Formulation and characterization of hydroxyethyl cellulose-based gel containing metronidazole-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for buccal mucosal drug delivery
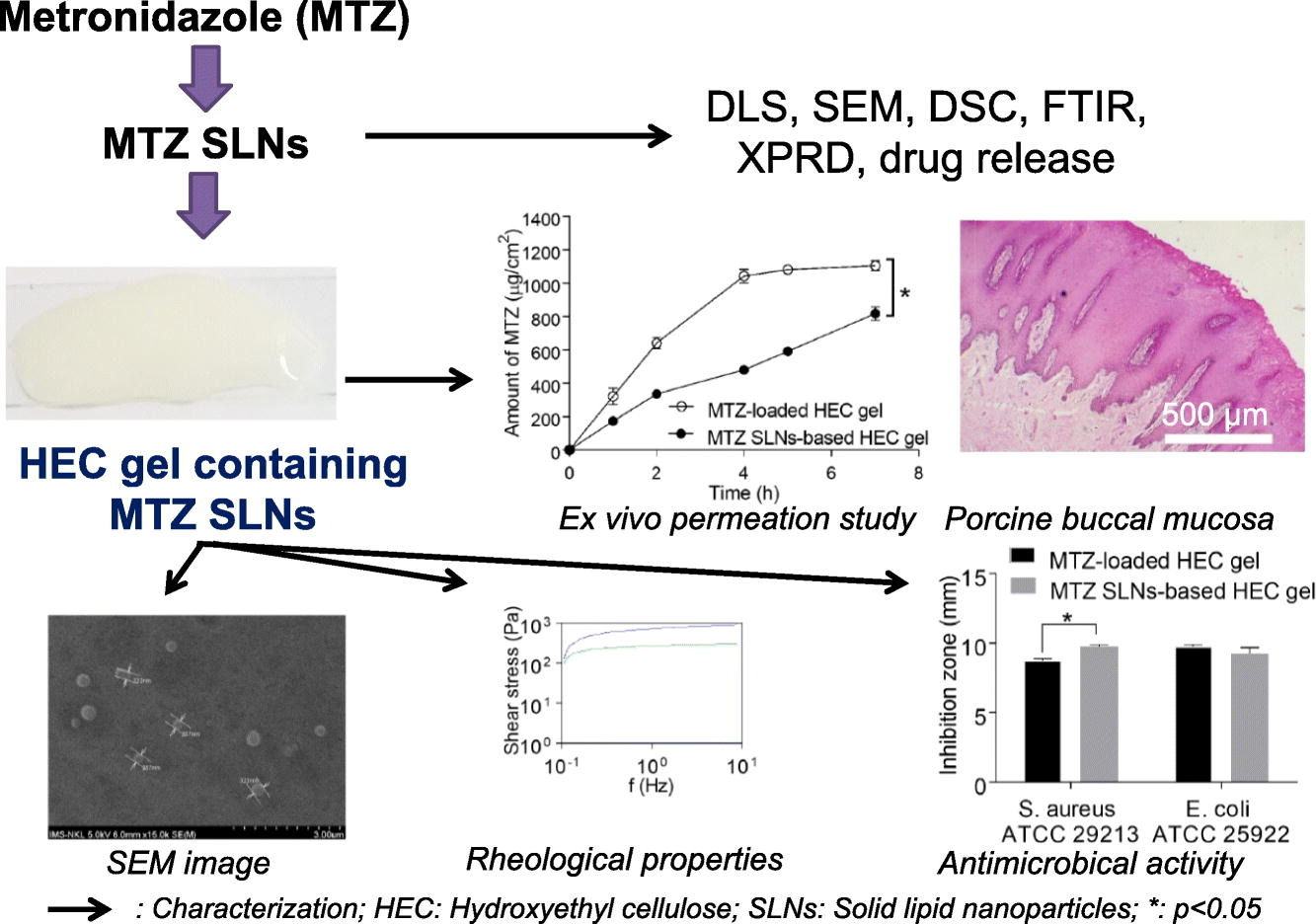
Local delivery of drug is a promising strategy to manage periodontitis characterized by chronic inflammation of the soft tissue surrounding the teeth. An optimized system should prolong the drug retention time and exhibit controlled drug permeation through the buccal mucosal layer. This study was aimed to develop hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC)-based gel containing metronidazole (MTZ) loaded in solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs), and to enhance the antimicrobial activity of MTZ. SLNs were prepared using a combination method of solvent evaporation and hot homogenization.
Highlights
- • The MTZ-loaded SLNs were incorporated into HEC-based gel.
- • The HEC gel had preferable mechanical and rheological properties.
- • The HEC gel exhibited a sustained drug release and optimal ex vivo permeability.
- • The HEC gel enhanced in vitro antimicrobial activity after 24 h of treatment.
The results showed that the fabricated SLNs, comprising of Precirol (2.93%, w/v), Tween 80 (1.8%, w/v), and the drug:lipid ratio of 19.3% (w/w), were approximately 200 nm in size, with a narrow distribution. The HEC (3%, w/w)-based gel formed a smooth, homogeneous structure and had preferable mechanical and rheological properties. Moreover, the MTZ-loaded SLNs-based HEC gel (equivalent to 1% of MTZ, w/w) exhibited a sustained in vitro drug release pattern, optimal ex vivo permeability, and enhanced in vitro antimicrobial activity after 24 h of treatment. These findings indicate the potential of the MTZ-loaded SLNs-based HEC formulation for local drug delivery at the buccal mucosa in managing periodontal disease.
Hoang Nhan Ho, Hoang Hao Le, Thien Giap Le, Thi Hong Anh Duong, Viet Quynh Tram Ngo, Cong Thuan Dang, Van Minh Nguyen, Tuan Hiep Tran, Chien Ngoc Nguyen,
Formulation and characterization of hydroxyethyl cellulose-based gel containing metronidazole-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for buccal mucosal drug delivery,
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,
2021, ISSN 0141-8130,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.11.161.

