Drying capacity of a continuous vibrated fluid bed dryer – Statistical and mechanistic model development
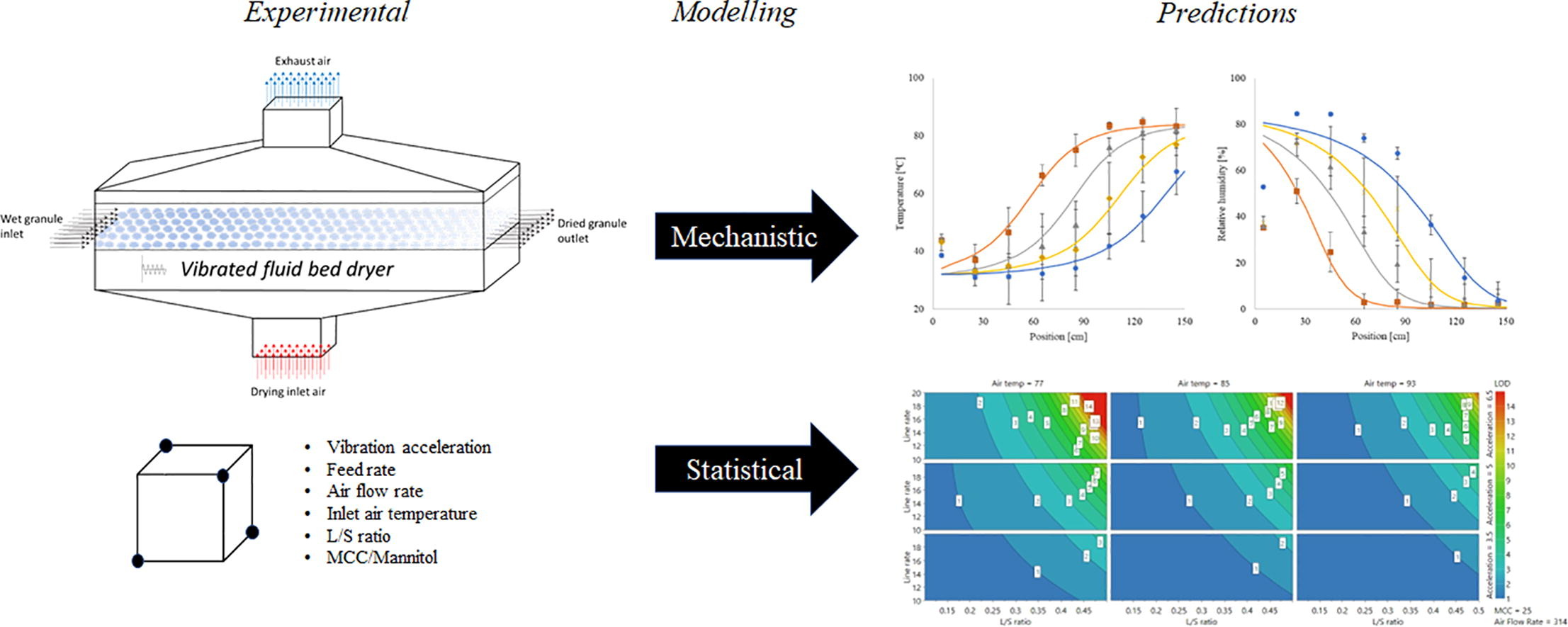
The drying capacity of a continuous vibrated fluid bed dryer was studied using a DoE by varying microcrystalline cellulose content in the formulation, water amount in the twin-screw granulation, inlet air temperature, air flow rate and the acceleration of the horizontal fluid-bed. Temperature and humidity profiles were measured along the dryer using wireless sensors. For the parameter space explored in this study, acceleration was the most influential process parameter of the dryer regarding the resulting granule moisture content. An empirical model was developed that allowed for fast and accurate moisture content prediction that could be incorporated into an enhanced control strategy. In addition, a mechanistic model was formulated that allow for prediction of temperature and moisture profiles, and most importantly the moisture content of the granules inside the dryer. The mechanistic model can be integrated to other unit operation models to provide overall understanding of an integrated continuous process line. The mechanistic model also makes it possible to define the equipment design requirements (e.g., length of the dryer) to meet the specific needs in terms of drying capacity, temperature and moisture profile.
Read more here
Materials
Three different placebo formulations consisting of mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), 3% hydroxypropyl cellulose and 4% croscarmellose sodium were used in the study (Table 1). Depending on the formulation (P25, P50 and P75) the ratio between MCC and mannitol was varied 25:75, 50:50 and 75:25.
Håkan Wikström, Luis Martin de Juan, Johan Remmelgas, Robin Meier, Andreas Altmeyer, Daniel Emanuele, Miika Jormanainen, Anne Juppo, Pirjo Tajarobi, Drying capacity of a continuous vibrated fluid bed dryer – Statistical and mechanistic model development, International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2023, 123368, ISSN 0378-5173, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2023.123368.
Read also more on Binder – Pharmaceutical Excipients here:


