Investigation of the effect of polymers on dermal foam properties using the QbD approach
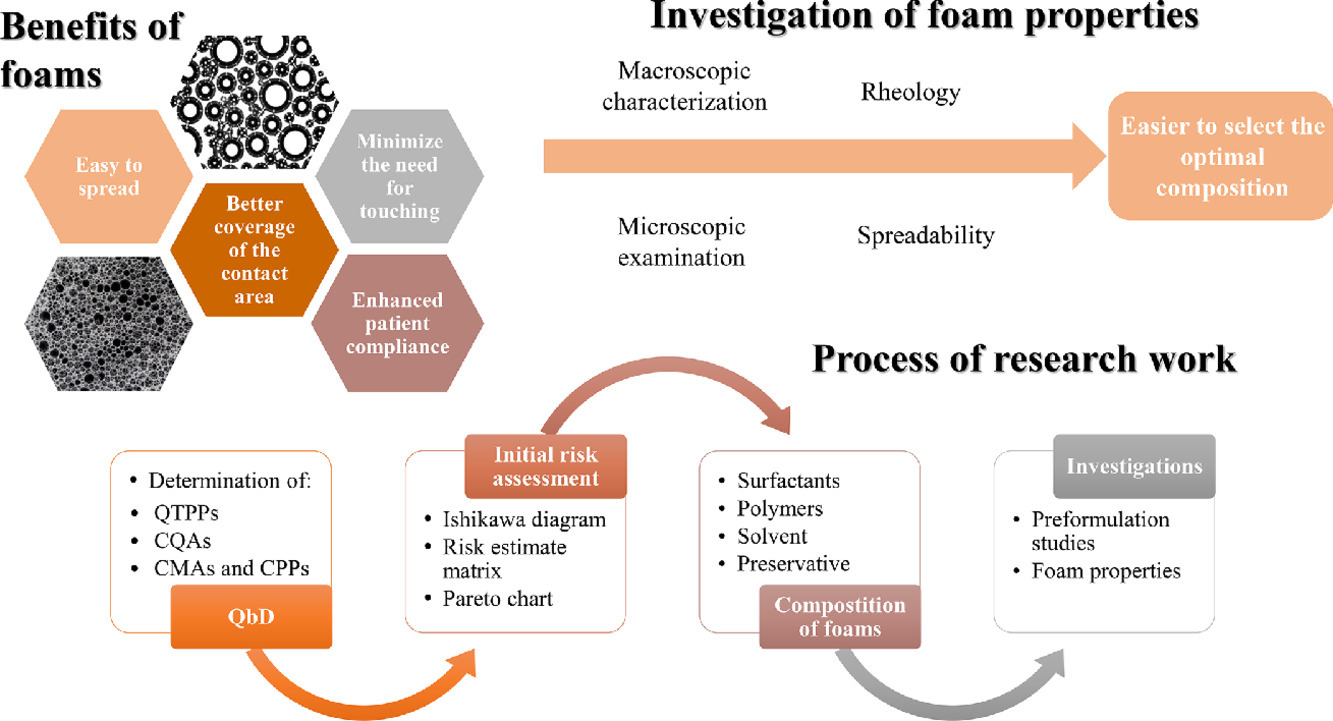
Dermal foams are promising drug delivery systems due to their many advantages and ease of application. Foams are also considered a novelty in the field of dermatology. In particular, they are beneficial for the treatment of skin conditions where patients have highly inflamed, swollen, infected and sensitive skin, as the application of the foam to the skin surface to be treated minimizes the need for skin contact. In order to formulate foams, it is necessary to know which material and process parameters influence the quality characteristics of foams and which methods can be used to study foams; this part of the research is assisted by the QbD approach. By using the QbD concept, it contributed during the development process to ensure quality-based development. With initial risk assessment, the critical material attributes (CMAs) and the critical process parameters (CPPs) were identified to ensure the required critical quality attributes (CQAs). During the initial risk assessment, five high-risk CQAs, namely foam volume stability, foam expansion, cross point, the initial values of the number and size of bubbles, and three medium-risk CQAs, namely spreadability, relative foam density and viscosity of the liquid system were identified and investigated. In this research, different types of polymers (xanthan gum, hydroxyethylcellulose, different types of hyaluronic acids) were used to improve the properties of foam formulations. The formulations containing xanthan gum and high molecular weight hyaluronic acid had good foam properties and will be appropriate delivery systems for an active pharmaceutical ingredient. Overall, the polymer content had a great effect on the properties of the foams. Different polymers affect the properties of foams in different ways. When used in combination, the methods reinforce each other and help to select a formula for dermal application.
About this article: Fanni Falusi, Mária Budai-Szűcs, Erzsébet Csányi, Szilvia Berkó, Tamás Spaits, Ildikó Csóka, Anita Kovács, Investigation of the effect of polymers on dermal foam properties using the QbD approach, European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2022, 106160, ISSN 0928-0987, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2022.106160. (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0928098722000458)
Materials
Kolliphor RH 40 was obtained from BASF SE Chemtrade GmbH (Ludwigshafen, Germany). Labrasol ALF was from Gattefossé (Saint-Priest Cedex, France), Xantural® 180 was provided by CP Kelco A Huber Company (Atlanta, GA, USA). Verstatil PC was purchased from Biesterfeld GmbH (Hamburg, Germany). Hydroxyethylcellulose (Ph. Eur. 9.) was supplied by Molar Chemicals Ltd. (Budapest, Hungary). Purified and deionized water was used (Milli-Q system, Millipore, Milford, MA, USA). HyaCare50, HyaCare Filler CL and HyaCare Tremella were product samples from Evonik Industries AG (Essen, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany).

