Current perspective on the challenges in the development of metformin orally disintegrating tablets (ODTs)
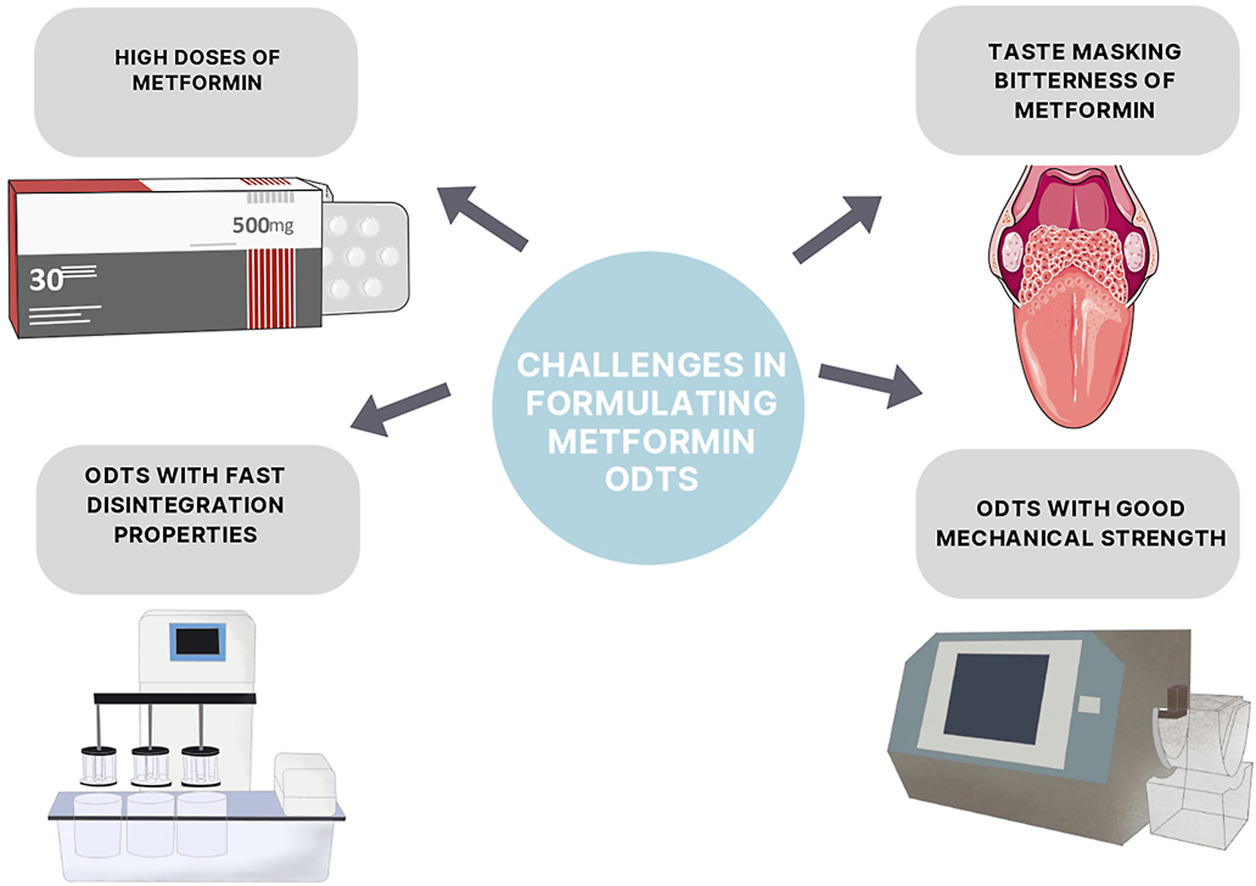
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a metabolic disorder characterized by persistent hyperglycaemia with significant morbidity and mortality rates. Currently, metformin is a drug used as first-line therapy during the management of T2DM patients. Despite metformin’s effectiveness and potency in lowering blood sugar levels, metformin had poor bioavailability and was prescribed in high doses of 500/1000 mg daily, which subsequently led to undesirable side effects. A high-dose regimen also needs a bigger pill size, which decreases patient compliance in dysphagic patients. To address these issues, many studies have attempted to develop metformin-based orally disintegrating tablets (ODTs) that possess rapid disintegration and dissolution properties to improve patient compliance and drug bioavailability. The present review aimed to highlight the recent studies on development and critical insights into addressing the challenges pertaining to designing the optimized formulation of metformin ODTs.
Read more here
Mohamad Farhan bin Roslan, Riyanto Teguh Widodo, Current perspective on the challenges in the development of metformin orally disintegrating tablets (ODTs), Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, Volume 86, 2023, 104650, ISSN 1773-2247, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2023.104650.
Visit our next webinar:
Solving capping challenges using mannitol as an excipient model
Get more information & register here:


