4-Hydroxynonenal is An Oxidative Degradation Product of Polysorbate 80
Introduction
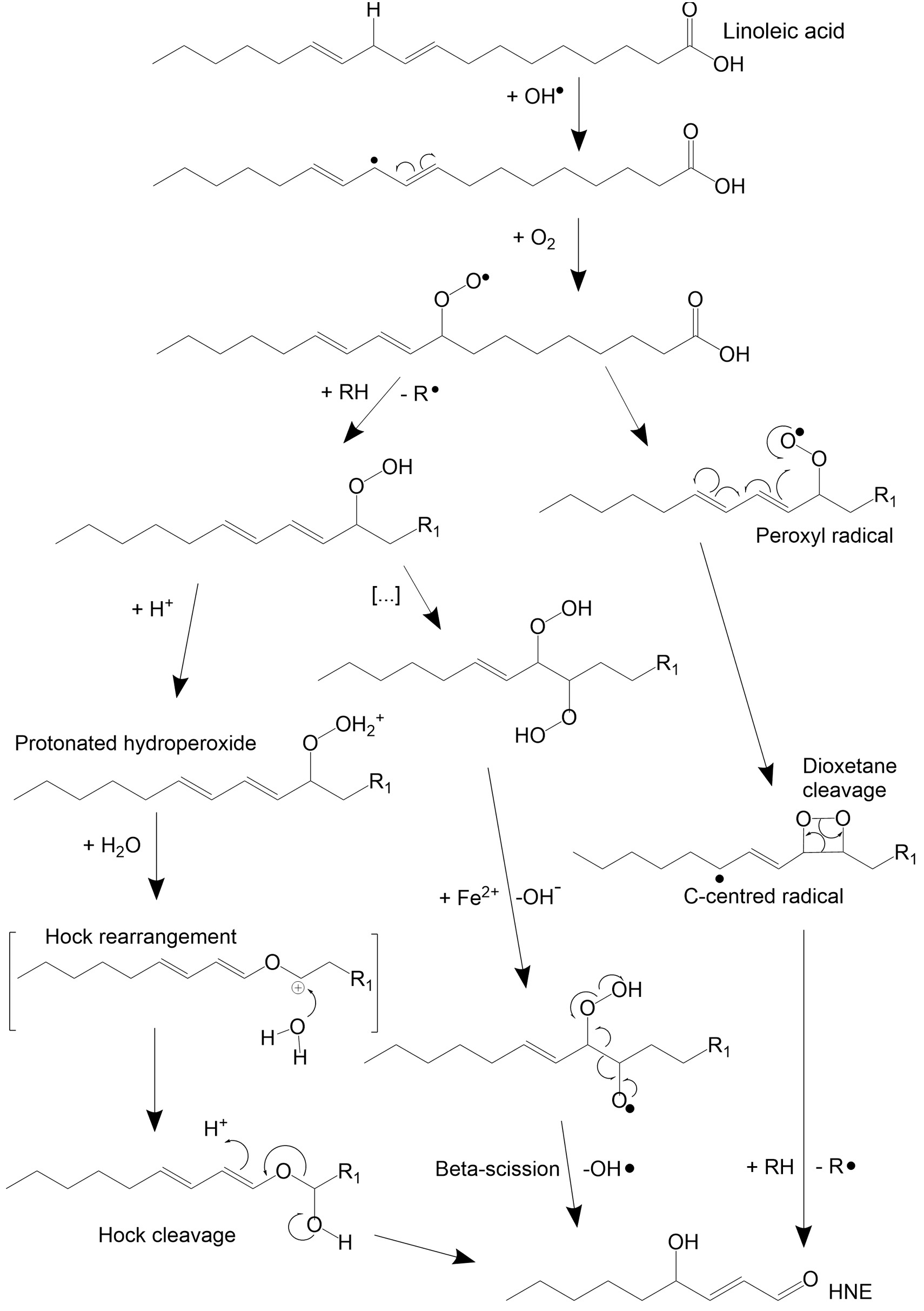
Polysorbates (PS) are used in biopharmaceuticals to stabilize therapeutic proteins. Oxidative degradation of (poly)unsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) contained in PS was shown to lead to α,β-unsaturated carbonyls.
Aim
The n-6-PUFA linoleic acid accounts for up to 18% of all FAs contained in multi-compendial grade PS80. 4-Hydroxynonenal (HNE) is highly reactive towards nucleophilic amino acids, potentially leading to covalent protein modifications. This study tests whether HNE may be a pharmaceutically relevant PS80 peroxidation product.
Methods
Since HNE was not directly detectable in the PS80 matrix by UV and MS, a new quantification method was established. After derivatization with 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine (DNPH) and extraction of the formed hydrazone with a salting-out assisted liquid-liquid extraction, the HNE-DNPH adduct was analyzed by multiple reaction monitoring. Kinetic oxidation studies were conducted incubating PS80 in presence and absence of the antioxidant butylhydroxytoluene (BHT).
Results
HNE was confirmed as PS80 degradant in oxidatively stressed samples. BHT was shown to prevent its formation.
Conclusion
HNE is a detectable PS80 degradation product raising questions about the potential impact on critical quality attributes of biopharmaceuticals formulated with PS80. Addition of BHT prevented HNE formation under oxidative stress. Consequently, BHT might be a valuable additive in PS used in biopharmaceuticals. Continue reading on 4-Hydroxynonenal is An Oxidative Degradation Product of Polysorbate 80
Ariane Schröter, Atanas V. Koulov, Jörg Huwyler, Hanns-Christian Mahler, Michael Jahn,
4-Hydroxynonenal is An Oxidative Degradation Product of Polysorbate 80,
Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2021,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xphs.2021.01.027.

