Role of Cyclodextrins and Drug Solid State Properties on Flufenamic Acid Dissolution Performance from Tablets
Flufenamic acid (FFA) is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug characterised by a low solubility and problems of variable dissolution rate and bio-inequivalence. Different FFA batches, obtained by different suppliers, showed different powder characteristics (particle size, shape and surface properties) that may affect its dissolution behaviour from solid dosage forms.
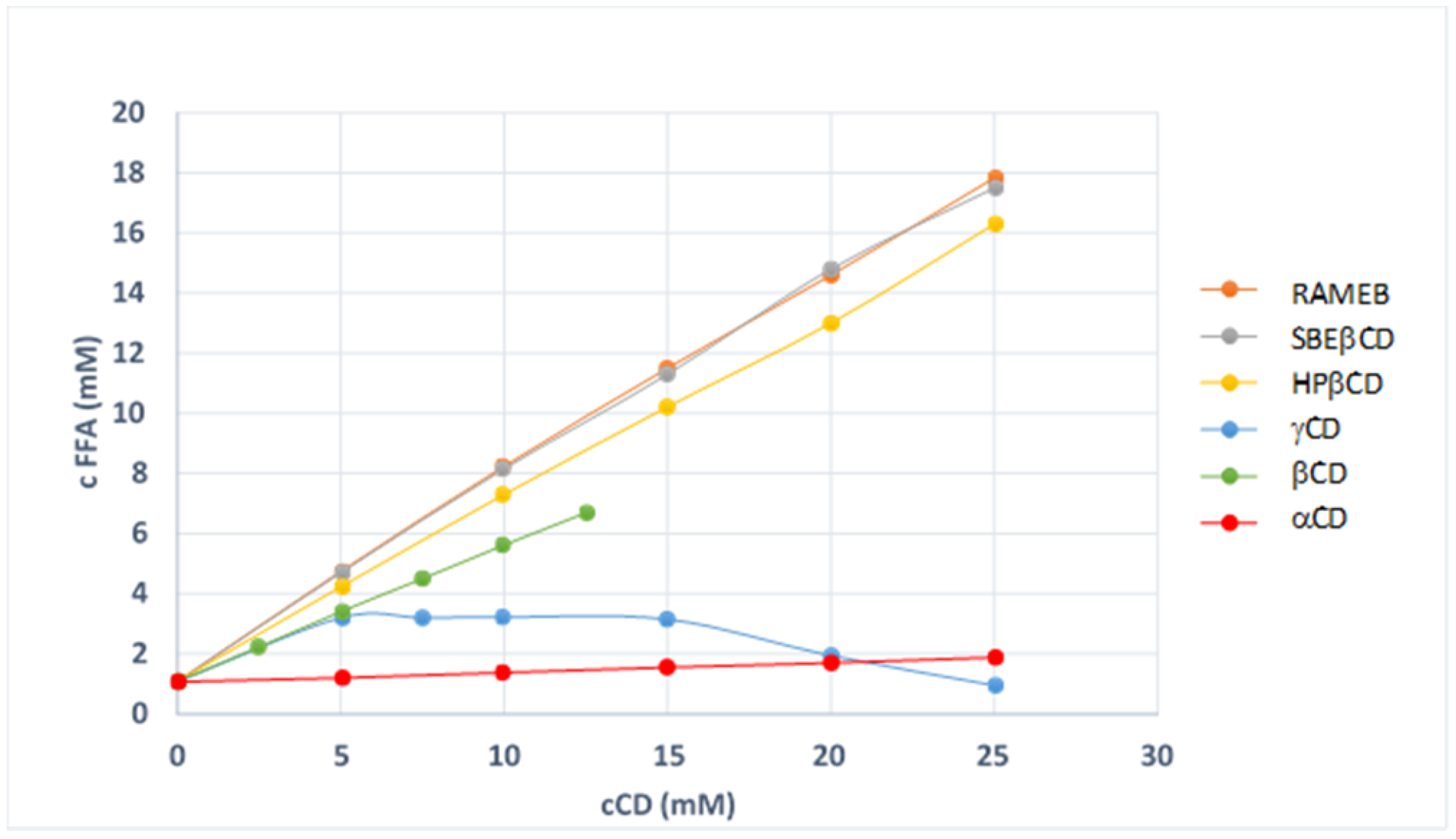
Aim of this work was the improvement of FFA solubility and dissolution rate by the use of cyclodextrins (CDs) and the obtainment of an effective tablet formulation by direct compression. Several CDs have been tested, both in solution and in solid state and several binary systems drug-CDs have been obtained with different techniques, with the scope to select the most effective system. Grinding technique with randomly methylated-β-cyclodextrin (RAMEB) was the only one that allowed the complete drug amorphization, together with the highest improvement in drug dissolution rate, and was then selected for tablets formulation.
Conventional and immediate release tablets were obtained and fully characterised for technological properties. In both cases an improved and well reproducible drug dissolution performance was obtained, independently from the FFA supplier and thus no more affected by the differences observed between the original FFA crystalline samples.
Download the full article as a PDF here or read it here
Materials: Two different batches of flufenamic acid (2-{[3-(trifluoromethyl) phenyl] amino} benzoic acid), FFA) were used: a batch donated by S.I.M.S. (FFA SIMS) (Florence, Italy) (purity 99.97% [13]) and another batch provided by TCI EUROPE N.V. (FFA TCI) (Zwijndrecht, Belgium) (purity 99.99% [13]). CDs were from Merck Life Science S.r.l. (Milan, Italy); βCD and HPβCD (MS 0.86) were a gift from Roquette (Lestrem, France); sulfobutylether-βCD (SBEβCD) was donated by Cyclolab (Budapest, Hungary) and randomly methylated-βCD (RAMEB) by Wacker-Chemie (Munich, Germany). Tablet excipients: partially pregelatinised starch was from Roquette (Lestrem, France); spray-dried lactose from Meggle Group (Wasserburg, Germany), magnesium stearate and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVPK90) from Merck Life Science S.r.l. (Milan, Italy). All other chemicals were of analytical reagent grade.
Article information: Maestrelli, F.; Cirri, M.; De Luca, E.; Biagi, D.; Mura, P. Role of Cyclodextrins and Drug Solid State Properties on Flufenamic Acid Dissolution Performance from Tablets. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14020284


