Oral fast-dissolving risperidone loaded electrospun nanofiber drug delivery systems for antipsychotic therapy
Abstract
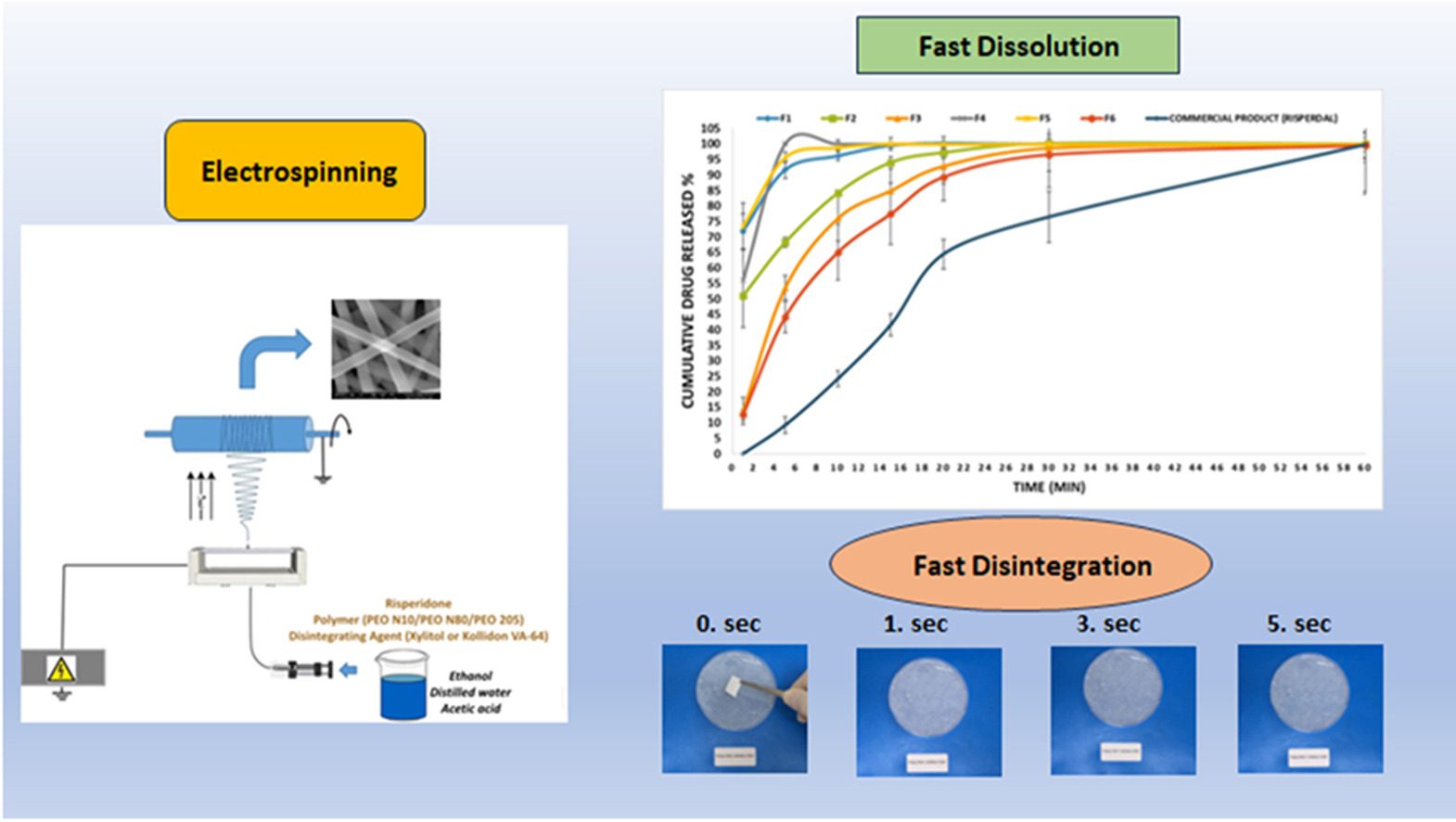
Risperidone is an antipsychotic drug classified as BCS Class II with low solubility at physiological pH and orally used in the treatment of schizophrenia. Electrospinning is one of the newest fabrication methods used for the development of fast soluble drug delivery systems. In this study, an orally disintegrating film (ODF) formulation of risperidone was developed with green electrospinning technique. Different molecular weight polyethylene oxide (PEO) as a polymer and xylitol or Kollidon VA64 as a disintegration agent were used for the preparation of formulations. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) and Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) analyses were conducted as part of pre-formulation studies to identify possible incompatibilities in formulation components. We characterized ODFs based on their mechanical properties, shape and diameter of nanofibers, disintegration behavior, and in vitro dissolution profiles. A few wrinkles appeared on the surface of fibers prepared with xylitol, but a smooth surface was evident on Kollidon VA64 fibers. Disintegration studies performed in the simulated oral environment showed that ODFs disintegrate in as little as 1 second. The dissolution behavior of developed ODFs and commercial products was compared with a dissolution study in distilled water. The chosen formulations had acceptable mechanical properties with much faster dissolution compared to the commercially available product. In this study, risperidone ODF formulation was successfully produced and characterized. The study showed that risperidone-loaded nanofibers could provide a promising alternative to conventional oral dosage forms like tablets and capsules.
Introduction
Risperidone is an antipsychotic drug classified as BCS (Biopharmaceutical Classification System) Class II and orally used in the treatment of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder [[1], [2], [3]]. Different drug delivery systems for risperidone to increase patient compliance and bioavailability were prepared such as transdermal microemulsion [1], nanoparticles for intranasal use [4], long-acting microspheres [5], and in-situ gel-forming implants [6]. However, according to the FDA database, oral and orodispersible tablets, oral solutions, and intramuscular, subcutaneous injectable solutions and suspensions are listed as “Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations” [7]. Therefore, there remains a need for innovative dosage forms that will provide greater patient compliance and bioavailability.
Electrospinning is a well-characterized, single-step technique to produce nanofibrous structures for various purposes such as oral drug delivery [8], tissue engineering [9], production of sensors [10], packaging materials [11], and wound healing [12].
Polyethylene oxide (PEO) is a novel, non-toxic, biodegradable, water, and ethanol-soluble polymer widely used in drug delivery systems [[13], [14], [15]]. PEO is an uncrosslinked polymer and available in ranging molecular weights starting from 100,000 to 8000000 g/mol. PEO has the same chemical structure as polyethylene glycol (PEG) but a higher molecular weight [20]. Even though, pure PEG solutions are not electrospinnable regardless of the solvent used [16,17], PEO solutions are suitable and there are several studies performed with PEO via electrospinning [[18], [19], [20], [21], [22]].
Kollidon VA64 (vinyl pyrrolidone/vinyl acetate copolymer at a ratio of 6:4) is used as a tablet binder, granulation, and film-forming agent in dosage forms [23]. Xylitol is a nonnutritive 5-carbon (pentose) sugar alcohol [24] used as a sweetener [25], binder [26], and disintegrating agent [27] in previous studies. They both are widely used in oral formulations and approved by FDA [25,28].
Patients with schizophrenia and other forms of psychosis present a biochemical imbalance involving the neurotransmitter dopamine and its signaling pathways. To control this imbalance, most of the neuroleptic drugs in clinical use are molecules that interact with proteins, which are the dopamine D2 receptor (DRD2) [29]. The D2 dopamine receptor (DRD2) is essential for mediating the actions of antipsychotic drugs, and also for medications used to treat Parkinson’s disease, hyperprolactinemia, nausea, and vomiting, among many other disorders [30]. Unfortunately, many drugs that target DRD2 cause serious and potentially life-threatening side effects due to promiscuous activities against related receptors [31]. Dopamine is an endogenous neurotransmitter and risperidone is a second-generation antipsychotic. The DRD2–risperidone structure reveals an unexpected mode of antipsychotic drug binding to dopamine receptors and highlights structural determinants that are essential for the actions of risperidone and related drugs at DRD2 [30].
Seo et al. previously identified a group of subjects with schizophrenia who, on average, have a 75 % decrease in the cholinergic receptor, muscarinic 1 (CHRM1) in Brodmann’s area (BA) 9 [32]. Post-mortem studies in patients with schizophrenia have shown significantly reduced M1 receptor expression rates in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) compared to controls [33]. From these data, it was proposed that activation of the muscarinic M1 and/or M4 receptors would reduce the severity of the symptoms of schizophrenia. In this study, both genes DRD2 and CHRM1 were selected as target genes due to their essential role in antipsychotic drug activities.
Patient compliance is crucial in the treatment of bipolar disorder and schizophrenia which drug rejects are very common. This study aims to prepare fast-dissolving risperidone-loaded orodispersible PEO nanofibers via electrospinning. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study on the preparation and characterization of risperidone-loaded nanofiber drug delivery system as an orodispersible film. Kollidon VA64 and Xylitol will be used as disintegrating agents. Electrospinning solutions and produced fibers will be characterized. The effects of the molecular weight of PEO and the type of disintegrating agent will be investigated by means of excipient compatibility, fiber diameter, and structure, disintegration, dissolution, in vitro cytotoxicity assay, and qPCR analysis studies.
Read more here
Materials
Polyethylene oxide with three different molecular weights [MW = 100,000 (WSR N10), 200,000 (WSR N80, 600,000 (WSR 205)] was used as the polymer. Xylitol or Kollidon® VA-64 were used as disintegrating agents. A mixture of ethanol, distilled water, and acetic acid was used to dissolve the polymer and the risperidone. Potassium dihydrogen phosphate, ethanol, sodium hydroxide, and potassium chloride were purchased from Merck KGaA, Germany.
Yasin Turanlı, Mehmet Birer, Yağmur Turgut Birer, Recep Uyar, Begüm Yurdakök Dikmen, Füsun Acartürk, Oral fast-dissolving risperidone loaded electrospun nanofiber drug delivery systems for antipsychotic therapy, Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 2023, 105262, ISSN 1773-2247, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2023.105262.
Read more on “Orally Disintegrating Tablets (ODTs)” here:


