Biocompatible hydroxy double salt tablet formulations
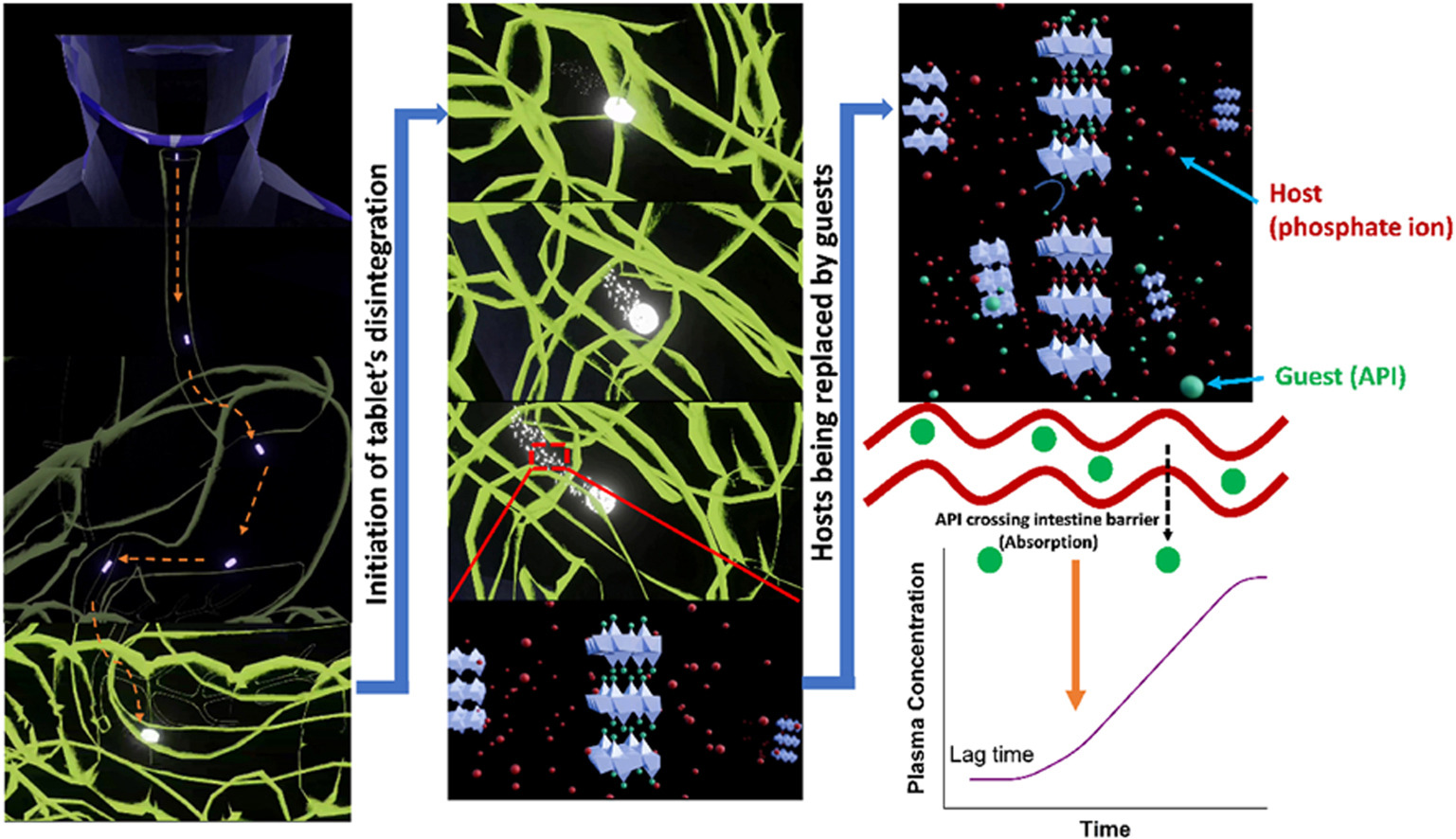
Generally, commercial extended release tablets are core-based, which can cause problems for certain patients if they split them prior to ingestion. There is a need to develop non-core-based extended release tablets. We have previously reported the synthesis of two new biocompatible hydroxy double salts (HDSs), [Mg2Zn3(OH)8]Cl2⋅3.4H2O (MgZn–Cl) and [Fe2.4Zn2.6(OH)8]Cl2⋅2H2O (FeZn–Cl) (J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 5789), and found them to be good candidates for the extended release of diclofenac (Dic), ibuprofen (SI) and valproate (Val) (Appl. Clay. Sci. 2022, 221, 106456). Here we build on these previous results and report scale-up synthesis of MgZn–Cl and FeZn–Cl loaded with Dic, SI, and Val.
Highlights
- Novel biocompatible hydroxy double salt (HDSs)-based tablets have been prepared.
- The tablets meet pharmacopeial quality requirements.
- The tablets have extended and delayed release properties.
- The metals present in the HDSs could treat common side-effects or co-morbidities.
The scaled-up products were blended with excipients and formulated into non-core based tablets. The post-compression parameters of the HDS-based tablets were assessed against the pharmacopeia requirements (friability, weight, and dose uniformity) and all passed the tests. Drug release studies were carried out using the paddle method (USPII) in conditions representative of the gastrointestinal tract. The HDS tablets were found to meet the pharmacopeia requirements for modified release dosage forms and showed similar release profiles to current commercial formulations. It is thus possible to develop modified release non-core based tablets using HDSs. These have additional benefits over standard commercial tablets, because the presence of the essential elements Zn, Fe and/or Mg in the layers can compensate for deficiencies induced over long-term treatment, and enhance therapeutic efficacy in some cases. Furthermore, the buffering effect of the HDS layers has the potential to prevent the gastric irritation often associated with the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
2.1. Materials
Materials were obtained as follows: Zinc oxide (ZnO) and magnesium chloride (MgCl2·6H2O) (99%; Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA); iron chloride (FeCl2·4H2O), potassium iodide (KI), ibuprofen sodium, and valproate sodium, polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP, MW ca. 44 000), microcrystalline cellulose (Avicel PH 101), magnesium stearate (Sigma-Aldrich; Gillingham, UK); diclofenac sodium (98%; Cambridge Bioscience, Cambridge, UK); spray dried mannitol (Pearlitol 200; a kind gift from Roquette-Pharma, Lestrem, France). All chemicals were used without further purification. Commercial tablets were sourced as follows: Dicloflex 75 mg (Almus, Chessington, UK), Brufen Retard 800 mg (Abbott, Chicago, IL, USA), Rheumatac Retard 75 mg (Amdipharm Mercury, Oakville, Canada), Clofenac 100 mg (Squarepharma, Dhaka, Bangladesh) and Epilim Chrono 200 mg (Sanofi, Paris, France).
Read more
Abdessamad Y.A. Kaassis, Gareth R. Williams, Biocompatible hydroxy double salt tablet formulations, Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 2023, 104989, ISSN 1773-2247,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2023.104989.

