Processed excipients for targeted drug delivery in cancer management: Enhancing efficacy and precision
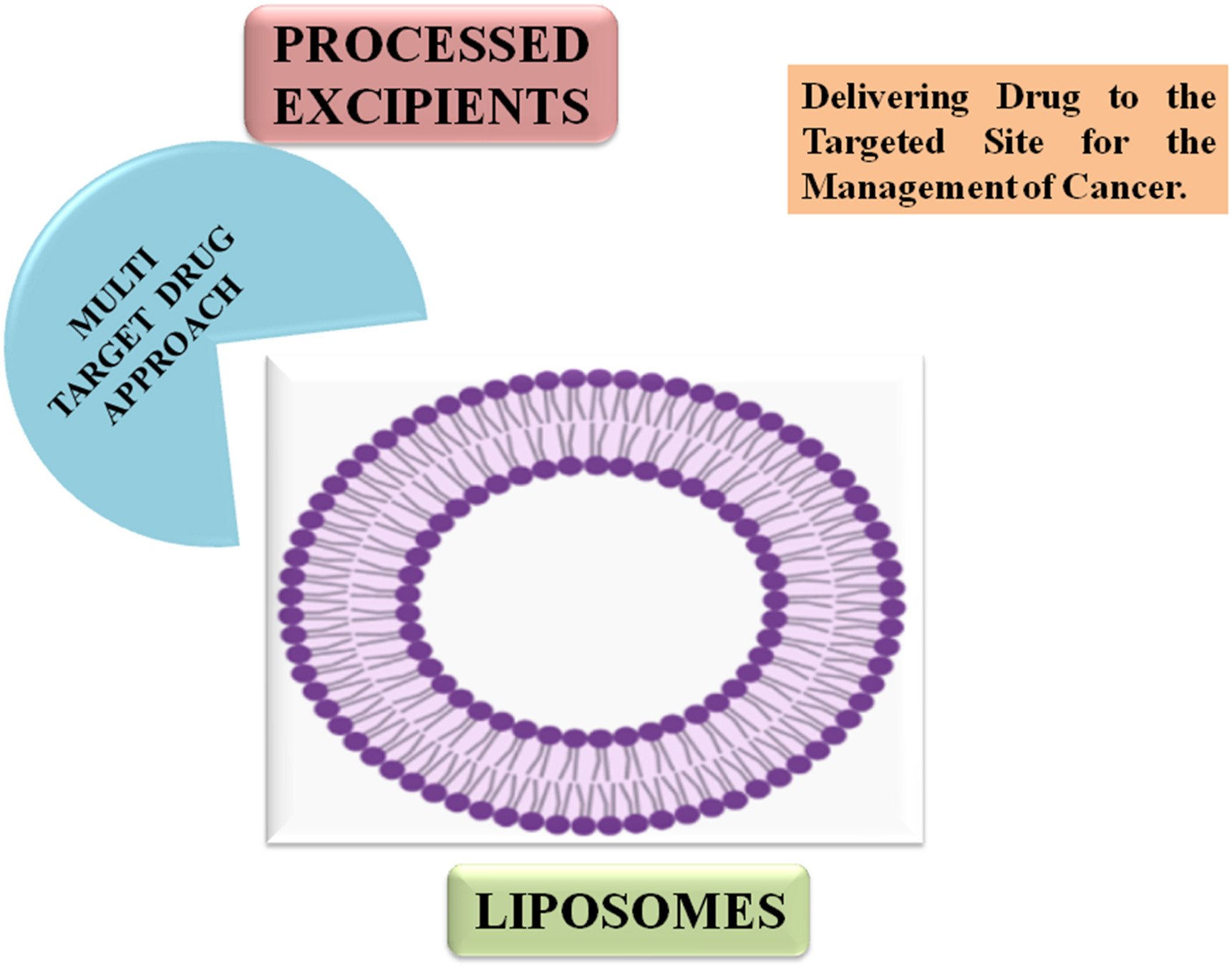
Processed excipients (PEs) function in creating various dosage forms and need no introduction. For instance, recent studies have shown that PEs oleic acid, which is used with the breast cancer medicine Herceptin, functions both as a liquid delivery system for drugs and has the ability to suppress the breast cancer gene. Gamma-linolenic acid and omega-3 fatty acids, respectively, have some positive impacts on anticancer activity and cardiovascular advantages. PEs can transport other medications in liquid form, but they can also destabilise APIs. The physical interactions between excipients can alter how quickly a solid dosage form dissolves.
The aim of the study is to investigate the crucial role of processed excipients (PEs) in creating diverse dosage forms, with a particular focus on their functions, effects, and interactions. The study also aims to explore recent research findings that demonstrate the potential of certain PEs, such as oleic acid, gamma-linolenic acid, and omega-3 fatty acids, in drug delivery and their potential therapeutic impact, including suppressing breast cancer genes and enhancing anticancer and cardiovascular activities. Furthermore, the study aims to delve into the dual nature of PEs, where they can both facilitate the delivery of drugs in liquid form and potentially influence the stability and dissolution characteristics of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). It seeks to examine the intricate interplay between different excipients and their effects on drug bioavailability and functionality.
The study acknowledges the global health burden posed by cancer and aims to highlight the application of traditional and emerging therapies, such as phytochemicals, in cancer treatment. It also intends to discuss the challenges associated with conventional chemotherapy, including the development of drug resistance. Additionally, the study aims to emphasise the continued relevance of PEs in the formulation of biologic medicinal products, particularly in the context of injection-based delivery methods. It aims to address the crucial considerations surrounding endotoxins and microbiological quality in these products. Overall, the study aims to contribute to a deeper understanding of the multifaceted roles and significance of PEs in pharmaceutical formulation and their impact on drug delivery, stability, and therapeutic outcomes.
Table 1. Types of PEs used in the formulation of lipid based carrier system.50
| Processed Excipients (PEs) | Processed Excipients (PEs) |
|---|---|
| Glyceryl monostearate (ImwitorÒ900) | The glycerol ester of stearic acid is glycerol monostearate, also referred to as GMS. It is frequently utilised in food as an emulsifier. |
| Soy lecithin (LipoidÒ S 75, LipoidÒ S 100) | Purified soybean phospholipids, which begin as crude soybean lecithin, serve a variety of purposes in medical, cosmetic, and food applications. As wetting agents, solubilizers, emulsifiers, liposome builders, and technical aids, these carefully specified products exhibit remarkable performance. In addition, they provide choline and vital fatty acids. The majority of goods are accessible in non-GMO varieties. |
| Egg lecithin | The highly purified portions that come from hen egg yolks are called egg phospholipids. Egg phospholipids are ideal for parenteral applications because they closely resemble the makeup of human cells. They are primarily found in fat emulsions used in drug-containing formulations or for parenteral feeding. |
| Poloxamer 188 | A nonionic block linear copolymer known as Poloxamer 188 (P188) has cytoprotective, antithrombotic. Once licenced by the FDA in the 1960s as a therapeutic agent to lessen blood viscosity prior to transfusions, P188 is no longer contained in any products that have received Regulatory approval. Owing to its sufactant qualities, P188 is also present in over-the-counter (OTC) items like toothpaste, bowel cleaners, and mouthwash and is employed in a variety of cosmetic, business, and pharmaceutical applications. |
| Phosphatidylcholine (Epikuron®170, Epikuron 200) | Wetting and dispersion agent, suspension and emulsifying agent and dispersion agent, anti-crystallization agent, for tablets and powders |
Download the full article as PDF here Processed excipients for targeted drug delivery in cancer management: Enhancing efficacy and precision
or read it here
Following excipients are mentioned in the study besides other: PROSOLV® EASYtab SP
Aditya Singh, Shubhrat Maheshwari, Vishal Kumar Vishwakarma, Saad Mohammed, Processed excipients for targeted drug delivery in cancer management: Enhancing efficacy and precision, Intelligent Pharmacy, 2023, ISSN 2949-866X, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipha.2023.10.006.
See the webinar:
“Rational Selection of Cyclodextrins for the Solubilization of Poorly Soluble Oral Drugs”, 8. November 2023:
Get more information & register here for free:


