Enhanced in vivo absorption and biodistribution of curcumin loaded into emulsions with high medium-chain triglyceride content
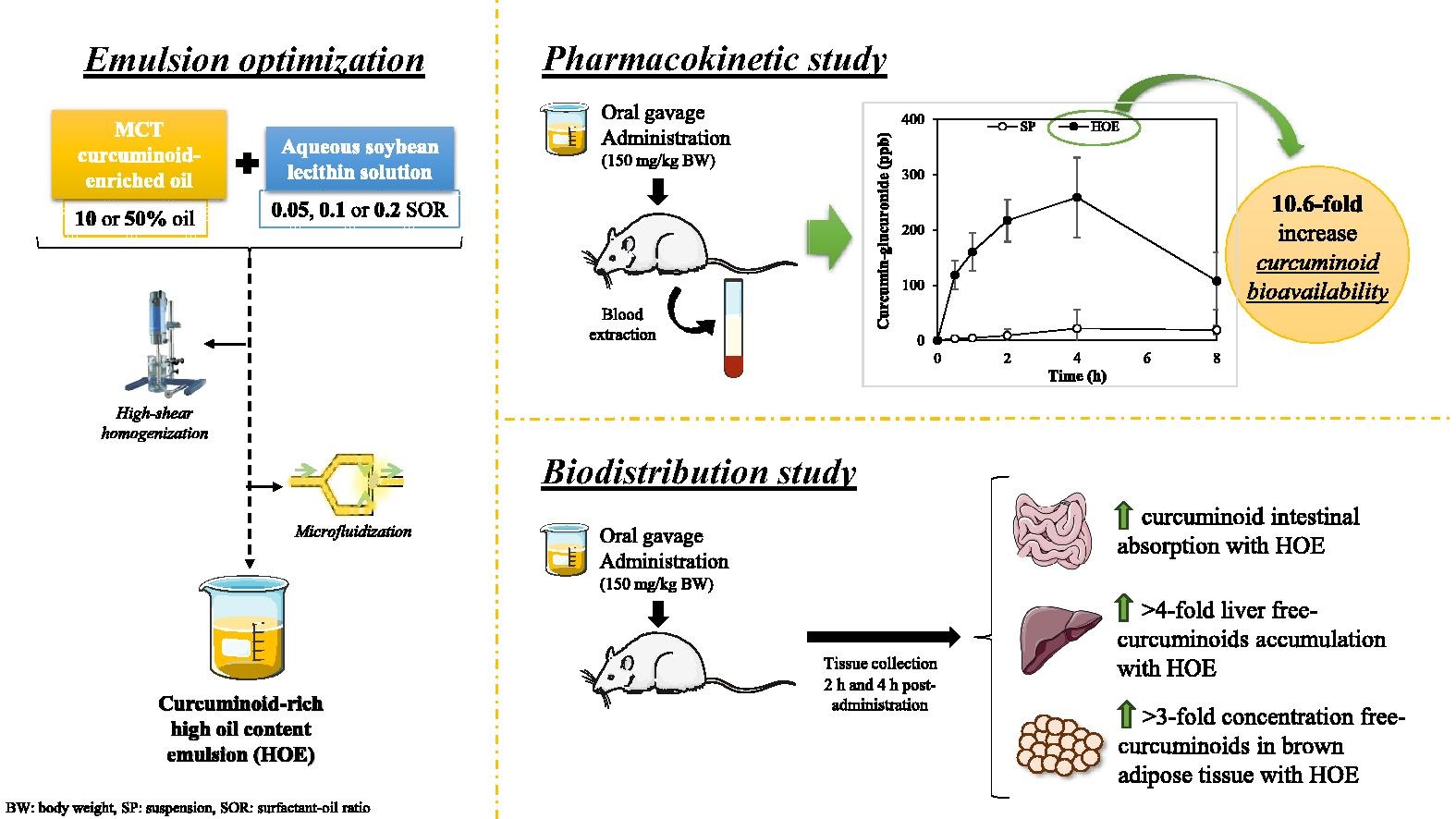
The health benefits of curcumin have been demonstrated by clinical studies, but its low bioavailability compromises its functionality. In this regard, emulsions have proven to be effective encapsulation systems for curcumin. Nevertheless, emulsions with a high oil content (50%) may offer some advantages due to the large amount of compound they can incorporate. Therefore, the aim of this work was to study the pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of curcumin when carried in optimized emulsions containing 50% MCT oil and a plant-based emulsifier (soybean lecithin) at 2 h or 4 h post-oral administration to rats. The most stable emulsion was obtained using 50% of oil and a surfactant-oil-ratio 0.1, through a microfluidization process. After the oral administration of the systems (150 mg curcumin/kg body weight), curcumin glucuronide was the main compound present in plasma (AUC0-t = 1556.3 ng·h·ml-1), especially at 2-4 h post-administration.
Highlights
- Stable high content MCT-emulsions containing lecithin were obtained using microfluidization.
- Curcumin enclosed in MCT-emulsion was better absorbed than in suspension.
- The curcuminoid bioavailability was increased by 10.6-fold when using the MCT-emulsion.
- MCT-emulsion increased free-form curcumin concentration in rat liver and brown adipose tissue.
The total curcuminoid bioavailability was increased by 10.6-fold when rats were fed with the curcumin emulsion rather than with a control suspension. Moreover, rats fed with the emulsion showed the highest accumulation of free curcuminoids, which present the highest biological activity, in the liver (129 ng curcumin/g tissue) and brown adipose tissue (193 ng curcumin/g tissue). The obtained results are of relevant interest since the presence of curcumin in the brown adipose tissue has been shown to play a relevant role in the prevention of obesity and its related metabolic disorders.
Download the full article as PDF here Enhanced in vivo absorption and biodistribution of curcumin loaded into emulsions with high medium-chain triglyceride content
or read it here
Materials
Powdered curcumin extract (mixture of ≥ 78% curcumin, 15% demethoxycurcumin, and 1% bisdemethoxycurcumin) with a purity of ≥ 98% was purchased from Acros Organics. As a lipid phase MCT oil (Miglyol, Oxi-med expres) (99.9% of purity) was used. Soybean lecithin was acquired from Alfa Aesar (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Massachusetts, USA). Curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, and bisdemethoxycurcumin standards were obtained from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO). Curcumin glucuronide was acquired from Toronto Research Chemicals (Toronto, Canada). Ultrapure water obtained from a milli-Q filtration system was used to the preparation of all solutions.
Júlia Teixé-Roig, Gemma Oms-Oliu, María Artiga-Artigas, Isabel Odriozola-Serrano, Olga Martín-Belloso, Enhanced in vivo absorption and biodistribution of curcumin loaded into emulsions with high medium-chain triglyceride content, Food Research International, 2023, 113595, ISSN 0963-9969, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2023.113595.
See the webinar:
“Rational Selection of Cyclodextrins for the Solubilization of Poorly Soluble Oral Drugs”, 8. November 2023:
Get more information & register here for free:


