Optimization and Evaluation of Lisinopril Mucoadhesive Sustained Release Matrix Pellets: In-Vitro and Ex-Vivo Studies
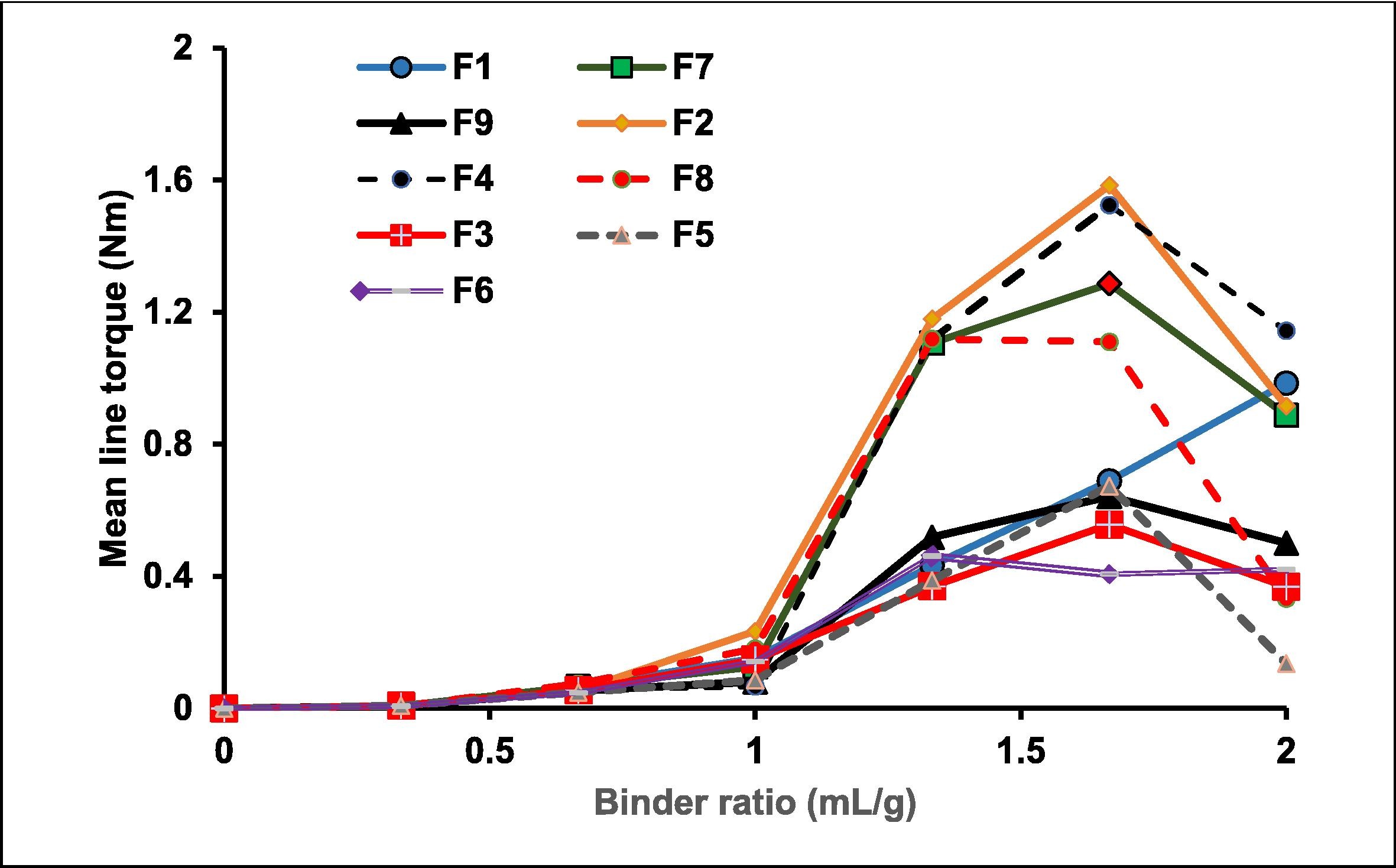
Lisinopril (LIS) it is antihypertensive drug, classified as a class III drug with a high water solubility and low permeability. To overcome the low permeability, 32 factorial designs aimed to formulate LIS as a sustained-release (LIS-SR) matrix pellet by extrusion/spheronization. Matrix pellets were composed of wet mass containing Avicel® and polymeric matrix polymers (sodium alginate (SA) and chitosan (CS)). Evaluation the effect of two independent variables, matrix-forming units (SA and CS) on mean line torque, on pellet size, dissolution rate after 6 h, and mucoadhesion strength of the pellets were assessed using Statgraphics software. The tested formulations (F1-F9) showed that mean line torque ranged from 1.583 – 0.461 Nm, with LIS content in the LIS-SR pellets ranged from 87.9-103%, sizes varied from 1906-1404 µm and high percentages of drug released from pellets formulations (68.48 to 74.18 %), while the mean zeta potential value of mucoadhesive range from -17.5 to -22.9 mV.
The selection of optimized formula must have the following desirability: maximum peak torque, maximum pellets’ particle size, and minimum % LIS release after 6hr. LIS optimized sustained release pellet formula composed of 2,159 % SA and 0.357 % CS was chosen as optimized formula. It’s showed a 1.055 Nm mean line torque was responsible for the increased pellet size to 1830.8 μm with decreased release rate 56.2 % after 6 hr, and -20.33 mV average mucin zeta potential.
Ex-vivo mucoadhesion studies revealed that that the optimize formula, exhibited excellent mucoadhesive properties, after 1 h, about 73% of the pellets were still attached to the mucus membrane. Additionally, ex-vivo permeation determination of LIS from the optimized LIS-SR formulation was found to be significantly higher (1.7-folds) as compared to free LIS.
In conclusion: LIS-SR matrix pellets, prepared with an extrusion/spheronization have desirable excellent characteristics in-vitro and ex-vivo sustained-release pellet formulation of LIS-SR was able to sustain the release of LIS for up to 8 h.
Download the full article as PDF here Optimization and Evaluation of Lisinopril Mucoadhesive Sustained Release Matrix Pellets: In-Vitro and Ex-Vivo Studies
or read it here
Materials
LIS was obtained from Aljazeera Pharmaceutical Industry (Riyadh, Saudi Arabia). Sodium alginate (SA) was obtained from Fluka Chemie (Buchs, Switzerland). Chitosan (CS) low molecular weight Poly (D-glucosamine) deacetylated chitin was obtained from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC; Avicel® PH101) was purchased from Serva Feinbiochemica (Heidelberg, Germany). Mucin of bovine submaxillary glands was obtained from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) enteric-coated capsules were purchased from DR T&T health (Corby, UK). The rest of the supplies and solvents were of the reagent or analytical grade, didn’t need to be further purified, and were utilized exactly as they were delivered.
Modhi F. Alagili, Bushra T. AlQuadeib, Lubna Y. Ashri, Ibrahim Abbas, Optimization and Evaluation of Lisinopril Mucoadhesive Sustained Release Matrix Pellets: In-Vitro and Ex-Vivo Studies, Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal,
2023, ISSN 1319-0164, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2023.06.023.
Read more on “Alginates as Pharmaceutical Excipients” here:


