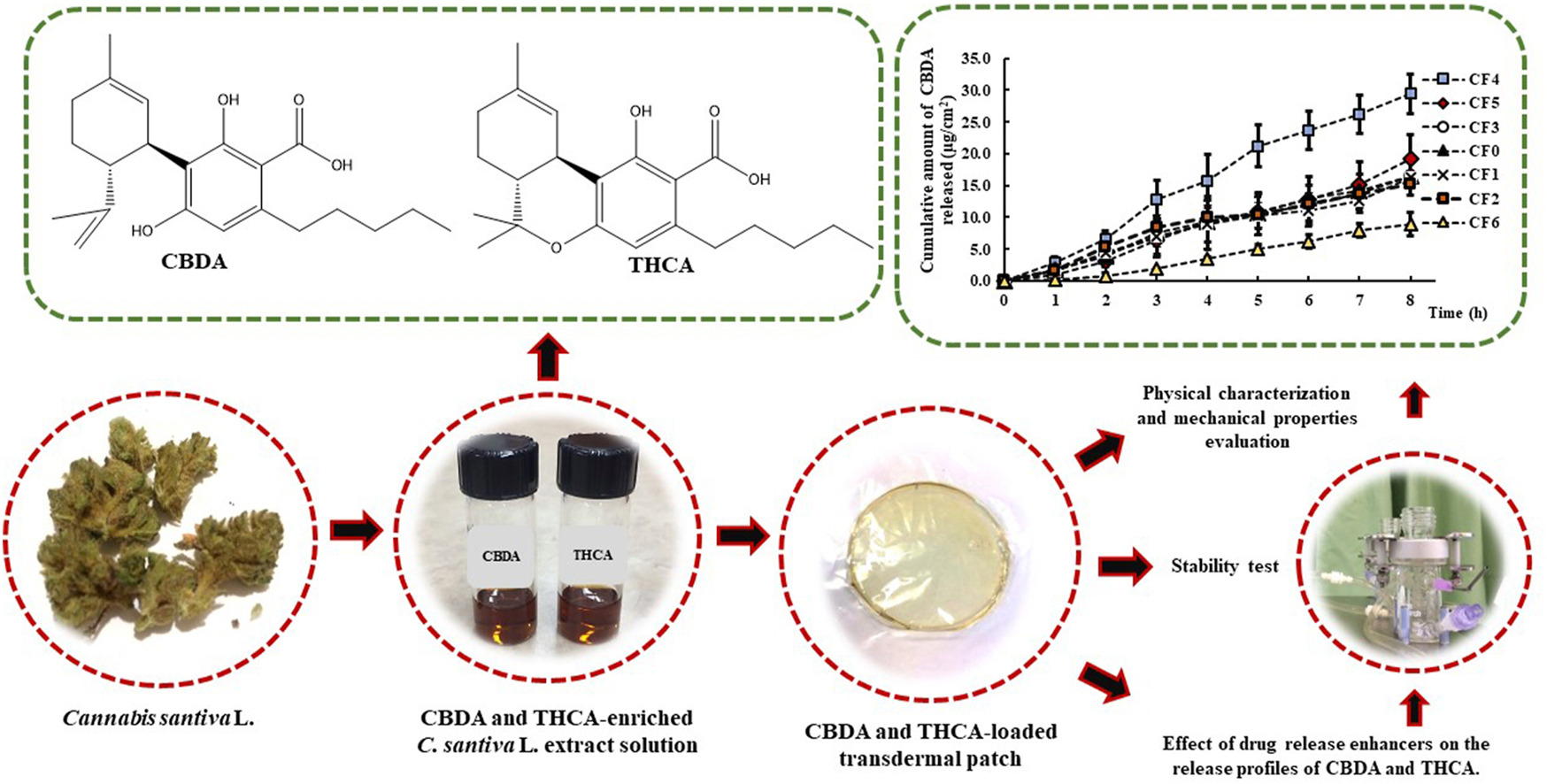
The main active cannabinoids in extracts of Cannabis sativa L., cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) and tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA), are known for their pharmacological effects, including anti-inflammatory, analgesic, psychedelic, anti-cancer, and anti-spasmodic activities. This study aimed to develop adhesive cannabinoid-loaded transdermal patches (CLTPs) to enhance the skin permeation of the active cannabinoids, CBDA and THCA, and evaluate their stability. Optimized CLTPs were prepared in 1.5% (w/w) polyvinyl alcohol-coated petri dishes using a solvent casting technique.
Highlights
- Ethoxydiglycol increased the steady-state flux for the cannabinoids.
- The CBDA-loaded patch exhibited greater permeation than the THCA-loaded patch.
- The stability of the CLTPs was maintained for at least 90 days at 4°C.
The casting solution consisted of mixtures of isopropyl alcohol and ethanol, along with Eudragit®E100, succinic acid, dibutyl phthalate, and permeation enhancers such as oleic acid, isopropyl myristate, mixtures of oleic acid and isopropyl myristate, ethoxydiglycol, sesame oil, and co-polymer (Kollidon®VA64). The physicochemical properties of the patches were characterized by uniformity, thickness, drug content, swelling, and mechanical properties. The in vitro release studies of CBDA and THCA through a synthetic hydrophobic membrane using various release enhancers from these patches were conducted using Franz diffusion cells. Using ethoxydiglycol as a release enhancer demonstrated the highest release profile for both cannabinoids.
The steady-state flux values of CBDA and THCA were 3.83 ± 0.45 μg/cm2/h (1.85-fold compared to the control) and 0.72 ± 0.14 μg/cm2/h (1.54-fold compared to the control) at 8 hrs. The stability studies of CLTPs demonstrated that both remained stable at 4°C for at least 90 days. In conclusion, transdermal patches containing cannabinoids have been successfully developed and characterized. These findings offer a promising avenue for further investigation of CLTPs, as they could serve as a versatile formulation strategy for pharmaceutical products.
Read more here
Eakkaluk Wongwad, Kornkanok Ingkaninan, Neti Waranuch, Chulhun Park, Vijay Somayaji, Nat Na-Ek, Raimar Löbenberg, Improved Transdermal Delivery of Novel Cannabinoid-Loaded Patches Using Eudragit Matrix,
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 2024, 105697, ISSN 1773-2247, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2024.105697.
Read also our introduction article on The Role of Excipients in CBD Products here:


