Lipid-based nanoparticles as a promising treatment for the skin cancer
Abstract
Introduction
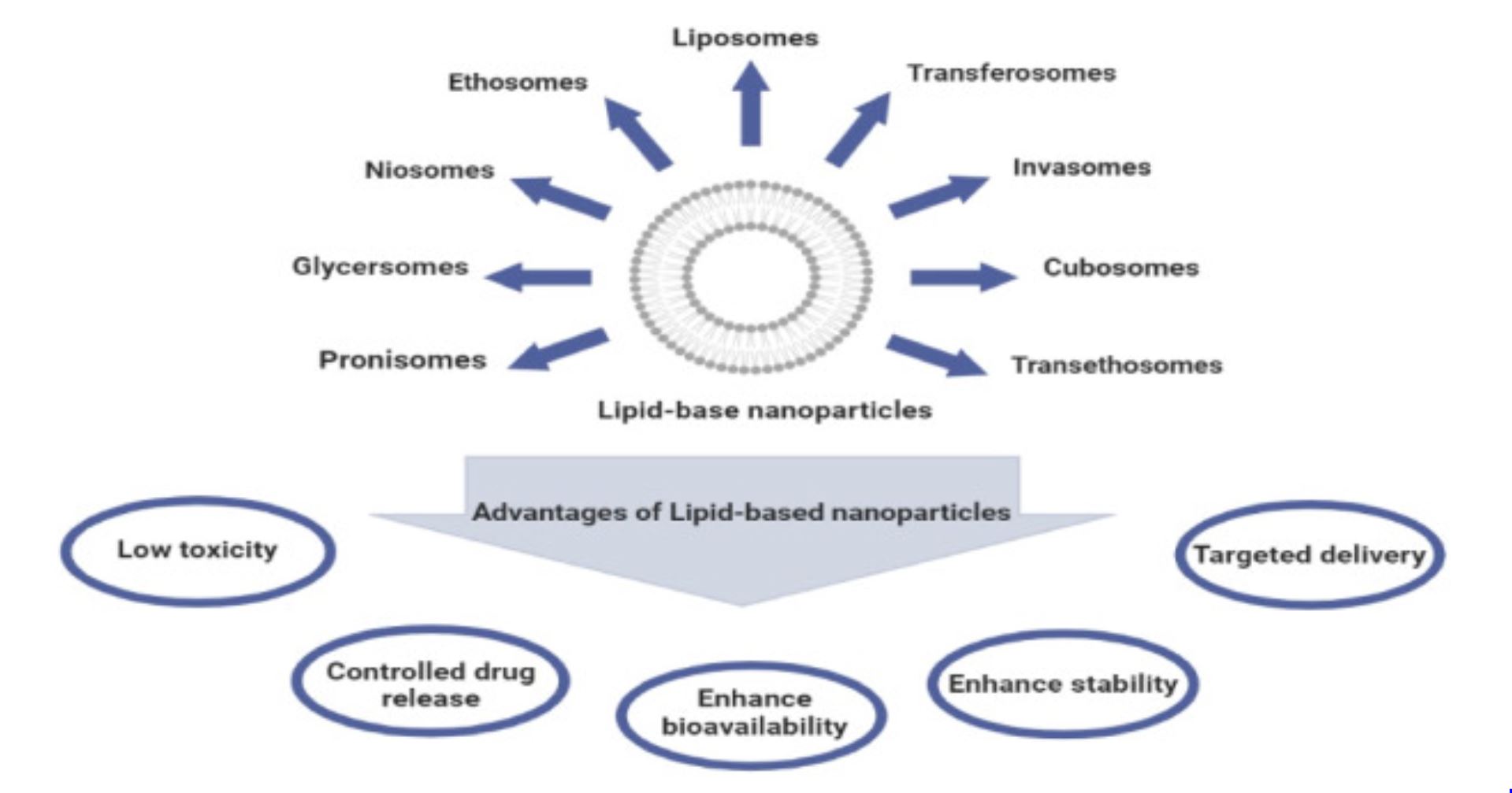
Liposomes can transport drugs well through the skin. However, they have several problems like susceptible phospholipids to oxidation that leads to the breakdown and collapse of its biolayer and leakage of encapsulated drugs [22]. Therefore, new generations of lipid-based nanoparticles were created, including transferosomes, phytosomes, ethosomes, niosomes, etc, and have been widely considered for transdermal delivery. This review investigates the characteristics of various types of lipid-based nanoparticles and their administrations in skin cancer drug delivery.
Download the full article as PDF here Lipid-based nanoparticles as a promising treatment for the skin cancer
or read it here
Parisa Golestani, Lipid-based nanoparticles as a promising treatment for the skin cancer, HELIYON, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29898, REVIEW ARTICLE VOLUME 10, ISSUE 9, E29898, MAY 15, 2024, Published: April 18, 2024DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29898
Read more on “Lipid Nanoparticles“ here:


